Restore a dropped Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server instance
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
When a server is dropped, the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server backup is retained for five days in the service. The database backup can be accessed and restored only from the Azure subscription where the server originally resided. The following recommended steps can be followed to recover a dropped Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server resource within five days from the time of server deletion. The recommended steps work only if the backup for the server is still available and not deleted from the system. While restoring a deleted server often succeeds, it isn't always guaranteed, as restoring a deleted server depends on several other factors.
Prerequisites
To restore a dropped Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance, you need
- Azure Subscription name hosting the original server
- Location where the server was created
- Use the 2024-08-01 api-version version
Steps to restore
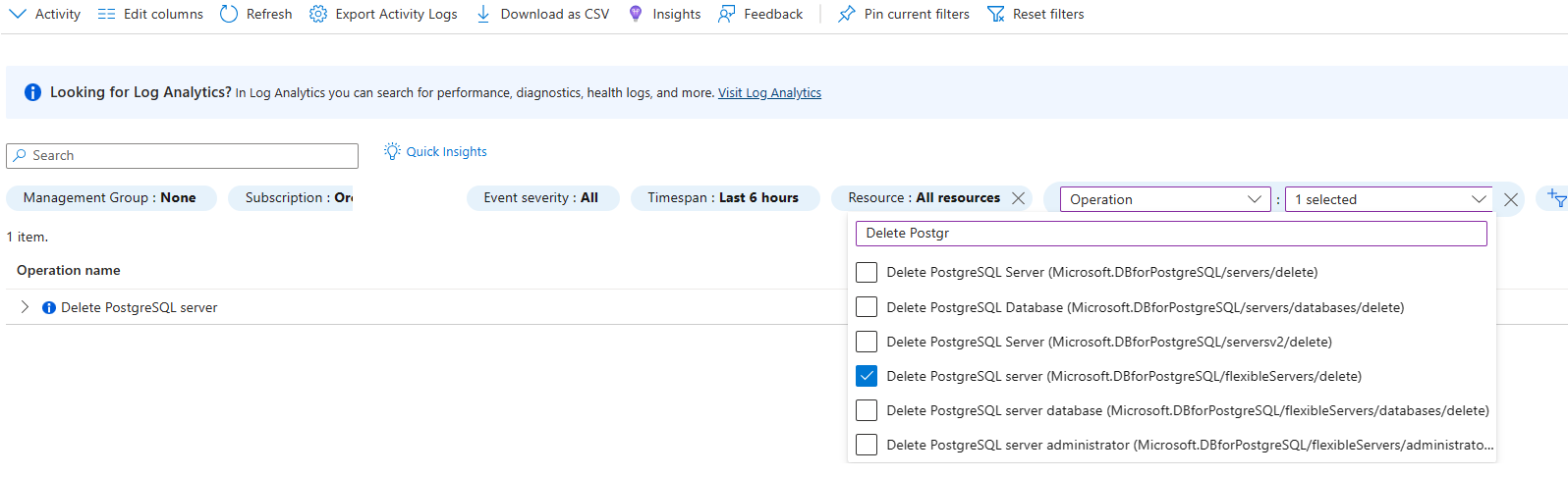
Browse to the Azure portal. Select the Monitor service, then select Activity Log.
In Activity Log, select on Add filter as shown and set following filters for the following
Select the Delete PostgreSQL Server event, then select the JSON tab. Copy the
resourceIdandsubmissionTimestampattributes in JSON output. The resourceId is in the following format:/subscriptions/ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff/resourceGroups/ResourceGroup-name/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/deletedserver.Browse to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server Create Server REST API Page and select the Try It tab highlighted in green. Sign in with your Azure account.
Important
Use this api-version 2024-08-01 rather than the default before running to enable this API function as expected as detailed in the following step.
Provide the resourceGroupName, serverName (Target server name), subscriptionId properties, based on the resourceId attribute JSON value captured in the preceding step 3. The api-version property is prepopulated and can be left alone.
Go to Request Body section and paste the following replacing the "Dropped server Location"(for example, CentralUS, EastUS etc.), "submissionTimestamp", and "resourceId". For "pointInTimeUTC", specify a value of "submissionTimestamp" plus 5 minutes to ensure the command doesn't error out.
{ "location": "Dropped Server Location", "properties": { "pointInTimeUTC": "submissionTimestamp + 10 minutes", "createMode": "ReviveDropped", "sourceServerResourceId": "resourceId" } }For example, if the submission timestamp is 2023-06-15T15:58:02Z, we recommend adding a minimum of 10 minutes to restore point in time 2023-06-15T16:05:02Z and ensure that you're changing three parameters (location,pointInTimeUTC,sourceServerResourceId) as per your restore requirements.
{ "location": "WestUS", "properties": { "pointInTimeUTC": "2023-06-15T16:08:02Z", "createMode": "ReviveDropped", "sourceServerResourceId": "/subscriptions/ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff/resourceGroups/SourceResourceGroup-Name/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/SourceServer-Name" } }Important
There is a time limit of five days after the server was dropped. After five days, an error is expected since the backup file cannot be found.
If you see Response Code 201 or 202, the restore request is successfully submitted.
The server creation can take time depending on the database size and compute resources provisioned on the original server. The restore status can be monitored from Activity log by filtering for
- Subscription = Your Subscription
- Resource Type = Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible servers (Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers)
- Operation = Update PostgreSQL Server Create
Restore a dropped virtual network enabled Server
Restoring a dropped virtual network enabled server involves specifying additional network properties such as the delegated subnet resource ID and the private DNS zone Azure Resource Manager resource ID. Follow the steps below to restore your server with the necessary network configurations.
{
"location": "EastUS",
"properties": {
"createMode": "ReviveDropped",
"sourceServerResourceId": "/subscriptions/ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff/resourceGroups/SourceResourceGroup-Name/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/SourceServer-Name",
"pointInTimeUTC": "2023-06-20T20:50:59.4078005+00:00",
"Network": {
"DelegatedSubnetResourceId": "/subscriptions/ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff/resourceGroups/SourceResourceGroup-Name/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/VirtualNetwork-Name/subnets/Subnet-Name",
"PrivateDnsZoneArmResourceId": "/subscriptions/ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff/resourceGroups/SourceResourceGroup-Name/providers/Microsoft.Network/privateDnsZones/privatednszonename"
}
}
}
Common errors
- If you utilize the incorrect API version, you might experience restore failures or timeouts. Use 2024-08-01 API to avoid such issues.
- To avoid potential DNS errors, it's recommended to use a different name when initiating the restore process, as some restore operations might fail with the same name.