Quickstart: Use .NET (C#) to connect and query data in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
This quickstart demonstrates how to connect to an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance by using a C# application. It shows how to use SQL statements to query, insert, update, and delete data in the database.
Prerequisites
For this quickstart you need:
- An Azure account with an active subscription.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin. Currently, with an Azure free account, you can try Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server free for 12 months. For more information, see Use an Azure free account to try Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server for free.
- Create an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance by using the Quickstart: Create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL with the Azure portal
or Quickstart: Create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server by using the Azure CLI if you do not have one. - Based on whether you are using public or private access, complete ONE of the actions below to enable connectivity.
- Create a database and non-admin user
- Install the .NET SDK for your platform (Windows, Ubuntu Linux, or macOS) for your platform.
Create a C# project
At a command prompt, run:
mkdir AzureMySqlExample
cd AzureMySqlExample
dotnet new console
dotnet add package MySqlConnector
Get connection information
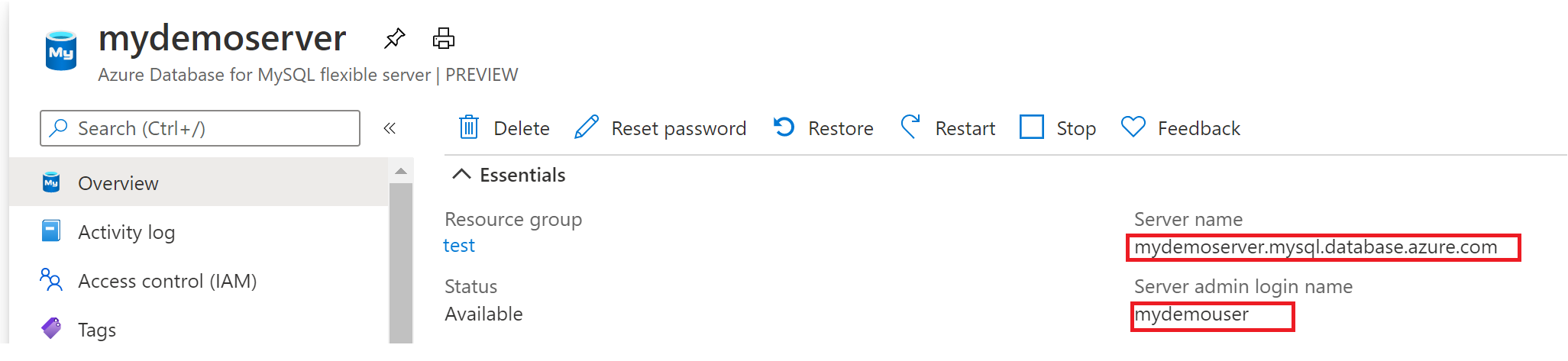
Get the connection information needed to connect to the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance. You need the fully qualified server name and login credentials.
- Log in to the Azure portal.
- From the left-hand menu in Azure portal, select All resources, and then search for the server you have created (such as mydemoserver).
- Select the server name.
- From the server's Overview panel, make a note of the Server name and Server admin login name. If you forget your password, you can also reset the password from this panel.
Step 1: Connect and insert data
Use the following code to connect and load the data by using CREATE TABLE and INSERT INTO SQL statements. The code uses the methods of the MySqlConnection class:
- OpenAsync() to establish a connection to MySQL.
- CreateCommand(), sets the CommandText property
- ExecuteNonQueryAsync() to run the database commands.
Replace the Server, Database, UserID, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MySqlConnector;
namespace AzureMySqlExample
{
class MySqlCreate
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = new MySqlConnectionStringBuilder
{
Server = "YOUR-SERVER.mysql.database.azure.com",
Database = "YOUR-DATABASE",
UserID = "USER",
Password = "PASSWORD",
SslMode = MySqlSslMode.Required,
};
using (var conn = new MySqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString))
{
Console.WriteLine("Opening connection");
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (var command = conn.CreateCommand())
{
command.CommandText = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS inventory;";
await command.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
Console.WriteLine("Finished dropping table (if existed)");
command.CommandText = "CREATE TABLE inventory (id serial PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), quantity INTEGER);";
await command.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
Console.WriteLine("Finished creating table");
command.CommandText = @"INSERT INTO inventory (name, quantity) VALUES (@name1, @quantity1),
(@name2, @quantity2), (@name3, @quantity3);";
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name1", "banana");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@quantity1", 150);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name2", "orange");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@quantity2", 154);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name3", "apple");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@quantity3", 100);
int rowCount = await command.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Number of rows inserted={0}", rowCount));
}
// connection will be closed by the 'using' block
Console.WriteLine("Closing connection");
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Having any issues? Let us know.
Step 2: Read data
Use the following code to connect and read the data by using a SELECT SQL statement. The code uses the MySqlConnection class with methods:
- OpenAsync() to establish a connection to MySQL.
- CreateCommand() to set the CommandText property.
- ExecuteReaderAsync() to run the database commands.
- ReadAsync() to advance to the records in the results. Then the code uses GetInt32 and GetString to parse the values in the record.
Replace the Server, Database, UserID, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MySqlConnector;
namespace AzureMySqlExample
{
class MySqlRead
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = new MySqlConnectionStringBuilder
{
Server = "YOUR-SERVER.mysql.database.azure.com",
Database = "YOUR-DATABASE",
UserID = "USER@YOUR-SERVER",
Password = "PASSWORD",
SslMode = MySqlSslMode.Required,
};
using (var conn = new MySqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString))
{
Console.WriteLine("Opening connection");
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (var command = conn.CreateCommand())
{
command.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM inventory;";
using (var reader = await command.ExecuteReaderAsync())
{
while (await reader.ReadAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format(
"Reading from table=({0}, {1}, {2})",
reader.GetInt32(0),
reader.GetString(1),
reader.GetInt32(2)));
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Closing connection");
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Step 3: Update data
Use the following code to connect and read the data by using an UPDATE SQL statement. The code uses the MySqlConnection class with method:
- OpenAsync() to establish a connection to MySQL.
- CreateCommand() to set the CommandText property
- ExecuteNonQueryAsync() to run the database commands.
Replace the Server, Database, UserID, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MySqlConnector;
namespace AzureMySqlExample
{
class MySqlUpdate
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = new MySqlConnectionStringBuilder
{
Server = "YOUR-SERVER.mysql.database.azure.com",
Database = "YOUR-DATABASE",
UserID = "USER",
Password = "PASSWORD",
SslMode = MySqlSslMode.Required,
};
using (var conn = new MySqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString))
{
Console.WriteLine("Opening connection");
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (var command = conn.CreateCommand())
{
command.CommandText = "UPDATE inventory SET quantity = @quantity WHERE name = @name;";
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@quantity", 200);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name", "banana");
int rowCount = await command.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Number of rows updated={0}", rowCount));
}
Console.WriteLine("Closing connection");
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Step 4: Delete data
Use the following code to connect and delete the data by using a DELETE SQL statement.
The code uses the MySqlConnection class with method
- OpenAsync() to establish a connection to MySQL.
- CreateCommand() to set the CommandText property.
- ExecuteNonQueryAsync() to run the database commands.
Replace the Server, Database, UserID, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MySqlConnector;
namespace AzureMySqlExample
{
class MySqlDelete
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = new MySqlConnectionStringBuilder
{
Server = "YOUR-SERVER.mysql.database.azure.com",
Database = "YOUR-DATABASE",
UserID = "USER",
Password = "PASSWORD",
SslMode = MySqlSslMode.Required,
};
using (var conn = new MySqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString))
{
Console.WriteLine("Opening connection");
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (var command = conn.CreateCommand())
{
command.CommandText = "DELETE FROM inventory WHERE name = @name;";
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name", "orange");
int rowCount = await command.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Number of rows deleted={0}", rowCount));
}
Console.WriteLine("Closing connection");
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Clean up resources
To clean up all resources used during this quickstart, delete the resource group using the following command:
az group delete \
--name $AZ_RESOURCE_GROUP \
--yes