Parse or chunk content for workflows in Azure Logic Apps (Preview)
Applies to: Azure Logic Apps (Consumption + Standard)
Important
This capability is in preview and is subject to the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Sometimes you have to convert content into tokens, which are words or chunks of characters, or divide a large document into smaller pieces before you can use this content with some actions. For example, the Azure AI Search or Azure OpenAI actions expect tokenized input and can handle only a limited number of tokens.
For these scenarios, use the Data Operations actions named Parse a document and Chunk text in your logic app workflow. These actions respectively transform content, such as a PDF document, CSV file, Excel file, and so on, into tokenized string output and then split the string into pieces, based on the number of tokens. You can then reference and use these outputs with subsequent actions in your workflow.
Tip
To learn more, you can ask Azure Copilot these questions:
- What is a token in AI?
- What is tokenized input?
- What is tokenized string output?
- What is parsing in AI?
- What is chunking in AI?
To find Azure Copilot, on the Azure portal toolbar, select Copilot.
This how-to guide shows how to add and set up these operations in your workflow.
Known issues and limitations
The Parse a document and Chunk text actions currently don't support host files, for example, mainframe and midrange binary files such as Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) files. However, if you're working with Standard workflows, you can use the IBM Host File built-in action named Parse Host File Contents instead.
Prerequisites
An Azure account and subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, sign up for a free Azure account.
A Consumption or Standard logic app workflow with an existing trigger because the Parse a document and Chunk text operations are available only as actions. Make sure that the action that retrieves the content that you want to parse or chunk precedes these data operations.
Parse a document
The Parse a document action converts content, such as a PDF document, CSV file, Excel file, and so on, into a tokenized string. For this example, suppose your workflow starts with the Request trigger named When a HTTP request is received. This trigger waits to receive an HTTP request sent from another component, such as an Azure function, another logic app workflow, and so on. The HTTP request includes the URL for a new uploaded document that is available for the workflow to retrieve and parse. An HTTP action immediately follows the trigger, and sends an HTTP request to the document's URL, and returns with the document content from its storage location.
If you use other content sources, such as Azure Blob Storage, SharePoint, OneDrive, File System, FTP, and so on, you can check whether triggers are available for these sources. You can also check whether actions are available to retrieve the content for these sources. For more information, see Built-in operations and Managed connectors.
In the Azure portal, open your logic app resource and workflow in the designer.
Under the existing trigger and actions, follow these general steps to add the Data Operations action named Parse a document to your workflow.
On the designer, select the Parse a document action.
After the action information pane opens, on the Parameters tab, in the Document Content property, specify the content to parse by following these steps:
Select inside the Document Content box.
The options for the dynamic content list (lightning icon) and the expression editor (function icon) appear.
To choose the output from a preceding action, select the dynamic content list.
To create an expression that manipulates output from a preceding action, select the expression editor.
This example continues by selecting the lightning icon for the dynamic content list.
After the dynamic content list opens, select the output that you want from a preceding operation.
In this example, the Parse a document action references the Body output from the HTTP action.
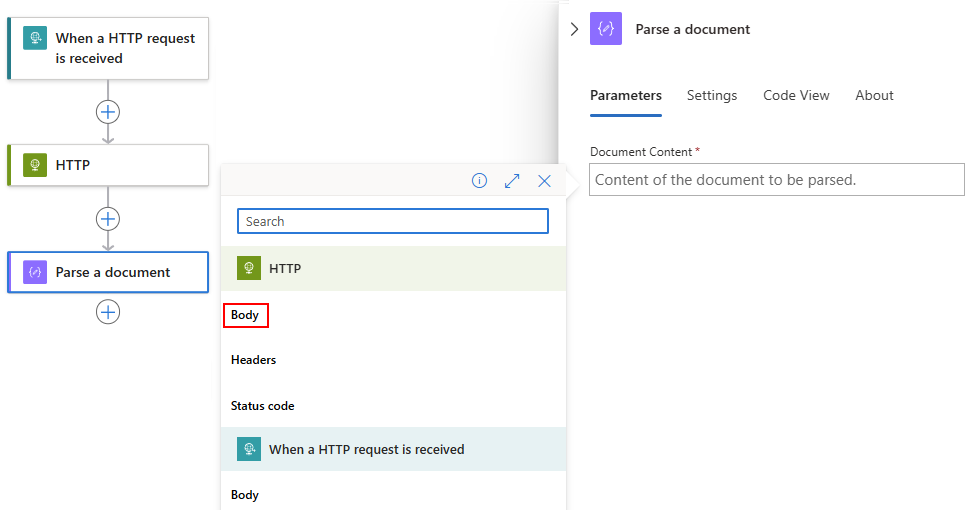
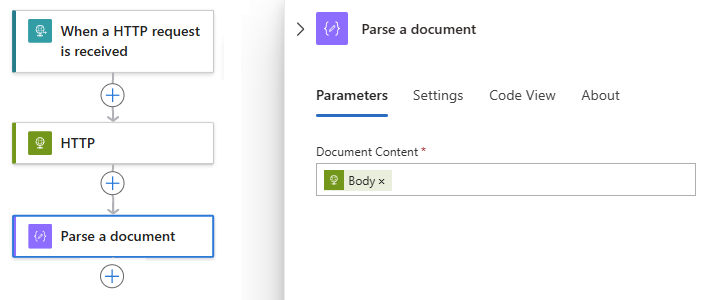
The Body output now appears in the Document Content box:
Under the Parse a document action, add the actions that you want to work with the tokenized string output, for example, Chunk text, which this guide describes later.
Parse a document - Reference
Parameters
| Name | Value | Data type | Description | Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document Content | <content-to-parse> | Any | The content to parse. | None |
Outputs
| Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parsed result text | String array | An array of strings. |
| Parsed result | Object | An object that contains the entire parsed text. |
Chunk text
The Chunk text action splits content into smaller pieces for subsequent actions to more easily use in the current workflow. The following steps build on the example from the Parse a document section and splits token string output for use with Azure AI operations that expect tokenized, small content chunks.
Note
Preceding actions that use chunking don't affect the Chunk text action, nor does the Chunk text action affect subsequent actions that use chunking.
In the Azure portal, open your logic app resource and workflow in the designer.
Under the Parse a document action, follow these general steps to add the Data Operations action named Chunk text.
On the designer, select the Chunk text action.
After the action information pane opens, on the Parameters tab, for the Chunking Strategy property, select TokenSize as the chunking method, if not already selected.
Strategy Description TokenSize Split the specified content, based on the number of tokens. After you select the strategy, select inside the Text box to specify the content for chunking.
The options for the dynamic content list (lightning icon) and the expression editor (function icon) appear.
To choose the output from a preceding action, select the dynamic content list.
To create an expression that manipulates output from a preceding action, select the expression editor.
This example continues by selecting the lightning icon for the dynamic content list.
After the dynamic content list opens, select the output that you want from a preceding operation.
In this example, the Chunk text action references the Parsed result text output from the Parse a document action.
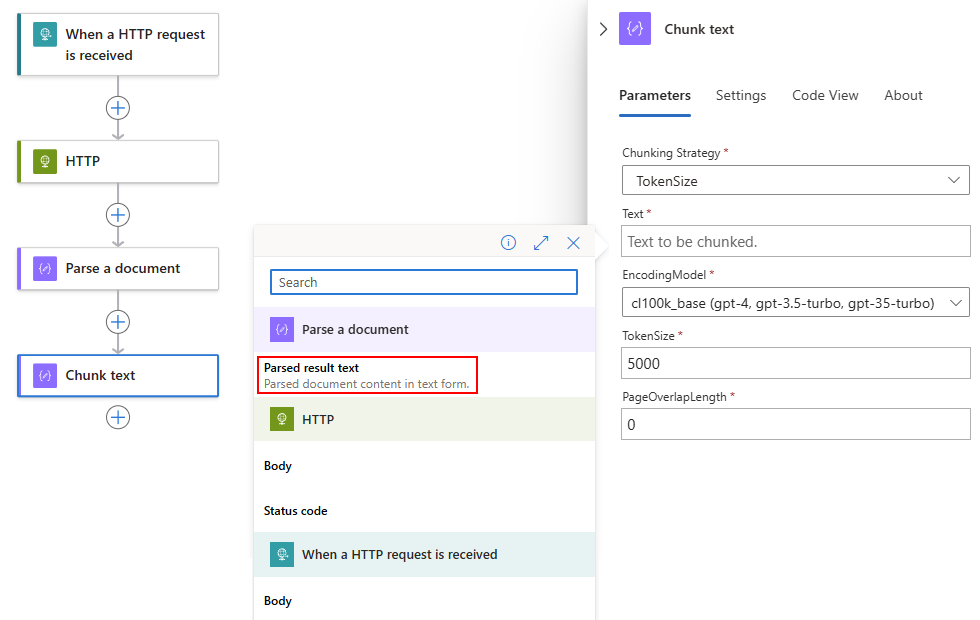
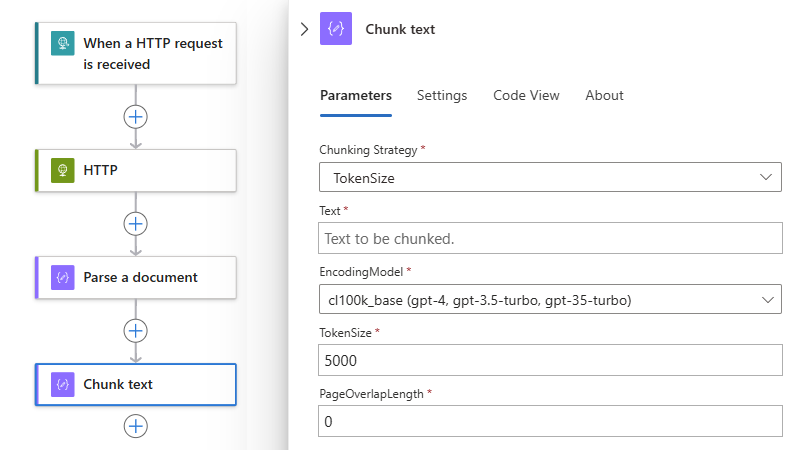
The Text box now shows the Parsed result action output:
Complete the setup for the Chunk text action, based on your selected strategy and scenario. For more information, see Chunk text - Reference.
Now, when you add other actions that expect and use tokenized input, such as the Azure AI actions, the input content is formatted for easier consumption.
Chunk text - Reference
Parameters
| Name | Value | Data type | Description | Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chunking Strategy | TokenSize | String enum | Split the content, based on the number of tokens. Default: TokenSize |
Not applicable |
| Text | <content-to-chunk> | Any | The content to chunk. | See Limits and configuration reference guide |
| EncodingModel | <encoding-method> | String enum | The encoding model to use: - Default: cl100k_base (gpt4, gpt-3.5-turbo, gpt-35-turbo) - r50k_base (gpt-3) - p50k_base (gpt-3) - p50k_edit (gpt-3) - cl200k_base (gpt-4o) For more information, see OpenAI - Models overview. |
Not applicable |
| TokenSize | <max-tokens-per-chunk> | Integer | The maximum number of tokens per content chunk. Default: None |
Minimum: 1 Maximum: 8000 |
| PageOverlapLength | <number-of-overlapping-characters> | Integer | The number of characters from the end of the previous chunk to include in the next chunk. This setting helps you avoid losing important information when splitting content into chunks and preserves continuity and context across chunks. Default: 0 - No overlapping characters exist. |
Minimum: 0 |
Tip
To learn more, you can ask Azure Copilot these questions:
- What is PageOverlapLength in chunking?
- What is encoding in Azure AI?
To find Azure Copilot, on the Azure portal toolbar, select Copilot.
Outputs
| Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Chunked result Text items | String array | An array of strings. |
| Chunked result Text items Item | String | A single string in the array. |
| Chunked result | Object | An object that contains the entire chunked text. |
Example workflow
The following example includes other actions that create a complete workflow pattern to ingest data from any source:
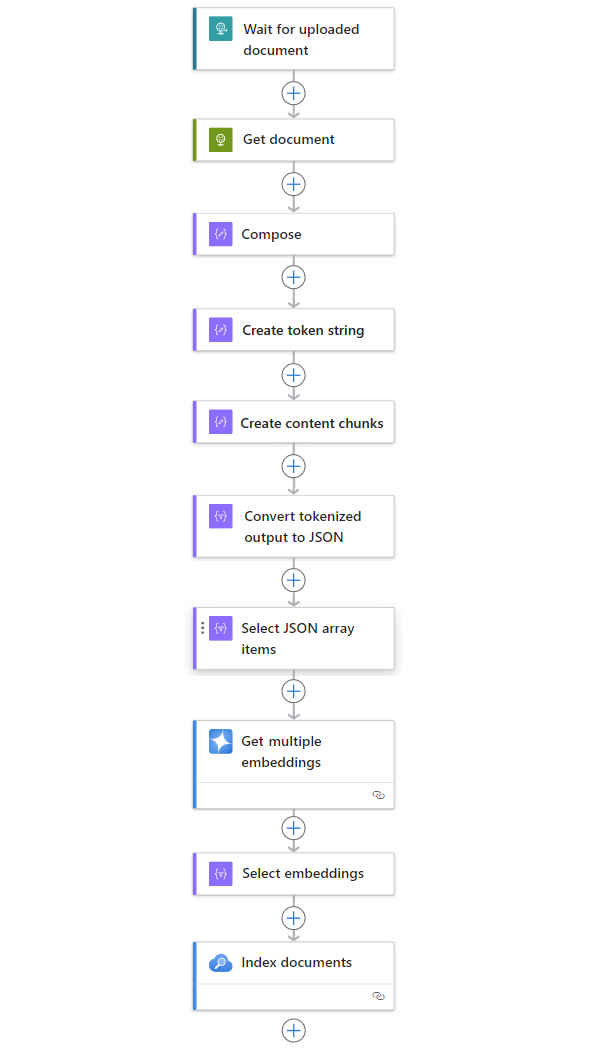
| Step | Task | Underlying operation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wait or check for new content. | When an HTTP request is received | A trigger that either polls or waits for new data to arrive, either based on a scheduled recurrence or in response to specific events respectively. Such an event might be a new file that's uploaded to a specific storage system, such as Azure Blob Storage, SharePoint, OneDrive, File System, FTP, and so on. In this example, the Request trigger operation waits for an HTTP or HTTPS request sent from another endpoint. The request includes the URL for a new uploaded document. |
| 2 | Get the content. | HTTP | An HTTP action that retrieves the uploaded document using the file URL from the trigger output. |
| 3 | Compose document details. | Compose | A Data Operations action that concatenates various items. This example concatenates key-value information about the document. |
| 4 | Create token string. | Parse a document | A Data Operations action that produces a tokenized string using the output from the Compose action. |
| 5 | Create content chunks. | Chunk text | A Data Operations action that splits the token string into pieces, based on the number of tokens per content chunk. |
| 6 | Convert tokenized and chunked text to JSON. | Parse JSON | A Data Operations action that converts the chunked output into a JSON array. |
| 7 | Select JSON array items. | Select | A Data Operations action that selects multiple items from the JSON array. |
| 8 | Generate the embeddings. | Get multiple embeddings | An Azure OpenAI action that creates embeddings for each JSON array item. |
| 9 | Select embeddings and other information. | Select | A Data Operations action that selects embeddings and other document information. |
| 10 | Index the data. | Index documents | An Azure AI Search action that indexes the data based on each selected embedding. |