Migrate from Inbound NAT rules version 1 to version 2
An inbound NAT rule is used to forward traffic from a load balancer’s frontend to one or more instances in the backend pool. These rules provide a 1:1 mapping between the load balancer’s frontend IP address and backend instances. There are currently two versions of Inbound NAT rules, version 1 and version 2.
Important
On September 30, 2027, Inbound NAT rules v1 will be retired. If you are currently using Inbound NAT rules v1, make sure to upgrade to Inbound NAT rules v2 prior to the retirement date.
NAT rule version 1
Version 1 is the legacy approach for assigning an Azure Load Balancer’s frontend port to each backend instance. Rules are applied to the backend instance’s network interface card (NIC). For Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) instances, inbound NAT rules are automatically created/deleted as new instances are scaled up/down. For VMSS instances use the Inbound NAT Pools property to manage Inbound NAT rules version 1.
NAT rule version 2
Version 2 of Inbound NAT rules provide the same feature set as version 1, with extra benefits.
- Simplified deployment experience and optimized updates.
- Inbound NAT rules now target the backend pool of the load balancer and no longer require a reference on the virtual machine's NIC. Previously on version 1, both the load balancer and the virtual machine's NIC needed to be updated whenever the Inbound NAT rule was changed. Version 2 only requires a single call on the load balancer’s configuration, resulting in optimized updates.
- Easily retrieve port mapping between Inbound NAT rules and backend instances.
- With the legacy offering, to retrieve the port mapping between an Inbound NAT rule and a virtual machine instance, the rule would need to be correlated with the virtual machine's NIC. Version 2 injects the port mapping between the rule and backend instance directly into the load balancer’s configuration.
How do I know if I’m using version 1 of Inbound NAT rules?
The easiest way to identify if your deployments are using version 1 of the feature is by inspecting the load balancer’s configuration. Version 1 nat rules will have a Type value of Azure Virtual Machine with a defined Target virtual machine value.
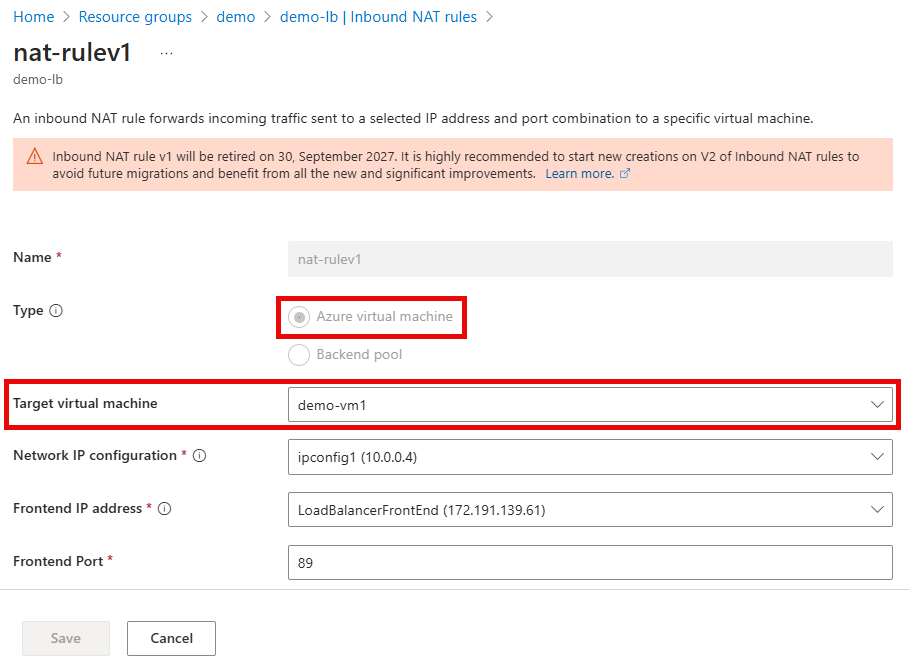
For version 2 NAT rules, the Type value will be Backend pool with a defined Target backend pool value.
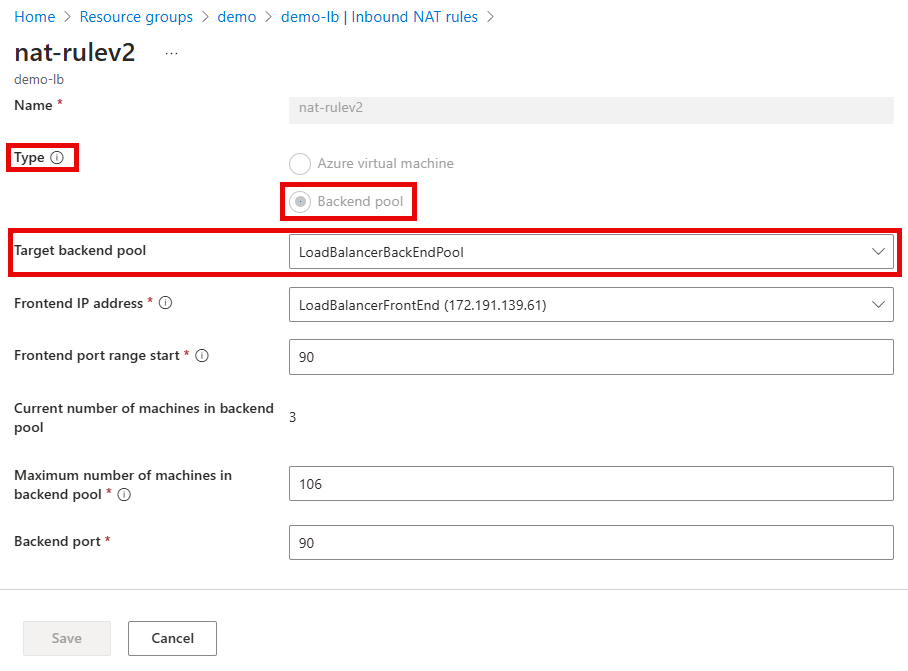
To programmatically determine if a deployment is using version 1 of Inbound NAT rules, inspect the load balancer’s configuration using the Azure CLI or PowerShell. If either the backendIPConfiguration property within the InboundNATRule configuration is populated, then the deployment is version 1 of Inbound NAT rules. Version 2 rules will have the backendAddressPool property instead of the backendIPConfiguration property.
How to migrate from version 1 to version 2?
Prior to migrating it's important to review the following information:
- Migrating to version 2 of Inbound NAT rules causes downtime to active traffic that is flowing through the NAT rules. Traffic flowing through load balancer rules or outbound rules aren't impacted during the migration process.
- Plan out the max number of instances in a backend pool. Since version 2 targets the load balancer’s backend pool, a sufficient number of ports need to be allocated for the NAT rule’s frontend.
- Each backend instance is exposed on the port configured in the new NAT rule.
- Multiple NAT rules can’t exist if they have an overlapping port range or have the same backend port.
- NAT rules and load balancing rules can’t share the same backend port.
Manual Migration
The following three steps need to be performed to migrate to version 2 of inbound NAT rules
- Delete the version 1 of inbound NAT rules on the load balancer’s configuration.
- Remove the reference to the NAT rule on the virtual machine or virtual machine scale set configuration.
- All virtual machine scale set instances need to be updated.
- Deploy version 2 of Inbound NAT rules.
Virtual Machine
The following steps are used to migrate from version 1 to version 2 of Inbound NAT rules for a virtual machine.
az network lb inbound-nat-rule delete -g MyResourceGroup --lb-name MyLoadBalancer --name NATruleV1
az network nic ip-config inbound-nat-rule remove -g MyResourceGroup --nic-name MyNic -n MyIpConfig --inbound-nat-rule MyNatRule
az network lb inbound-nat-rule create -g MyResourceGroup --lb-name MyLoadBalancer -n MyNatRule --protocol Tcp --frontend-port-range-start 201 --frontend-port-range-end 500 --backend-port 22 --backend-address-pool MybackendPool
Virtual Machine Scale Set
The following steps are used to migrate from version 1 to version 2 of Inbound NAT rules for a virtual machine scale set. It assumes the virtual machine scale set's upgrade mode is set to Manual. For more information, see Orchestration modes for Virtual Machine Scale Sets in Azure
az network lb inbound-nat-pool delete -g MyResourceGroup --lb-name MyLoadBalancer -n MyNatPool
az vmss update -g MyResourceGroup -n MyVMScaleSet --remove virtualMachineProfile.networkProfile.networkInterfaceConfigurations[0].ipConfigurations[0].loadBalancerInboundNatPools
az vmss update-instances --instance-ids '*' --resource-group MyResourceGroup --name MyVMScaleSet
az network lb inbound-nat-rule create -g MyResourceGroup --lb-name MyLoadBalancer -n MyNatRule --protocol Tcp --frontend-port-range-start 201 --frontend-port-range-end 500 --backend-port 22 --backend-address-pool MybackendPool
Migration with automation script for Virtual Machine Scale Set
The migration process will reuse existing backend pools with membership matching the NAT Pools to be migrated; if no matching backend pool is found, the script will exit (without making changes). Alternatively, use the -backendPoolReuseStrategy parameter to either always create new backend pools (NoReuse) or create a new backend pool if a matching one doesn't exist (OptionalFirstMatch). Backend pools and NAT Rule associations can be updated post migration to match your preference.
Prerequisites
Before beginning the migration process, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- The load balancer's SKU must be Standard to migrate a load balancer's NAT Pools to NAT Rules. To automate this upgrade process, see the steps provided in Upgrade a Basic Load Balancer to Standard with PowerShell.
- The Virtual Machine Scale Sets associated with the target Load Balancer must use either a 'Manual' or 'Automatic' upgrade policy--'Rolling' upgrade policy isn't supported. For more information, see Virtual Machine Scale Sets Upgrade Policies.
- Install the latest version of PowerShell.
- Install the Azure PowerShell modules.
Install the AzureLoadBalancerNATPoolMigration module
With the following command, install the AzureLoadBalancerNATPoolMigration module from the PowerShell Gallery:
# Install the AzureLoadBalancerNATPoolMigration module
Install-Module -Name AzureLoadBalancerNATPoolMigration -Scope CurrentUser -Repository PSGallery -Force
Upgrade NAT Pools to NAT Rules
With the azureLoadBalancerNATPoolMigration module installed, upgrade your NAT Pools to NAT Rules with the following steps:
Connect to Azure with
Connect-AzAccount.Collect the names of the target load balancer for the NAT Rules upgrade and its Resource Group name.
Run the migration command with your resource names replacing the placeholders of
<loadBalancerResourceGroupName>and<loadBalancerName>:# Run the migration command Start-AzNATPoolMigration -ResourceGroupName <loadBalancerResourceGroupName> -LoadBalancerName <loadBalancerName>
Next steps
- Learn about Managing Inbound NAT Rules
- Learn about Azure Load Balancer NAT Pools and NAT Rules