Spring Cloud Azure support for Spring Security
This article applies to: ✅ Version 4.19.0 ✅ Version 5.20.0
This article describes how Spring Cloud Azure and Spring Security can be used together.
Spring Security with Microsoft Entra ID
When you're building a web application, identity and access management will always be foundational pieces.
Azure offers a great platform to democratize your application development journey, as it not only offers a cloud-base identity service, but also deep integration with the rest of the Azure ecosystem.
Spring Security has made it easy to secure your Spring based applications with powerful abstractions and extensible interfaces. However, as powerful as the Spring framework can be, it isn't tailored to a specific identity provider.
The spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory provides the most optimal way to connect your web application to a Microsoft Entra ID (Microsoft Entra ID for short) tenant and protect your resource server with Microsoft Entra ID. It uses the Oauth 2.0 protocol to protect web applications and resource servers.
Accessing a web application
This scenario uses The OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant flow to log in a user with a Microsoft account.
System Diagram
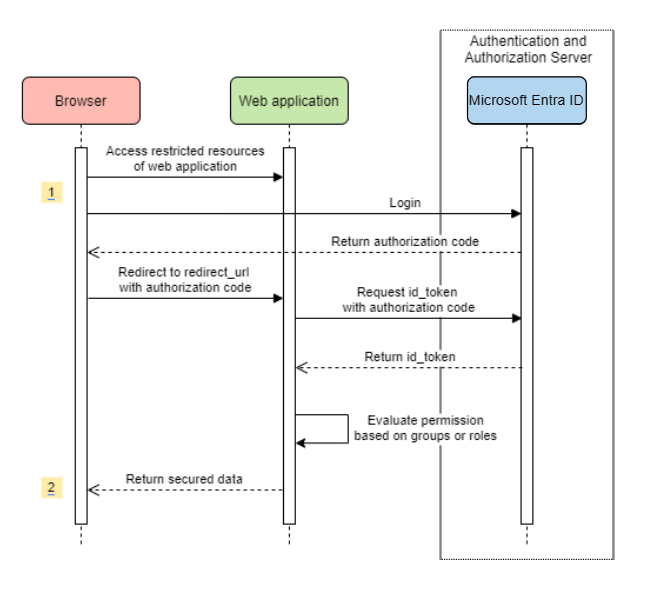
Create required resources in Azure
Read Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Create an app registration. Get
AZURE_TENANT_ID,AZURE_CLIENT_ID, andAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET.Set
redirect URItoAPPLICATION_BASE_URI/login/oauth2/code/- for examplehttp://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/. The tailing/is required.
Add required dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add required properties
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Now, start your application and access your application through the browser. You'll be redirected into the Microsoft login page.
Advanced usages
Add extra security configurations
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class AadOAuth2LoginSecurityConfig {
/**
* Add configuration logic as needed.
*/
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.apply(AadWebApplicationHttpSecurityConfigurer.aadWebApplication())
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
// Do some custom configuration.
return http.build();
}
}
Authorize access by app roles
Create required resources in Azure:
Read Add app roles to your application and receive them in the token.
Create an app role with the following parameters:
- Display name: Admin
- Allowed member types: Users/Groups
- Value: Admin
- Do you want to enable this app role: yes
Note
If you want to use app role based access control, you can't put group names in the role claim. For more information, see the Configuring groups optional claims section of Provide optional claims to your app.
Protect the specific method.
class Demo {
@GetMapping("Admin")
@ResponseBody
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('APPROLE_Admin')")
public String admin() {
return "Admin message";
}
}
Authorize access by group name or group ID
Add related configuration properties.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
user-group:
allowed-group-names: group1_name_1, group2_name_2
# 1. If allowed-group-ids == all, then all group ID will take effect.
# 2. If "all" is used, we should not configure other group ids.
# 3. "all" is only supported for allowed-group-ids, not supported for allowed-group-names.
allowed-group-ids: group_id_1, group_id_2
Protect the specific method.
@Controller
public class RoleController {
@GetMapping("group1")
@ResponseBody
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_group1')")
public String group1() {
return "group1 message";
}
@GetMapping("group2")
@ResponseBody
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_group2')")
public String group2() {
return "group2 message";
}
@GetMapping("group1Id")
@ResponseBody
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_<group1-id>')")
public String group1Id() {
return "group1Id message";
}
@GetMapping("group2Id")
@ResponseBody
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_<group2-id>')")
public String group2Id() {
return "group2Id message";
}
}
Use National Azure instead of Global Azure
Now except global Azure cloud, Microsoft Entra ID is deployed in the following national clouds:
Azure Government
Azure China 21Vianet
Azure Germany
Here's a sample using Azure China 21Vianet.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
base-uri: https://login.partner.microsoftonline.cn
graph-base-uri: https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn
For more information, see National cloud deployments.
Configure redirect URI template
Developers can customize the redirect-uri.
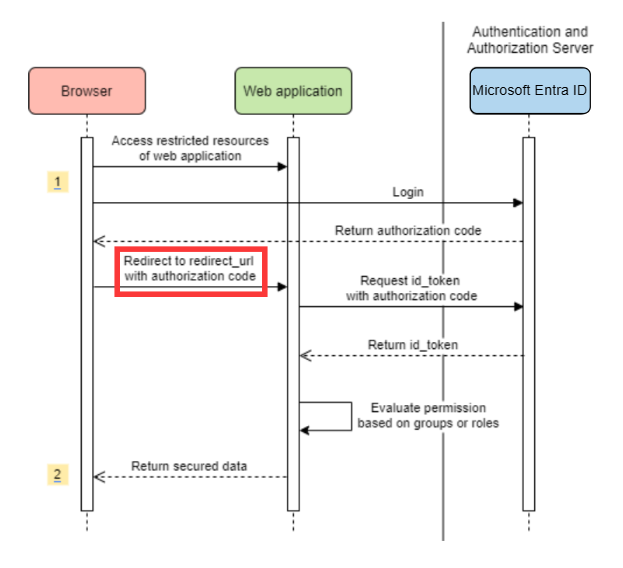
Add redirect-uri-template properties in your application.yml file.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
redirect-uri-template: ${REDIRECT-URI-TEMPLATE}
Update redirect-uri in the Azure portal.
After we set redirect-uri-template, we need to update the security builder:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class AadOAuth2LoginSecurityConfig {
/**
* Add configuration logic as needed.
*/
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain htmlFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.apply(AadWebApplicationHttpSecurityConfigurer.aadWebApplication())
.and()
.oauth2Login()
.loginProcessingUrl("${REDIRECT-URI-TEMPLATE}")
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
// @formatter:on
return http.build();
}
}
Connecting to Microsoft Entra ID via proxy
To connect Microsoft Entra ID via proxy, provide a RestTemplateCustomizer bean like the one shown in the following example:
@Configuration
class DemoConfiguration {
@Bean
public RestTemplateCustomizer proxyRestTemplateCustomizer() {
return (RestTemplate restTemplate) -> {
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(Proxy.Type.HTTP, new InetSocketAddress(PROXY_SERVER_HOST, PROXY_SERVER_PORT));
SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory();
requestFactory.setProxy(proxy);
restTemplate.setRequestFactory(requestFactory);
};
}
}
Samples
Sample project: aad-web-application.
Web application accessing resource servers
System Diagram
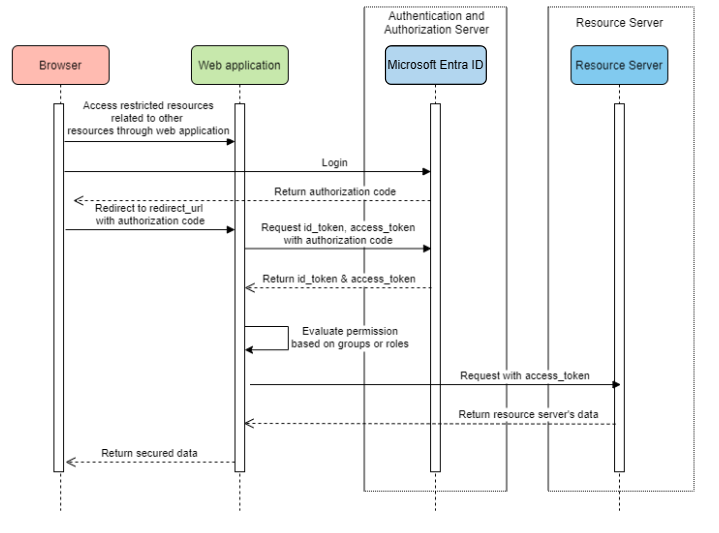
Create Required Resources in Azure
Read Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Create an app registration. Get
AZURE_TENANT_ID,AZURE_CLIENT_ID, andAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET.Set
redirect URItoAPPLICATION_BASE_URI/login/oauth2/code/, for examplehttp://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/. The tailing/is required.
Add required dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add required properties
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
authorization-clients:
graph:
scopes: https://graph.microsoft.com/Analytics.Read, email
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Here, graph is the name of OAuth2AuthorizedClient, scopes means the scopes needed to consent when logging in.
Use OAuth2AuthorizedClient in your application
public class Demo {
@GetMapping("/graph")
@ResponseBody
public String graph(
@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("graph") OAuth2AuthorizedClient graphClient) {
// toJsonString() is just a demo.
// oAuth2AuthorizedClient contains access_token. We can use this access_token to access resource server.
return toJsonString(graphClient);
}
}
Now, start your application and access your application in the browser. Then, you'll be redirected to the Microsoft login page.
Advanced usages
Client Credential Flow
The default flow is authorization code flow, if you want to use client credentials flow, you can configure like this:
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
authorization-clients:
graph:
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials # Change type to client_credentials
scopes: https://graph.microsoft.com/Analytics.Read, email
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Access multiple resource servers
In one web application, you can access multiple resource servers by configuring like this:
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
authorization-clients:
resource-server-1:
scopes: # Scopes for resource-server-1
resource-server-2:
scopes: # Scopes for resource-server-2
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Then you can use OAuth2AuthorizedClient in application like this
public class Demo {
@GetMapping("/resource-server-1")
@ResponseBody
public String graph(
@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("resource-server-1") OAuth2AuthorizedClient client) {
return callResourceServer1(client);
}
@GetMapping("/resource-server-2")
@ResponseBody
public String graph(
@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("resource-server-2") OAuth2AuthorizedClient client) {
return callResourceServer2(client);
}
}
Samples
Sample project: aad-web-application.
Accessing a resource server
This scenario doesn't support login, just protect the server by validating the access token. If the access token is valid, the server serves the request.
System Diagram
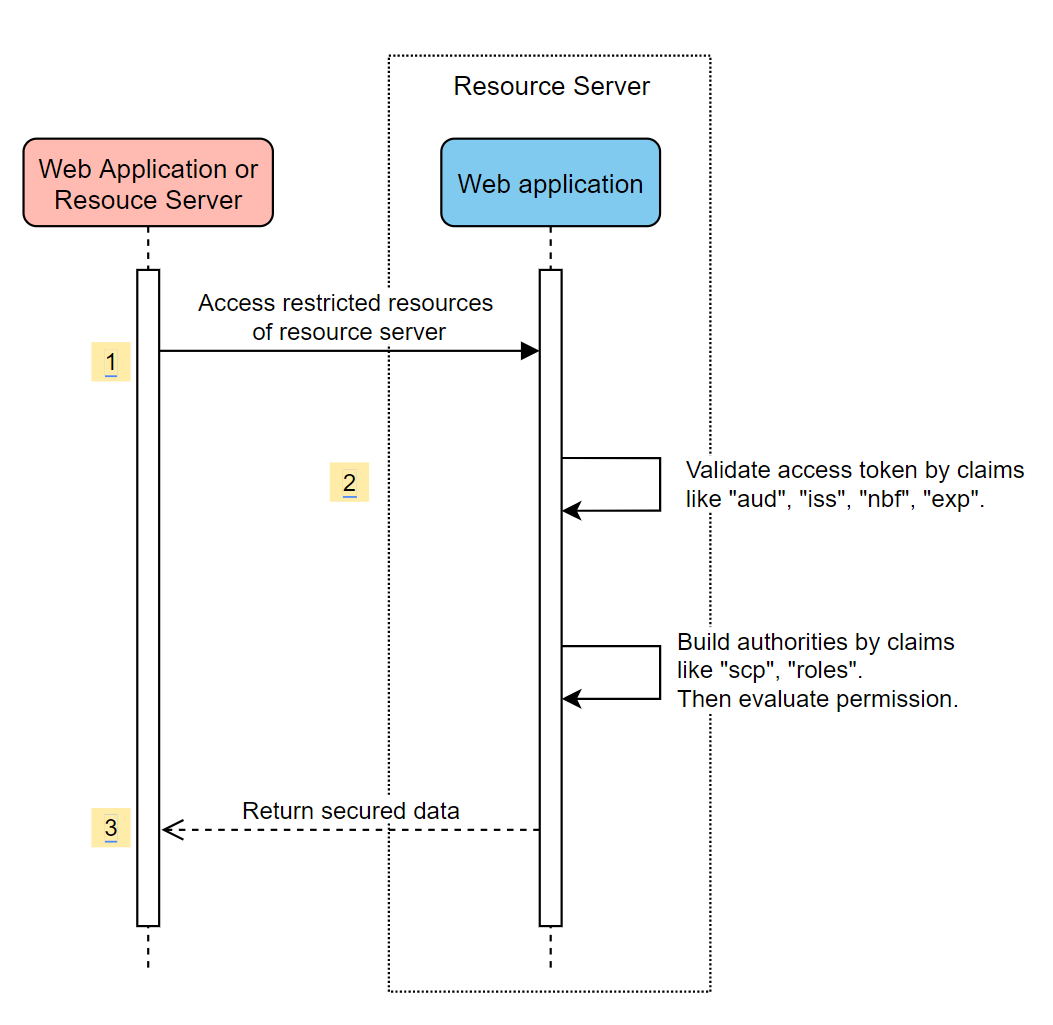
Create required resources in Azure
Read Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Create an app registration. Get
AZURE_CLIENT_ID.Read Quickstart: Configure an application to expose a web API.
Expose a web API with a scope named
Scope-1.
Add required dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add required properties
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
Now start your application and access your application's web api.
You'll get 401 without an access token.
Access your application with an access token. The following claims in the access token will be validated:
iss: The access token must be issued by Microsoft Entra ID.nbf: The current time can't be beforenbf.exp: The current time can't afterexp.aud: Ifspring.cloud.azure.active-directory.credential.client-idorspring.cloud.azure.active-directory.credential.app-id-uriconfigured, the audience must equal to the configuredclient-idorapp-id-uri. If the two properties aren't configured, this claim won't be validated.
For more information about the access token, see MS docs about Microsoft identity platform access tokens.
Advanced usages
Add extra security configurations
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class AadOAuth2ResourceServerSecurityConfig {
/**
* Add configuration logic as needed.
*/
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain htmlFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.apply(AadResourceServerHttpSecurityConfigurer.aadResourceServer())
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
// @formatter:on
return http.build();
}
}
Validate permission by scopes
Create required resources in Azure.
Read Quickstart: Configure an application to expose a web API.
Expose a web API with a scope named
Scope1.
Protect the specific method.
class Demo { @GetMapping("scope1") @ResponseBody @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('SCOPE_Scope1')") public String scope1() { return "Congratulations, you can access `scope1` endpoint."; } }
By doing this, when access /scope1 endpoint, the following claims in access token will be validated:
scp: The value must containScope1.
Validate permission by app roles
Create required resources in Azure.
Read Add app roles to your application and receive them in the token.
Create an app role with the following parameters:
- Display name: AppRole1
- Allowed member types: Users/Groups
- Value: AppRole1
- Do you want to enable this app role: yes
Protect the specific method.
class Demo { @GetMapping("app-role1") @ResponseBody @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('APPROLE_AppRole1')") public String appRole1() { return "Congratulations, you can access `app-role1` endpoint."; } }
By doing this, when access /app-role1 endpoint, the following claims in access token will be validated:
roles: The value must containAppRole1.
Use JWT client authentication
To use a JSON Web Token (JWT) for client authentication, use the following steps:
- See the Register your certificate with Microsoft identity platform section of Microsoft identity platform application authentication certificate credentials.
- Upload a .pem certificate to the application registered in the Azure portal.
- Configure the certificate path and password of a .PFX or .P12 certificate.
- Add the property
spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.authorization-clients.azure.client-authentication-method=private_key_jwtconfiguration to the client to be authenticated through JWT client authentication.
The following example configuration file is for a web application scenario. The certificate information is configured in the global properties.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-certificate-path: ${AZURE_CERTIFICATE_PATH}
client-certificate-password: ${AZURE_CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD}
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
active-directory:
enabled: true
user-group:
allowed-group-names: group1,group2
allowed-group-ids: <group1-id>,<group2-id>
post-logout-redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080
authorization-clients:
azure:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
arm:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes: https://management.core.windows.net/user_impersonation
graph:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes:
- https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read
- https://graph.microsoft.com/Directory.Read.All
webapiA:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes:
- ${WEB_API_A_APP_ID_URL}/Obo.WebApiA.ExampleScope
webapiB:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes:
- ${WEB_API_B_APP_ID_URL}/.default
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
You can also configure the certificate information in the active-directory service properties, as shown in this example:
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-certificate-path: ${AZURE_CERTIFICATE_PATH}
client-certificate-password: ${AZURE_CERTIFICATE_PASSWORD}
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
user-group:
allowed-group-names: group1,group2
allowed-group-ids: <group1-id>,<group2-id>
post-logout-redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080
authorization-clients:
azure:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
arm:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes: https://management.core.windows.net/user_impersonation
graph:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes:
- https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read
- https://graph.microsoft.com/Directory.Read.All
webapiA:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes:
- ${WEB_API_A_APP_ID_URL}/Obo.WebApiA.ExampleScope
webapiB:
client-authentication-method: private_key_jwt
scopes:
- ${WEB_API_B_APP_ID_URL}/.default
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Connecting to Microsoft Entra ID via proxy
To connect Microsoft Entra ID via proxy, provide a RestTemplateCustomizer bean. For more information, see the Connecting to Microsoft Entra ID via proxy section.
Samples
Sample project: aad-resource-server.
Resource server visiting other resource servers
System Diagram
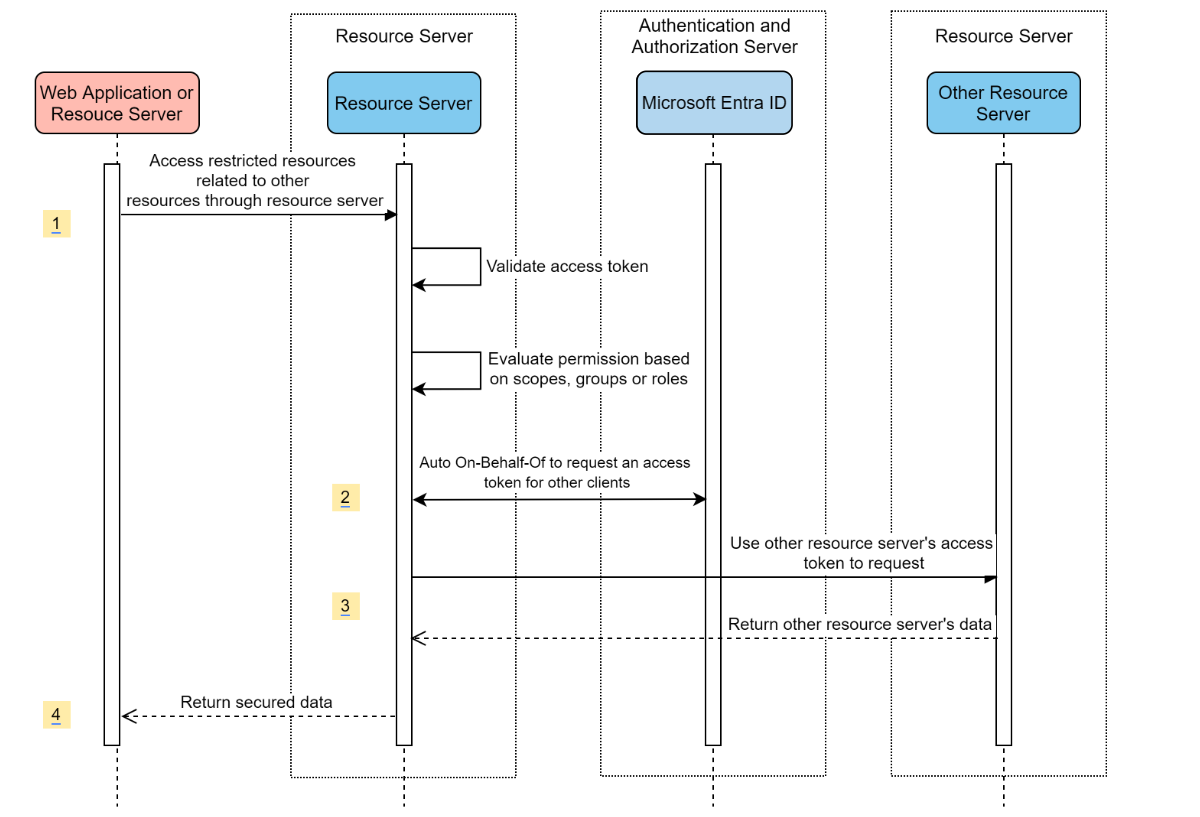
Create required resources in Azure
Read Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Create an app registration. Get
AZURE_TENANT_ID,AZURE_CLIENT_ID, andAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET.
Add required dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add required properties
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
authorization-clients:
graph:
scopes:
- https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Use OAuth2AuthorizedClient in your application
public class SampleController {
@GetMapping("call-graph")
public String callGraph(@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("graph") OAuth2AuthorizedClient graph) {
return callMicrosoftGraphMeEndpoint(graph);
}
}
Samples
Sample project: aad-resource-server-obo.
Web application and resource server in one application
Create required resources in Azure
Read Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Create an app registration. Get
AZURE_TENANT_ID,AZURE_CLIENT_ID, andAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET.
Add required dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add required properties
Set property spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.application-type to web_application_and_resource_server, and specify the authorization type for each authorization client.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
enabled: true
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
app-id-uri: ${WEB_API_ID_URI}
application-type: web_application_and_resource_server # This is required.
authorization-clients:
graph:
authorizationGrantType: authorization_code # This is required.
scopes:
- https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read
- https://graph.microsoft.com/Directory.Read.All
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Define SecurityFilterChain
Configure multiple SecurityFilterChain instances. AadWebApplicationAndResourceServerConfig contains two security filter chain configurations for resource server and web application.
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class AadWebApplicationAndResourceServerConfig {
@Bean
@Order(1)
public SecurityFilterChain apiFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.apply(AadResourceServerHttpSecurityConfigurer.aadResourceServer())
.and()
// All the paths that match `/api/**`(configurable) work as the resource server. Other paths work as the web application.
.securityMatcher("/api/**")
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain htmlFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.apply(AadWebApplicationHttpSecurityConfigurer.aadWebApplication())
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.requestMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
// @formatter:on
return http.build();
}
}
Configuration
Configurable properties of spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.app-id-uri | App ID URI that might be used in the "aud" claim of an id_token. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.application-type | Type of the Microsoft Entra application. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.authenticate-additional-parameters | Add additional parameters to the Authorization URL. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.authorization-clients | The OAuth2 authorization clients. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.credential.client-id | Client Id to use when performing service principal authentication with Azure. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.credential.client-secret | Client secret to use when performing service principal authentication with Azure. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.jwk-set-cache-lifespan | The lifespan of the cached JWK set before it expires, default is 5 minutes. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.jwk-set-cache-refresh-time | The refresh time of the cached JWK set before it expires, default is 5 minutes. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.jwt-connect-timeout | Connection Timeout for the JWKSet Remote URL call. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.jwt-read-timeout | Read Timeout for the JWKSet Remote URL call. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.jwt-size-limit | Size limit in Bytes of the JWKSet Remote URL call. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.post-logout-redirect-uri | The redirect uri after logout. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.profile.cloud-type | Name of the Azure cloud to connect to. Supported types are: AZURE, AZURE_CHINA, AZURE_GERMANY, AZURE_US_GOVERNMENT, OTHER. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.profile.environment | Properties to Microsoft Entra endpoints. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.profile.tenant-id | Azure Tenant ID. The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.redirect-uri-template | Redirection Endpoint: Used by the authorization server to return responses containing authorization credentials to the client via the resource owner user-agent. The default value is {baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.resource-server.claim-to-authority-prefix-map | Configure which claim will be used to build GrantedAuthority, and prefix of the GrantedAuthority's string value. Default value is: "scp" -> "SCOPE_", "roles" -> "APPROLE_". |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.resource-server.principal-claim-name | Configure which claim in access token be returned in AuthenticatedPrincipal#getName. Default value is "sub". |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.session-stateless | If true activates the stateless auth filter AadAppRoleStatelessAuthenticationFilter. The default is false which activates AadAuthenticationFilter. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.user-group.allowed-group-ids | The group ids can be used to construct GrantedAuthority. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.user-group.allowed-group-names | The group names can be used to construct GrantedAuthority. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.user-group.use-transitive-members | If "true", use "v1.0/me/transitiveMemberOf" to get members. Otherwise, use "v1.0/me/memberOf". The default value is false. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.user-name-attribute | Decide which claim to be principal's name. |
Here are some examples about how to use these properties:
Application type
The application type can be inferred from the dependencies: spring-security-oauth2-client or spring-security-oauth2-resource-server. If the inferred value isn't the value you want, you can specify the application type. Here's the table of valid values and inferred values:
Application type of spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory:
Has dependency: spring-security-oauth2-client |
Has dependency: spring-security-oauth2-resource-server |
Valid values of application type | Inferred value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | web_application |
web_application |
| No | Yes | resource_server |
resource_server |
| Yes | Yes | web_application, resource_server, resource_server_with_obo, web_application_and_resource_server |
resource_server_with_obo |
Spring Security with Azure Active Directory B2C
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) B2C is an identity management service that enables you to customize and control how customers sign up, sign in, and manage their profiles when using your applications. Azure AD B2C enables these actions while protecting the identities of your customers at the same time.
Dependency setup
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory-b2c</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Configuration
Configurable properties of spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory-b2c:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.app-id-uri | App ID URI that might be used in the "aud" claim of a token. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.authenticate-additional-parameters | Additional parameters for authentication. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.authorization-clients | Specify client configuration. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.base-uri | Azure AD B2C endpoint base uri. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.credential | Azure AD B2C credential information. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.jwt-connect-timeout | Connection Timeout for the JWKSet Remote URL call. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.jwt-read-timeout | Read Timeout for the JWKSet Remote URL call. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.jwt-size-limit | Size limit in Bytes of the JWKSet Remote URL call. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.login-flow | Specify the primary sign-in flow key. The default value is sign-up-or-sign-in. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.logout-success-url | Redirect URL after logout. The default value is http://localhost:8080/login. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.profile | Azure AD B2C profile information. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.reply-url | Reply URL after get authorization code. The default value is {baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.user-flows | User flows. |
| spring.cloud.azure.active-directory.b2c.user-name-attribute-name | User name attribute name. |
For full configurations, check Spring Cloud Azure configuration properties.
Basic usage
A web application is any web-based application that allows user to login with Microsoft Entra ID, whereas a resource server will either accept or deny access after validating access_token obtained from Microsoft Entra ID. We'll cover 4 scenarios in this guide:
Accessing a web application.
Web application accessing resource servers.
Accessing a resource server.
Resource server accessing other resource servers.
Usage 1: Accessing a web application
This scenario uses The OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant flow to log in a user with your Azure AD B2C user.
Select Azure AD B2C from the portal menu, select Applications, and then select Add.
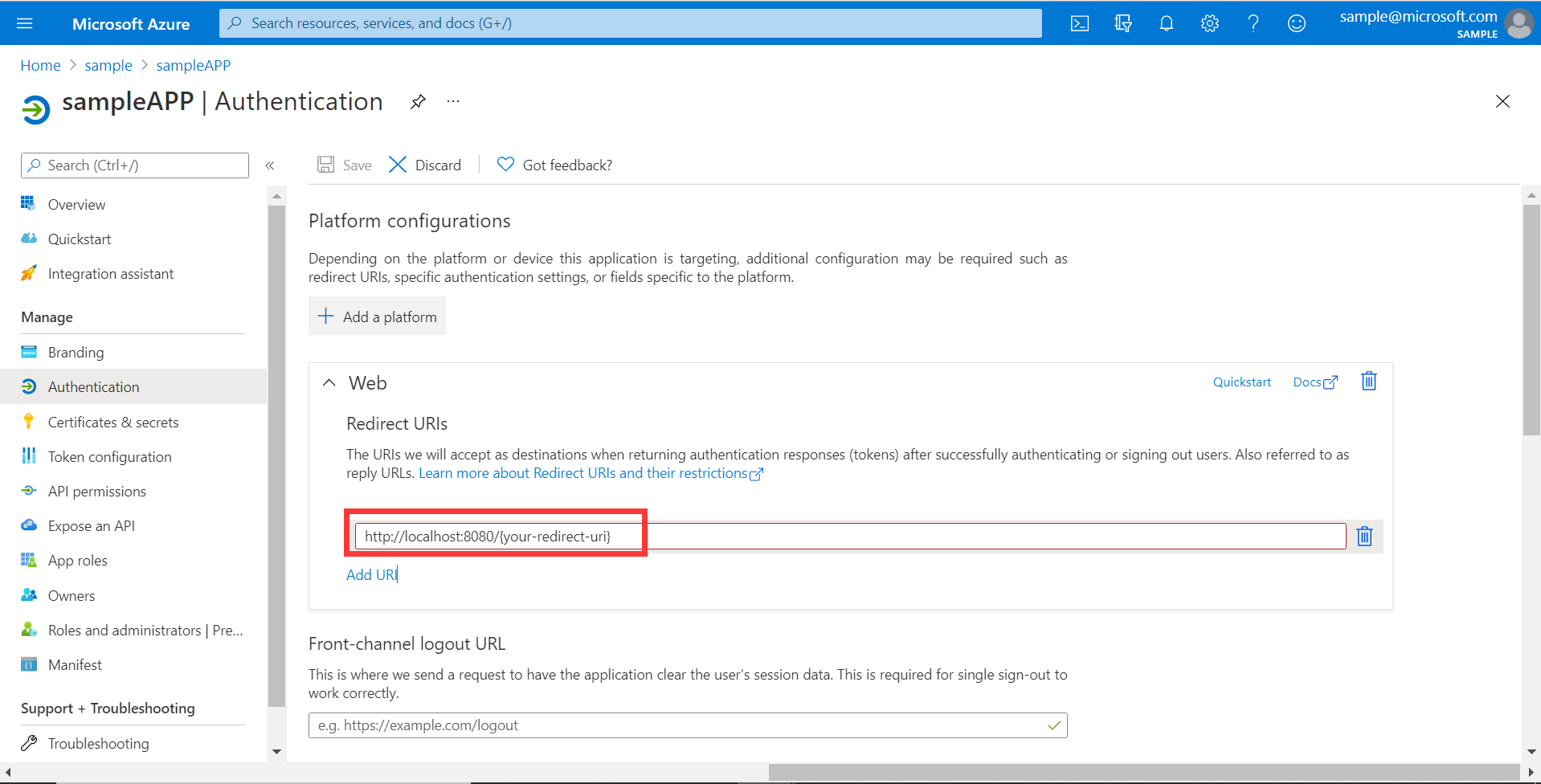
Specify your application Name (such as webapp), add http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/ for the Reply URL, record the Application ID as your WEB_APP_AZURE_CLIENT_ID, and then select Save.
Select Keys from your application, select Generate key to generate WEB_APP_AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET, and then select Save.
Select User flows on your left, and then select New user flow.
Choose Sign up or in, Profile editing, and Password reset to create user flows respectively. Specify your user flow Name and User attributes and claims, then select Create.
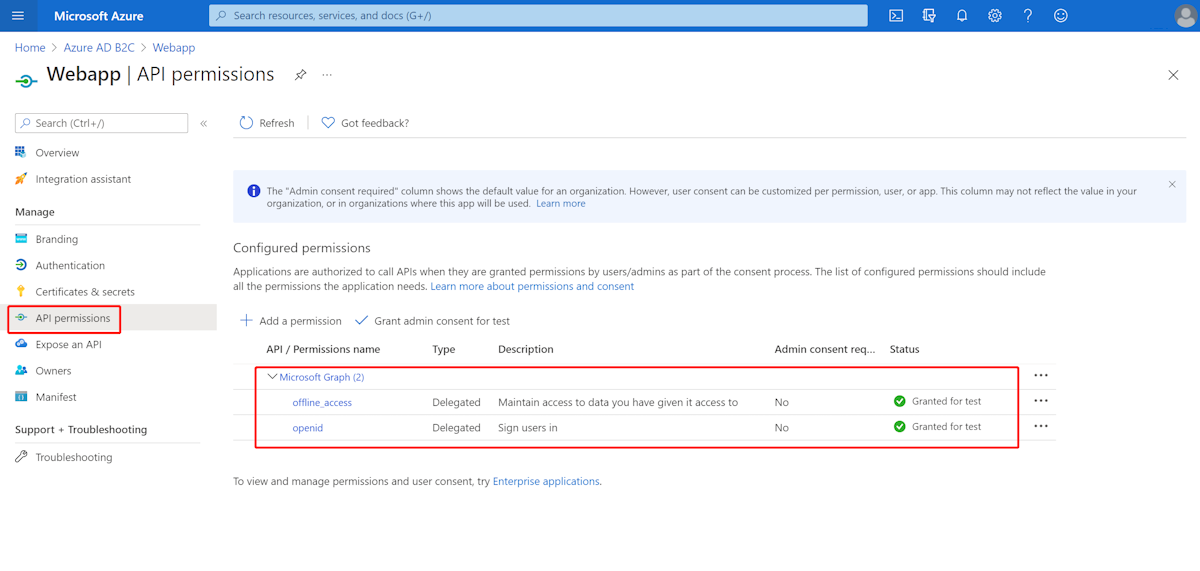
Select API permissions > Add a permission > Microsoft APIs, select Microsoft Graph, select Delegated permissions, select the offline_access and openid permissions, and then select Add permission to complete the process.
Grant admin consent for Graph permissions.
Add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-spring-boot-starter-active-directory-b2c</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add properties to your application.yml file using the values you created earlier, as shown in the following example:
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
b2c:
enabled: true
authenticate-additional-parameters:
domain_hint: xxxxxxxxx # optional
login_hint: xxxxxxxxx # optional
prompt: [login,none,consent] # optional
base-uri: ${BASE_URI}
credential:
client-id: ${WEBAPP_AZURE_CLIENT_ID}
client-secret: ${WEBAPP_AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
login-flow: ${LOGIN_USER_FLOW_KEY} # default to sign-up-or-sign-in, will look up the user-flows map with provided key.
logout-success-url: ${LOGOUT_SUCCESS_URL}
user-flows:
${YOUR_USER_FLOW_KEY}: ${USER_FLOW_NAME}
user-name-attribute-name: ${USER_NAME_ATTRIBUTE_NAME}
Write your Java code.
For your controller code, you can refer to the following example:
@Controller
public class WebController {
private void initializeModel(Model model, OAuth2AuthenticationToken token) {
if (token != null) {
final OAuth2User user = token.getPrincipal();
model.addAllAttributes(user.getAttributes());
model.addAttribute("grant_type", user.getAuthorities());
model.addAttribute("name", user.getName());
}
}
@GetMapping(value = { "/", "/home" })
public String index(Model model, OAuth2AuthenticationToken token) {
initializeModel(model, token);
return "home";
}
}
For your security configuration code, you can refer to the following example:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfiguration {
private final AadB2cOidcLoginConfigurer configurer;
public WebSecurityConfiguration(AadB2cOidcLoginConfigurer configurer) {
this.configurer = configurer;
}
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.apply(configurer);
// @formatter:on
return http.build();
}
}
Copy the home.html from aad-b2c-web-application sample, and replace the PROFILE_EDIT_USER_FLOW and PASSWORD_RESET_USER_FLOW with your user flow names that you used previously.
Build and test your app. Let Webapp run on port 8080.
After your application is built and started by Maven, open http://localhost:8080/ in a web browser. You should be redirected to the login page.
Select the link with the login user flow. You should be redirected Azure AD B2C to start the authentication process.
After you've logged in successfully, you should see the sample home page from the browser.
Usage 2: Web application accessing resource servers
This scenario is based on the Accessing a web application scenario to allow an application to access other resources. This scenario is The OAuth 2.0 client credentials grant flow.
Select Azure AD B2C from the portal menu, select Applications, and then select Add.
Specify your application Name (such as webApiA), record the Application ID as your WEB_API_A_AZURE_CLIENT_ID, and then select Save.
Select Keys from your application, select Generate key to generate WEB_API_A_AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET, and then select Save.
Select Expose an API from the navigation pane, and then select Set. Record the Application ID URI as your WEB_API_A_APP_ID_URL, and then select Save.
Select Manifest from the navigation pane, and then paste the following JSON segment into appRoles array. Record the Application ID URI as your WEB_API_A_APP_ID_URL, record the value of the app role as your WEB_API_A_ROLE_VALUE, and then select Save.
{
"allowedMemberTypes": [
"Application"
],
"description": "WebApiA.SampleScope",
"displayName": "WebApiA.SampleScope",
"id": "04989db0-3efe-4db6-b716-ae378517d2b7",
"isEnabled": true,
"value": "WebApiA.SampleScope"
}
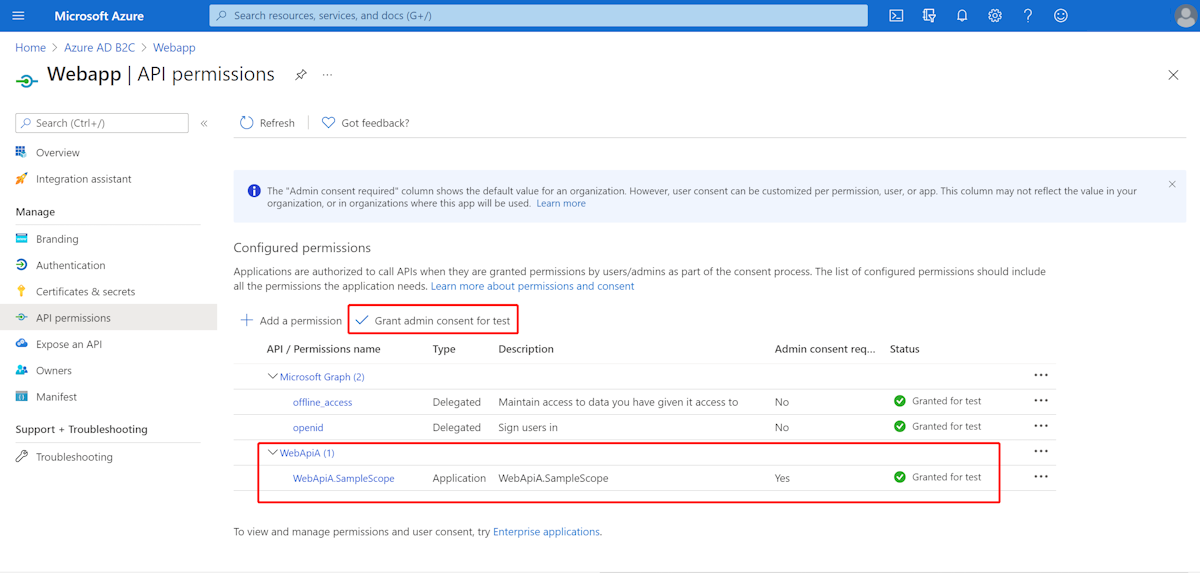
Select API permissions > Add a permission > My APIs, select WebApiA application name, select Application Permissions, select WebApiA.SampleScope permission, and then select Add permission to complete the process.
Grant admin consent for WebApiA permissions.
Add the following dependency on the basis of the Accessing a web application scenario.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
Add the following configuration on the basis of the Accessing a web application scenario.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
b2c:
enabled: true
base-uri: ${BASE_URI} # Such as: https://xxxxb2c.b2clogin.com
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
authorization-clients:
${RESOURCE_SERVER_A_NAME}:
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials
scopes: ${WEB_API_A_APP_ID_URL}/.default
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Write your Webapp Java code.
For your controller code, you can refer to the following example:
class Demo {
/**
* Access to protected data from Webapp to WebApiA through client credential flow. The access token is obtained by webclient, or
* <p>@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("webApiA")</p>. In the end, these two approaches will be executed to
* DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager#authorize method, get the access token.
*
* @return Respond to protected data from WebApi A.
*/
@GetMapping("/webapp/webApiA")
public String callWebApiA() {
String body = webClient
.get()
.uri(LOCAL_WEB_API_A_SAMPLE_ENDPOINT)
.attributes(clientRegistrationId("webApiA"))
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.block();
LOGGER.info("Call callWebApiA(), request '/webApiA/sample' returned: {}", body);
return "Request '/webApiA/sample'(WebApi A) returned a " + (body != null ? "success." : "failure.");
}
}
Security configuration code is the same as in the Accessing a web application scenario. Add another bean webClient as follows:
public class SampleConfiguration {
@Bean
public WebClient webClient(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager oAuth2AuthorizedClientManager) {
ServletOAuth2AuthorizedClientExchangeFilterFunction function =
new ServletOAuth2AuthorizedClientExchangeFilterFunction(oAuth2AuthorizedClientManager);
return WebClient.builder()
.apply(function.oauth2Configuration())
.build();
}
}
To write your WebApiA Java code, see the Accessing a resource server section.
Build and test your app. Let Webapp and WebApiA run on port 8080 and 8081 respectively. Start the Webapp and WebApiA applications. Return to the home page after logging in successfully. You can then access http://localhost:8080/webapp/webApiA to get the WebApiA resource response.
Usage 3: Accessing a resource server
This scenario doesn't support login. Just protect the server by validating the access token, and if valid, it serves the request.
To build your WebApiA permission, see Usage 2: Web Application Accessing Resource Servers.
Add WebApiA permission and grant admin consent for your web application.
Add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-spring-boot-starter-active-directory-b2c</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add the following configuration.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
b2c:
enabled: true
base-uri: ${BASE_URI} # Such as: https://xxxxb2c.b2clogin.com
profile:
tenant-id: <tenant>
app-id-uri: ${APP_ID_URI} # If you're using v1.0 token, configure app-id-uri for `aud` verification
credential:
client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID} # If you're using v2.0 token, configure client-id for `aud` verification
user-flows:
sign-up-or-sign-in: ${SIGN_UP_OR_SIGN_IN_USER_FLOW_NAME}
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Write your Java code.
For your controller code, you can refer to the following example:
class Demo {
/**
* webApiA resource api for web app
* @return test content
*/
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('APPROLE_WebApiA.SampleScope')")
@GetMapping("/webApiA/sample")
public String webApiASample() {
LOGGER.info("Call webApiASample()");
return "Request '/webApiA/sample'(WebApi A) returned successfully.";
}
}
For your security configuration code, you can refer to the following example:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class ResourceServerConfiguration {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain htmlFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
JwtAuthenticationConverter authenticationConverter = new JwtAuthenticationConverter();
JwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter jwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter = new JwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter();
jwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter.setAuthorityPrefix("APPROLE_");
authenticationConverter.setJwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter(jwtGrantedAuthoritiesConverter);
// @formatter:off
http.authorizeHttpRequests((requests) -> requests.anyRequest().authenticated())
.oauth2ResourceServer()
.jwt()
.jwtAuthenticationConverter(authenticationConverter);
// @formatter:on
return http.build();
}
}
Build and test your app. Let WebApiA run on port 8081. Get the access token for the webApiA resource and then access http://localhost:8081/webApiA/sample as the Bearer authorization header.
Usage 4: Resource server accessing other resource servers
This scenario is an upgrade of Accessing a resource server, and supports access to other application resources, based on OAuth2 client credentials flow.
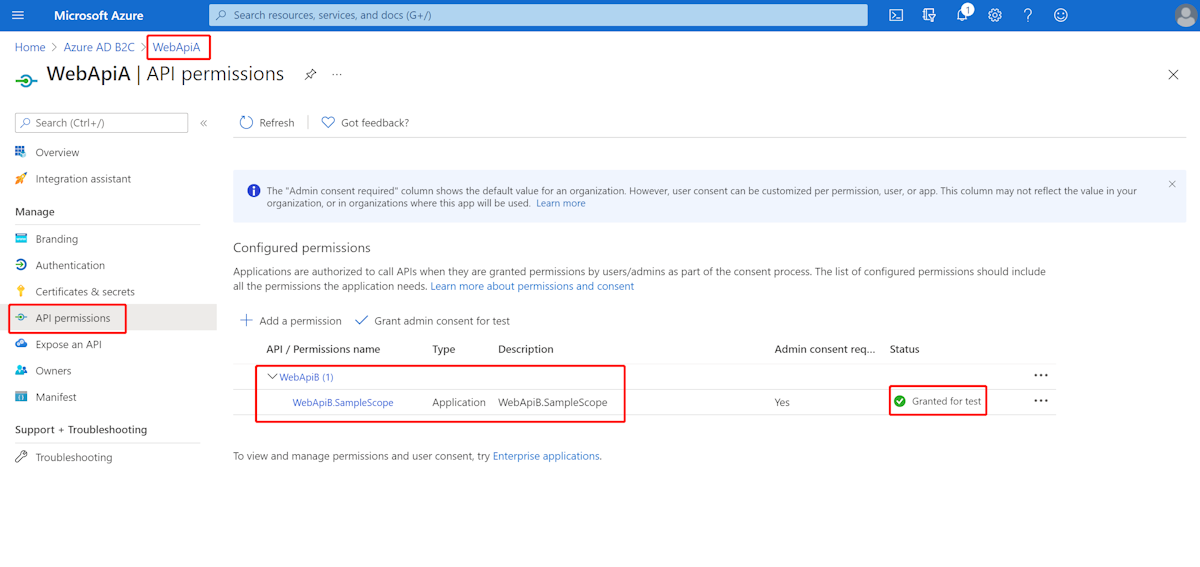
Referring to the previous steps, we create a WebApiB application and expose an application permission WebApiB.SampleScope.
{
"allowedMemberTypes": [
"Application"
],
"description": "WebApiB.SampleScope",
"displayName": "WebApiB.SampleScope",
"id": "04989db0-3efe-4db6-b716-ae378517d2b7",
"isEnabled": true,
"lang": null,
"origin": "Application",
"value": "WebApiB.SampleScope"
}
Grant admin consent for WebApiB permissions.
On the basis of Accessing a resource server, add the following dependency to your pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
Add the following configuration on the basis of the Accessing a resource server scenario configuration.
spring:
cloud:
azure:
active-directory:
b2c:
enabled: true
credential:
client-secret: ${WEB_API_A_AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET}
authorization-clients:
${RESOURCE_SERVER_B_NAME}:
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials
scopes: ${WEB_API_B_APP_ID_URL}/.default
Write your Java code.
For your WebApiA controller code, you can refer to the following example:
public class SampleController {
/**
* Access to protected data from WebApiA to WebApiB through client credential flow. The access token is obtained by webclient, or
* <p>@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("webApiA")</p>. In the end, these two approaches will be executed to
* DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager#authorize method, get the access token.
*
* @return Respond to protected data from WebApi B.
*/
@GetMapping("/webApiA/webApiB/sample")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('APPROLE_WebApiA.SampleScope')")
public String callWebApiB() {
String body = webClient
.get()
.uri(LOCAL_WEB_API_B_SAMPLE_ENDPOINT)
.attributes(clientRegistrationId("webApiB"))
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.block();
LOGGER.info("Call callWebApiB(), request '/webApiB/sample' returned: {}", body);
return "Request 'webApiA/webApiB/sample'(WebApi A) returned a " + (body != null ? "success." : "failure.");
}
}
For your WebApiB controller code, you can refer to the following example:
public class SampleController {
/**
* webApiB resource api for other web application
* @return test content
*/
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('APPROLE_WebApiB.SampleScope')")
@GetMapping("/webApiB/sample")
public String webApiBSample() {
LOGGER.info("Call webApiBSample()");
return "Request '/webApiB/sample'(WebApi B) returned successfully.";
}
}
Security configuration code is the same with Accessing a resource server scenario, another bean webClient is added as follows
public class SampleConfiguration {
@Bean
public WebClient webClient(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager oAuth2AuthorizedClientManager) {
ServletOAuth2AuthorizedClientExchangeFilterFunction function =
new ServletOAuth2AuthorizedClientExchangeFilterFunction(oAuth2AuthorizedClientManager);
return WebClient.builder()
.apply(function.oauth2Configuration())
.build();
}
}
Build and test your app. Let WebApiA and WebApiB run on port 8081 and 8082 respectively. Start the WebApiA and WebApiB applications, get the access token for webApiA resource, and access http://localhost:8081/webApiA/webApiB/sample as the Bearer authorization header.
Samples
For more information, see the spring-cloud-azure-starter-active-directory-b2c samples.