Verify SQL machine protection
After enabling protection for SQL VMs with the Defender for SQL Servers on Machines plan, verify that your SQL servers are protected as expected.
Verify protection on multiple Azure VMs
Retrieve and review the Defender for SQL Servers on Machines protection status report for all SQL VMs within a specified Azure subscription by running the Get-SqlVMProtectionStatusReport.ps1 PowerShell script. The script applies to Azure VMs only.
Verify protection on multiple Azure Arc-enabled VMs
In the Azure portal, Search for and select Azure Resource Graph.
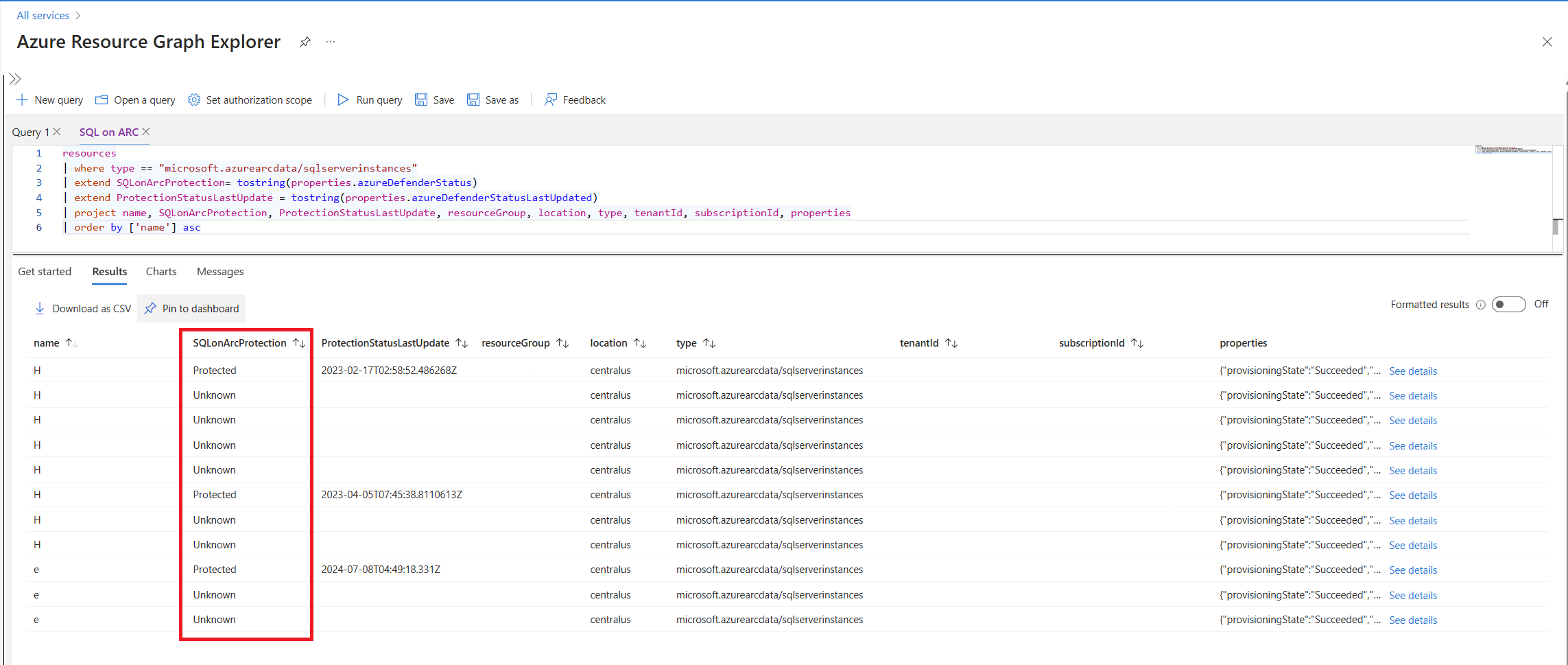
Copy and run the following query to identify Azure Arc-enabled VMs that aren't in a protected state.
resources | where type == "microsoft.azurearcdata/sqlserverinstances" | extend SQLonArcProtection= tostring(properties.azureDefenderStatus) | extend ProtectionStatusLastUpdate = tostring(properties.azureDefenderStatusLastUpdated) | project name, SQLonArcProtection, ProtectionStatusLastUpdate, resourceGroup, location, type, tenantId, subscriptionId, properties | order by ['name'] ascReview the results, specifically checking the SQLonArcProtection status. Any result that doesn't state
Protectedindicates that the SQL Server VM, or Azure Arc-enabled SQL Server isn't protected.If the
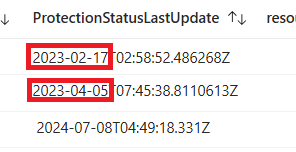
ProtectionStatusLastUpdatefield doesn't show a date within the last day, the machine might not be protected. Verify the protection of the single SQL server VM.
The script can return the following possible protection statuses:
- Protected: Defender for SQL actively protects the instance. Ensure the information isn't outdated by checking the Last Update field.
- Not Protected: Defender for SQL encountered issues while protecting the instance. This status indicates that some intervention is required to enable successful protection.
- Inactive: Defender for SQL runs on the machine, but the SQL instance is either paused or stopped.
- Empty or Unknown: The protection status couldn't be retrieved or doesn't exist on the machine. In this case, assume that the instance isn't protected by Defender for SQL.
Verify protection on a single SQL server VM
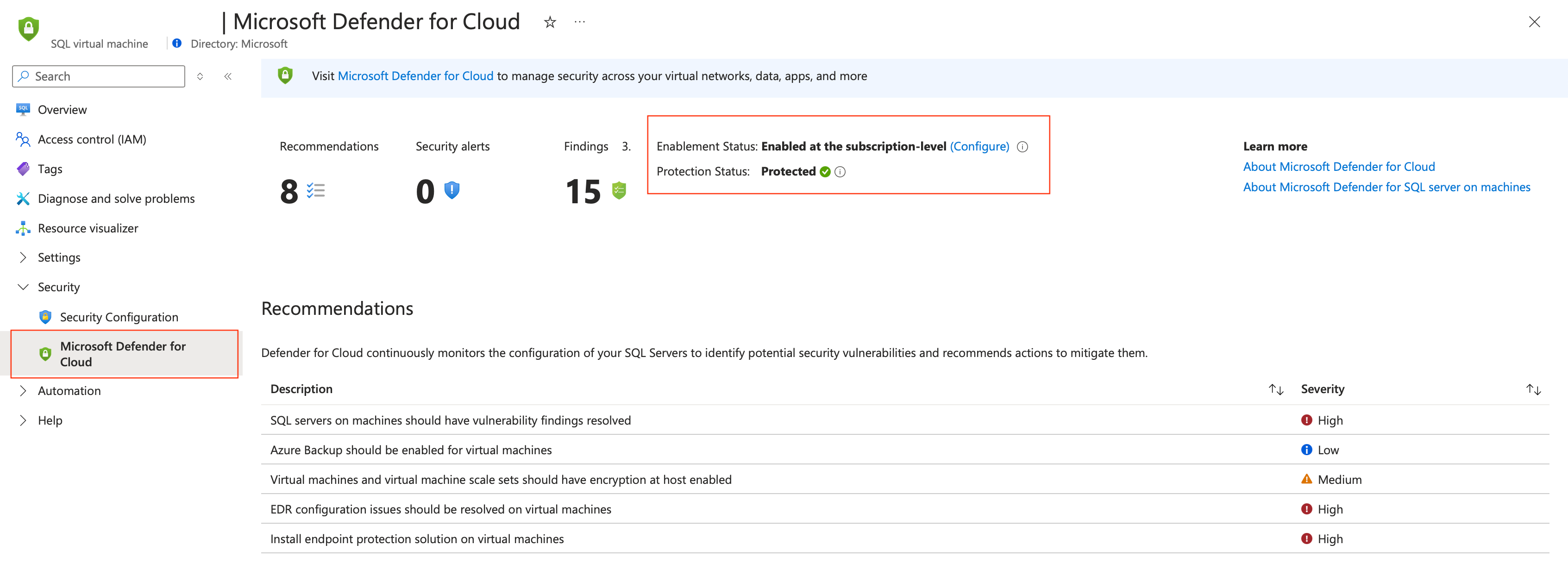
Depending on the resources in your environment, search for and select SQL virtual machines or SQL Server - Azure Arc in the Azure portal.
Locate and select the relevant resource.
Under the Security tab, select Defender for Cloud.
Check the Protection status. If the status is Protected, the deployment was successful.
Troubleshoot unprotected machines
If databases aren't protected, follow the instructions in the troubleshooting guide to remediate.