Gain end-user context for AI alerts
Microsoft Defender for Cloud's threat protection for AI workloads allows you to enhance the actionability and security value of the generated AI alerts by providing end-user context.
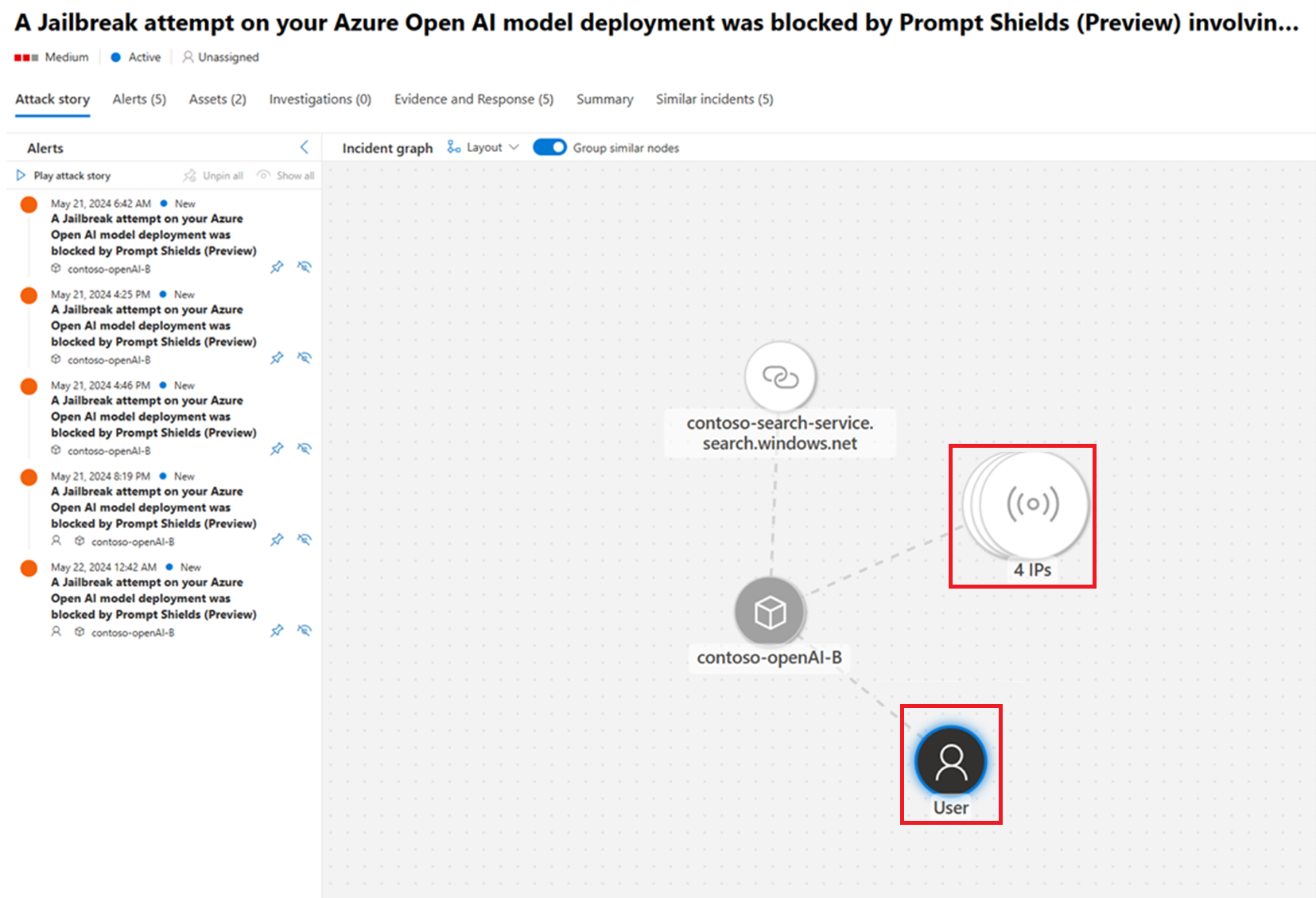
Add parameters to your Azure OpenAI API calls to enable your Azure AI to pass critical end-user context to Defender for Cloud's AI alerts. This end-user context provides greater visibility into end-users, and leads to more effective investigations and results. For example, you can block a specific user or correlate incidents and alerts by end-user.
Prerequisites
Read up on Overview - AI threat protection.
Enable threat protection for AI workloads (preview) on an AI application, with Azure OpenAI underlying model, directly through the Azure Open AI service. Note, this feature is currently not supported when leveraging models deployed through the Azure AI model inference API.
Add security parameters to your Azure OpenAI call
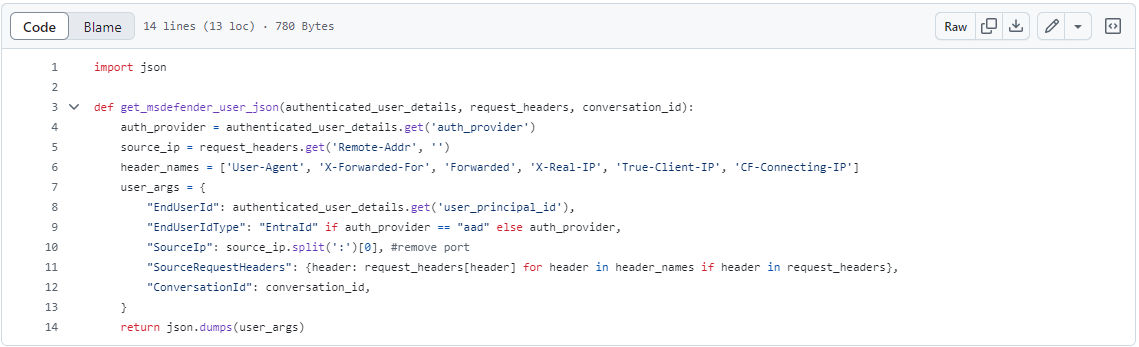
To receive AI security alerts with more context, you can add any or all of the following sample SecurityContext parameters to your Azure OpenAI API calls.
All of the fields in the SecurityContext are optional. We recommend passing the EndUserId and SourceIP fields at a minimum. The EndUserId and SourceIP fields provide Security Operations Center (SOC) analysts the ability to investigate security incidents that involve AI resources and generative AI applications. For examples, see the SecurityContext schema.
If a field’s name is misspelled, the Azure OpenAI API call will still succeed. The SecurityContext schema doesn't require validation to pass through the Azure OpenAI user field. Application developers should ensure that a valid JSON is passed to the user field in every request made by the application to Azure OpenAI.
SecurityContext schema
The provided schema consists of the SecurityContext objects that contains several parameters that describe the application itself, and the end user that interacts with the application. These fields assist your security operations teams to investigate and mitigate security incidents by providing a comprehensive approach to protecting your AI applications.
End user ID
End user type
End user tenant's ID
Source IP address
Source request headers
Application name
| Field name | Type | Description | Optional | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EndUserId | string | Acts as a unique identifier for the end user within the generative AI application. If Microsoft Entra ID authorization is used to authenticate end-users in the generative AI application, this should be a Microsoft Entra ID (previously known as Azure Active Directory) user object ID. | Yes | 1234a123-12a3-1234-1ab2-a1b2c34d56e |
| EndUserIdType | string | Specifies the type of end user identifier. It should be set to Microsoft Entra ID when using Microsoft Entra (previously known as Azure Active Directory) user object ID. | Yes, unless EndUserId is passed, in that case this must be set to proper value. | Microsoft Entra ID |
| EndUserTenantId | string | This property specifies the Microsoft 365 tenant ID the end user belongs to. It's required when the generative AI application is multitenant and end users from different tenants can sign-in. | Yes | 1234a123-12a3-1234-1ab2-a1b2c34d56e |
| SourceIP | string | Captures the IP address of the client as seen directly by the server. It represents the most immediate client IP address that made the connection to the server. If the client connects through a proxy or load balancer, SourceIP is the IP address of that proxy or load balancer, not the original client's IP address: - ASP.NET: HttpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress - Python: request.remote_addr |
Yes | 12.34.567.891, 1234:1:123a:123:1a2b:ab1:ab1c:ab12 |
| SourceRequestHeaders | Dictionary<string, string> | Captures a subset of end user's request headers that proxies or load balancers add. Headers like X-Forwarded-For, X-Real-IP, or Forwarded are used by Microsoft Defender for Cloud to get the original client's IP address. User-Agent headers provide context about the client software initiating the API request. Recommended header names include: User-Agent, X-Forwarded-For, X-Real-IP, Forwarded, CF-Connecting-IP, True-Client-IP, X-Client-IP, X-Forwarded, Forwarded-For |
Yes | - |
| ApplicationName | string | The name of the application, used for identification and UI purposes. | Yes | Contoso HR Copilot, Customer sales chat bot. |
Add the SecurityContext to your application
We recommend adding all of the parameters provided in this document to your generative AI application's API calls to Azure OpenAI.
Select one of these examples:
Locate and copy the sample code.
Add the code to your generative AI application's code where Azure OpenAI API is called.
Alter the code parameters to match your requirements.
Save the changes.
After following the procedure, you should ensure that a valid JSON is passed to the user field in every request made by the application to Azure OpenAI.