Update Machine Learning Studio (classic) models by using Update Resource activity
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
Important
Support for Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic) will end on August 31, 2024. We recommend that you transition to Azure Machine Learning by that date.
As of December 1, 2021, you can't create new Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources (workspace and web service plan). Through August 31, 2024, you can continue to use the existing Machine Learning Studio (classic) experiments and web services. For more information, see:
- Migrate to Azure Machine Learning from Machine Learning Studio (classic)
- What is Azure Machine Learning?
Machine Learning Studio (classic) documentation is being retired and might not be updated in the future.
Note
Since Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources can no longer be created after 1 Dec 2021, users are encouraged to use Azure Machine Learning with the Machine Learning Execute Pipeline activity rather than using the Update Resource activity to update Machine Learning Studio (classic) models.
This article complements the main Machine Learning Studio (classic) integration article: Create predictive pipelines using Machine Learning Studio (classic). If you didn't already do so, review the main article before reading through this article.
Overview
As part of the process of operationalizing Machine Learning Studio (classic) models, your model is trained and saved. You then use it to create a predictive Web service. The Web service can then be consumed in web sites, dashboards, and mobile apps.
Models you create using Machine Learning Studio (classic) are typically not static. As new data becomes available or when the consumer of the API has their own data the model needs to be retrained.
Retraining could occur frequently. With Batch Execution activity and Update Resource activity, you can operationalize the Machine Learning Studio (classic) model retraining and updating the predictive Web Service.
The following picture depicts the relationship between training and predictive Web Services.
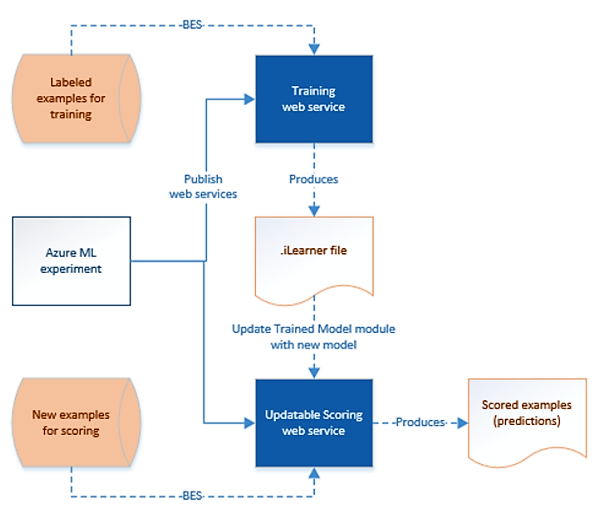
Machine Learning Studio (classic) update resource activity
The following JSON snippet defines a Machine Learning Studio (classic) Batch Execution activity.
{
"name": "amlUpdateResource",
"type": "AzureMLUpdateResource",
"description": "description",
"linkedServiceName": {
"type": "LinkedServiceReference",
"referenceName": "updatableScoringEndpoint2"
},
"typeProperties": {
"trainedModelName": "ModelName",
"trainedModelLinkedServiceName": {
"type": "LinkedServiceReference",
"referenceName": "StorageLinkedService"
},
"trainedModelFilePath": "ilearner file path"
}
}
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| name | Name of the activity in the pipeline | Yes |
| description | Text describing what the activity does. | No |
| type | For Machine Learning Studio (classic) Update Resource activity, the activity type is AzureMLUpdateResource. | Yes |
| linkedServiceName | Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked service that contains updateResourceEndpoint property. | Yes |
| trainedModelName | Name of the Trained Model module in the Web Service experiment to be updated | Yes |
| trainedModelLinkedServiceName | Name of Azure Storage linked service holding the ilearner file uploaded by the update operation | Yes |
| trainedModelFilePath | The relative file path in trainedModelLinkedService to represent the ilearner file uploaded by the update operation | Yes |
End-to-end workflow
The entire process of operationalizing retraining a model and update the predictive Web Services involves the following steps:
- Invoke the training Web Service by using the Batch Execution activity. Invoking a training Web Service is the same as invoking a predictive Web Service described in Create predictive pipelines using Machine Learning Studio (classic) and the Batch Execution activity. The output of the training Web Service is an iLearner file that you can use to update the predictive Web Service.
- Invoke the update resource endpoint of the predictive Web Service by using the Update Resource activity to update the Web Service with the newly trained model.
Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked service
For the previously mentioned end-to-end workflow to work, you need to create two Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked services:
- A Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked service to the training web service, this linked service is used by Batch Execution activity in the same way as what's mentioned in Create predictive pipelines using Machine Learning Studio (classic) and the Batch Execution activity. Difference is the output of the training web service is an iLearner file, which is then used by Update Resource activity to update the predictive web service.
- A Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked service to the update resource endpoint of the predictive web service. This linked service is used by Update Resource activity to update the predictive web service using the iLearner file returned from previous step.
For the second Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked service, the configuration is different when your Machine Learning Studio (classic) Web Service is a classic Web Service or a new Web Service. The differences are discussed separately in the following sections.
Web service is new Azure Resource Manager web service
If the web service is the new type of web service that exposes an Azure Resource Manager endpoint, you don't need to add the second non-default endpoint. The updateResourceEndpoint in the linked service is of the format:
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearning/webServices/{web-service-name}?api-version=2016-05-01-preview
You can get values for place holders in the URL when querying the web service on the Azure Machine Learning studio.
The new type of update resource endpoint requires service principal authentication. To use service principal authentication, register an application entity in Microsoft Entra ID and grant it the Contributor or Owner role of the subscription or the resource group where the web service belongs to. The See how to create service principal and assign permissions to manage Azure resource. Make note of the following values, which you use to define the linked service:
- Application ID
- Application key
- Tenant ID
Here's a sample linked service definition:
{
"name": "AzureMLLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureML",
"description": "The linked service for AML web service.",
"typeProperties": {
"mlEndpoint": "https://ussouthcentral.services.azureml.net/workspaces/0000000000000000 000000000000000000000/services/0000000000000000000000000000000000000/jobs?api-version=2.0",
"apiKey": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "APIKeyOfEndpoint1"
},
"updateResourceEndpoint": "https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearning/webServices/{web-service-name}?api-version=2016-05-01-preview",
"servicePrincipalId": "000000000-0000-0000-0000-0000000000000",
"servicePrincipalKey": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "servicePrincipalKey"
},
"tenant": "mycompany.com"
}
}
}
The following scenario provides more details. It has an example for retraining and updating Machine Learning Studio (classic) models from a pipeline.
Sample: Retraining and updating a Machine Learning Studio (classic) model
This section provides a sample pipeline that uses the Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic) Batch Execution activity to retrain a model. The pipeline also uses the Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic) Update Resource activity to update the model in the scoring web service. The section also provides JSON snippets for all the linked services, datasets, and pipeline in the example.
Azure Blob storage linked service:
The Azure Storage holds the following data:
- training data. The input data for the Machine Learning Studio (classic) training web service.
- iLearner file. The output from the Machine Learning Studio (classic) training web service. This file is also the input to the Update Resource activity.
Here's the sample JSON definition of the linked service:
{
"name": "StorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=name;AccountKey=key"
}
}
}
Linked service for Machine Learning Studio (classic) training endpoint
The following JSON snippet defines a Machine Learning Studio (classic) linked service that points to the default endpoint of the training web service.
{
"name": "trainingEndpoint",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureML",
"typeProperties": {
"mlEndpoint": "https://ussouthcentral.services.azureml.net/workspaces/xxx/services/--training experiment--/jobs",
"apiKey": "myKey"
}
}
}
In Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic), do the following to get values for mlEndpoint and apiKey:
- Select WEB SERVICES on the left menu.
- Select the training web service in the list of web services.
- Select copy next to API key text box. Paste the key in the clipboard into the Data Factory JSON editor.
- In the Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic), select BATCH EXECUTION link.
- Copy the Request URI from the Request section and paste it into the JSON editor.
Linked service for Azure Machine Learning studio (classic) updatable scoring endpoint:
The following JSON snippet defines an Azure Machine Learning studio (classic) linked service that points to updatable endpoint of the scoring web service.
{
"name": "updatableScoringEndpoint2",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureML",
"typeProperties": {
"mlEndpoint": "https://ussouthcentral.services.azureml.net/workspaces/00000000eb0abe4d6bbb1d7886062747d7/services/00000000026734a5889e02fbb1f65cefd/jobs?api-version=2.0",
"apiKey": "sooooooooooh3WvG1hBfKS2BNNcfwSO7hhY6dY98noLfOdqQydYDIXyf2KoIaN3JpALu/AKtflHWMOCuicm/Q==",
"updateResourceEndpoint": "https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/ffffffff-eeee-dddd-cccc-bbbbbbbbbbb0/resourceGroups/Default-MachineLearning-SouthCentralUS/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearning/webServices/myWebService?api-version=2016-05-01-preview",
"servicePrincipalId": "fe200044-c008-4008-a005-94000000731",
"servicePrincipalKey": "zWa0000000000Tp6FjtZOspK/WMA2tQ08c8U+gZRBlw=",
"tenant": "mycompany.com"
}
}
}
Pipeline
The pipeline has two activities: AzureMLBatchExecution and AzureMLUpdateResource. The Batch Execution activity takes the training data as input and produces an iLearner file as an output. The Update Resource activity then takes this iLearner file and use it to update the predictive web service.
{
"name": "LookupPipelineDemo",
"properties": {
"activities": [
{
"name": "amlBEGetilearner",
"description": "Use AML BES to get the ilearner file from training web service",
"type": "AzureMLBatchExecution",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "trainingEndpoint",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"typeProperties": {
"webServiceInputs": {
"input1": {
"LinkedServiceName":{
"referenceName": "StorageLinkedService",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"FilePath":"azuremltesting/input"
},
"input2": {
"LinkedServiceName":{
"referenceName": "StorageLinkedService",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"FilePath":"azuremltesting/input"
}
},
"webServiceOutputs": {
"output1": {
"LinkedServiceName":{
"referenceName": "StorageLinkedService",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"FilePath":"azuremltesting/output"
}
}
}
},
{
"name": "amlUpdateResource",
"type": "AzureMLUpdateResource",
"description": "Use AML Update Resource to update the predict web service",
"linkedServiceName": {
"type": "LinkedServiceReference",
"referenceName": "updatableScoringEndpoint2"
},
"typeProperties": {
"trainedModelName": "ADFV2Sample Model [trained model]",
"trainedModelLinkedServiceName": {
"type": "LinkedServiceReference",
"referenceName": "StorageLinkedService"
},
"trainedModelFilePath": "azuremltesting/output/newModelForArm.ilearner"
},
"dependsOn": [
{
"activity": "amlbeGetilearner",
"dependencyConditions": [ "Succeeded" ]
}
]
}
]
}
}
Related content
See the following articles that explain how to transform data in other ways: