Monitor Azure Managed Redis (preview) data using diagnostic settings
Diagnostic settings in Azure are used to collect resource logs. An Azure resource emits resource logs and provides rich, frequent data about the operation of that resource. These logs are captured per request and are also referred to as "data plane logs". See diagnostic settings in Azure Monitor for a recommended overview of the functionality in Azure. The content of these logs varies by resource type. In Azure Managed Redis (preview), two options are available to log:
- Cache Metrics (that is "AllMetrics") used to log metrics from Azure Monitor
- Connection Logs logs connections to the cache for security and diagnostic purposes.
Cache Metrics
Azure Managed Redis (preview) emits many metrics such as Server Load and Connections per Second that are useful to log. Selecting the AllMetrics option allows these and other cache metrics to be logged. You can configure how long the metrics are retained. See here for an example of exporting cache metrics to a storage account.
Connection Logs
Azure Managed Redis uses Azure diagnostic settings to log information on client connections to your cache. Logging and analyzing this diagnostic setting helps you understand who is connecting to your caches and the timestamp of those connections. The log data could be used to identify the scope of a security breach and for security auditing purposes.
Azure Managed Redis uses the audit connection events functionality built into the Redis Enterprise stack. Audit connection events allow every connection, disconnection, and authentication event to be logged, including failed authentication events.
Important
Logging in Azure Managed Redis is focused on each connection event. Logs only occur when the actual event occurred for the first time.
Prerequisites/Limitations of Connection Logging
- When you use OSS Cluster Policy, logs are emitted from each data node. When you use Enterprise Cluster Policy, only the node being used as a proxy emits logs. Both versions still cover all connections to the cache. This is just an architectural difference.
- Data loss (that is, missing a connection event) is rare, but possible. Data loss is typically caused by networking issues.
- Disconnection logs aren't yet fully stable and events may be missed.
- Because connection logs on Azure Managed Redis are event-based, be careful of your retention policies. For instance, if retention is set to 10 days, and a connection event occurred 15 days ago, that connection might still exist, but the log for that connection isn't retained.
- If using active geo-replication, logging must be configured for each cache instance in the geo-replication group individually.
- All diagnostic settings may take up to 90 minutes to start flowing to your selected destination.
- Enabling connection logs may cause a small performance degradation to the Redis instance.
Note
It is always possible to use the INFO or CLIENT LIST commands to check who is connected to a cache instance on-demand.
Important
When selecting logs, you can chose either the specific Category or Category groups, which are predefined groupings of logs across Azure services. When you use Category groups, you can no longer configure the retention settings. If you need to determine retention duration for your connection logs, select the item in the Categories section instead.
Log Destinations
You can turn on diagnostic settings for Azure Managed Redis instances and send resource logs to the following destinations:
- Log Analytics workspace - doesn't need to be in the same region as the resource being monitored.
- Storage account - must be in the same region as the cache. Premium storage accounts are not supported as a destination, however.
- Event hub - diagnostic settings can't access event hub resources when virtual networks are enabled. Enable the Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall? setting in event hubs to grant access to your event hub resources. The event hub must be in the same region as the cache.
- Partner Solution - a list of potential partner logging solutions can be found here
For more information on diagnostic requirements, see diagnostic settings.
You're charged normal data rates for storage account and event hub usage when you send diagnostic logs to either destination. You're billed under Azure Monitor not Azure Managed Redis. When sending logs to Log Analytics, you're only charged for Log Analytics data ingestion.
For more pricing information, Azure Monitor pricing.
Enable connection logging using the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to your Azure Managed Redis account. Open the Diagnostic Settings - Auditing pane under the Monitoring section on the left. Then, select Add diagnostic setting.
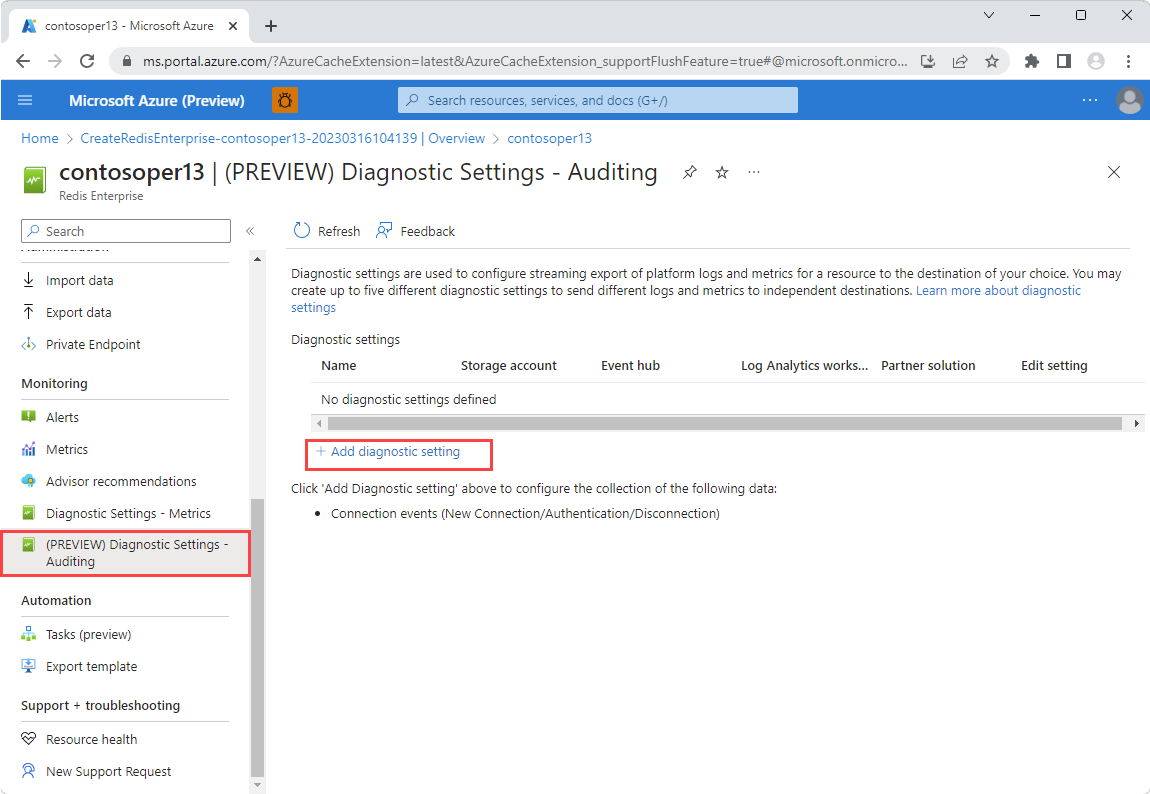
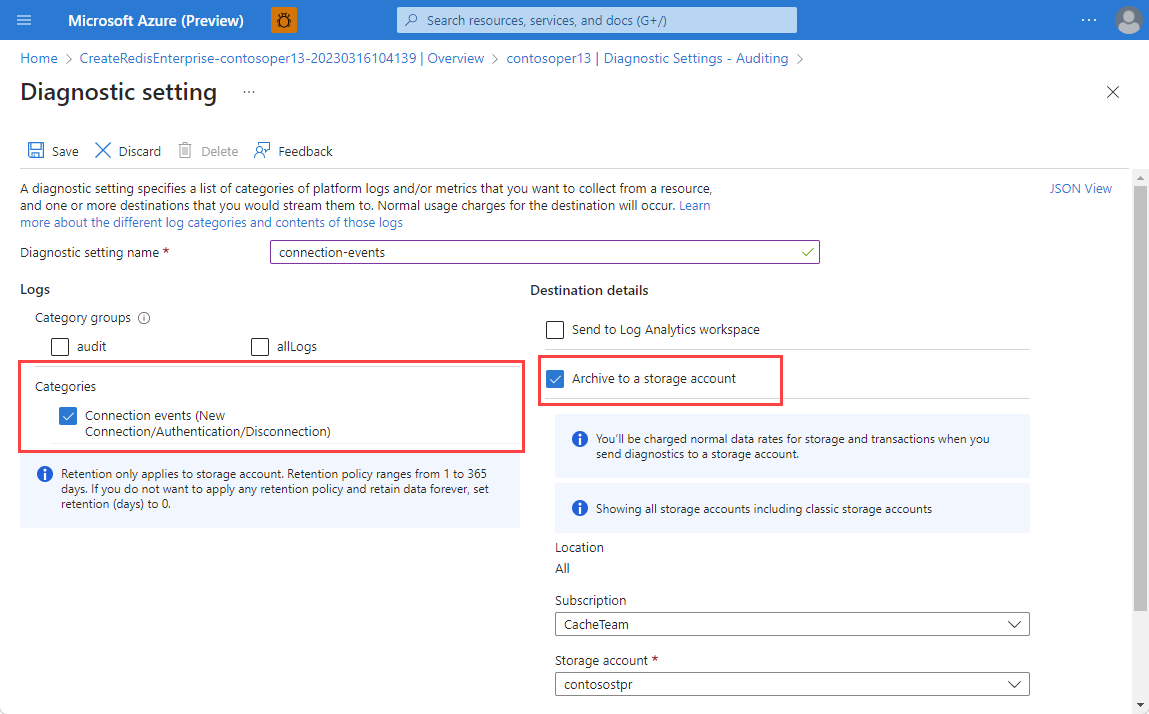
In the Diagnostic Setting - Auditing pane, select Connection events from Categories.
For more detail on the data logged, see below Contents of the Connection Logs.
Once you select Connection events, send your logs to your preferred destination. Select the information in the working pane.
Enable connection logging using the REST API
Use the Azure Monitor REST API for creating a diagnostic setting via the interactive console. For more information, see Create or update.
Request
PUT https://management.azure.com/{resourceUri}/providers/Microsoft.Insights/diagnosticSettings/{name}?api-version=2017-05-01-preview
Headers
| Parameters/Headers | Value/Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of your diagnostic setting. |
resourceUri |
subscriptions/{SUBSCRIPTION_ID}/resourceGroups/{RESOURCE_GROUP}/providers/Microsoft.Cache/RedisEnterprise/{CACHE_NAME}/databases/default |
api-version |
2017-05-01-preview |
Content-Type |
application/json |
Body
{
"properties": {
"storageAccountId": "/subscriptions/df602c9c-7aa0-407d-a6fb-eb20c8bd1192/resourceGroups/apptest/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/myteststorage",
"eventHubAuthorizationRuleID": "/subscriptions/1a66ce04-b633-4a0b-b2bc-a912ec8986a6/resourceGroups/montest/providers/microsoft.eventhub/namespaces/mynamespace/authorizationrules/myrule",
"eventHubName": "myeventhub",
"marketplacePartnerId": "/subscriptions/abcdeabc-1234-1234-ab12-123a1234567a/resourceGroups/test-rg/providers/Microsoft.Datadog/monitors/mydatadog",
"workspaceId": "/subscriptions/4b9e8510-67ab-4e9a-95a9-e2f1e570ea9c/resourceGroups/insights integration/providers/Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/myworkspace",
"logs": [
{
"category": "ConnectionEvents",
"enabled": true,
"retentionPolicy": {
"enabled": false,
"days": 0
}
}
]
}
}
Enable Connection Logging using Azure CLI
Use the az monitor diagnostic-settings create command to create a diagnostic setting with the Azure CLI. For more for information on command and parameter descriptions, see Create diagnostic settings to send platform logs and metrics to different destinations. This example shows how to use the Azure CLI to stream data to four different endpoints:
az monitor diagnostic-settings create
--resource /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.Cache/redisenterprise/{cacheName}/databases/default
--name {logName}
--logs '[{"category": "ConnectionEvents","enabled": true,"retentionPolicy": {"enabled": false,"days": 0}}]'
--event-hub {eventHubName}
--event-hub-rule /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/microsoft.eventhub/namespaces/{eventHubNamespace}/authorizationrule/{ruleName}
--storage-account /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storageAccountName}
--workspace /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/{logAnalyticsWorkspaceName}
--marketplace-partner-id/subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resourceGroups{resourceGroupname}/providers/Microsoft.Datadog/monitors/mydatadog
Contents of the Connection Logs
These fields and properties appear in the ConnectionEvents log category. In Azure Monitor, logs are collected in the REDConnectionEvents table under the resource provider name of MICROSOFT.CACHE.
| Azure Storage field or property | Azure Monitor Logs property | Description |
|---|---|---|
time |
TimeGenerated |
The timestamp (UTC) when event log was captured. |
location |
Location |
The location (region) the Azure Managed Redis instance was accessed in. |
category |
n/a | Available log categories: ConnectionEvents. |
resourceId |
_ResourceId |
The Azure Managed Redis resource for which logs are enabled. |
operationName |
OperationName |
The Redis operation associated with the log record. |
properties |
n/a | The contents of this field are described in the rows that follow. |
eventEpochTime |
EventEpochTime |
The UNIX timestamp (number of seconds since January 1, 1970) when the event happened in UTC. The timestamp can be converted to datetime format using function unixtime_seconds_todatetime in log analytics workspace. |
clientIP |
ClientIP |
The Redis client IP address. If using Azure storage, the IP address is IPv4 or private link IPv6 format based on cache type. If using Log Analytics, the result is always in IPv4, as a separate IPv6 field is provided. |
| n/a | PrivateLinkIPv6 |
The Redis client private link IPv6 address (only emitted if using both Private Link and log analytics). |
id |
ConnectionId |
Unique connection ID assigned by Redis. |
eventType |
EventType |
Type of connection event (new_conn, auth, or close_conn). |
eventStatus |
EventStatus |
Results of an authentication request as a status code (only applicable for authentication event). |
Note
If private link is used, only a IPv6 address will be logged (unless you are streaming the data to log analytics). You can convert the IPv6 address to the equivalent IPv4 address by looking at the last four bytes of data in the IPv6 address. For instance, in the private link IPv6 address "fd40:8913:31:6810:6c31:200:a01:104", the last four bytes in hexadecimal are "0a", "01", "01", and "04". (Note that leading zeros are omitted after each colon.) These correspond to "10", "1", "1", and "4" in decimal, giving us the IPv4 address "10.1.1.4".
Sample storage account log
If you send your logs to a storage account, a log for a connection event looks like this:
{
"time": "2023-01-24T10:00:02.3680050Z",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/4A1C78C6-5CB1-422C-A34E-0DF7FCB9BD0B/RESOURCEGROUPS/TEST/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.CACHE/REDISENTERPRISE/AUDITING-SHOEBOX/DATABASES/DEFAULT",
"category": "ConnectionEvents",
"location": "westus",
"operationName": "Microsoft.Cache/redisEnterprise/databases/ConnectionEvents/Read",
"properties": {
"eventEpochTime": 1674554402,
"id": 6185063009002,
"clientIP": "20.228.16.39",
"eventType": "new_conn"
}
}
And the log for an auth event looks like this:
{
"time": "2023-01-24T10:00:02.3680050Z",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/4A1C78C6-5CB1-422C-A34E-0DF7FCB9BD0B/RESOURCEGROUPS/TEST/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.CACHE/REDISENTERPRISE/AUDITING-SHOEBOX/DATABASES/DEFAULT",
"category": "ConnectionEvents",
"location": "westus",
"operationName": "Microsoft.Cache/redisEnterprise/databases/ConnectionEvents/Read",
"properties": {
"eventEpochTime": 1674554402,
"id": 6185063009002,
"clientIP": "20.228.16.39",
"eventType": "auth",
"eventStatus": 8
}
}
And the log for a disconnection event looks like this:
{
"time": "2023-01-24T10:00:03.3680050Z",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/4A1C78C6-5CB1-422C-A34E-0DF7FCB9BD0B/RESOURCEGROUPS/TEST/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.CACHE/REDISENTERPRISE/AUDITING-SHOEBOX/DATABASES/DEFAULT",
"category": "ConnectionEvents",
"location": "westus",
"operationName": "Microsoft.Cache/redisEnterprise/databases/ConnectionEvents/Read",
"properties": {
"eventEpochTime": 1674554402,
"id": 6185063009002,
"clientIP": "20.228.16.39",
"eventType": "close_conn"
}
}
Next steps
For detailed information about how to create a diagnostic setting by using the Azure portal, CLI, or PowerShell, see create diagnostic setting to collect platform logs and metrics in Azure article.