Custom locations
As an extension of the Azure location construct, a custom location provides a reference as a deployment target that administrators can set up when creating an Azure resource. The custom location feature abstracts the backend infrastructure details from application developers, database admin users, or other users in the organization. These users can then reference the custom location without having to be aware of these details.
Custom locations can be used to enable Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters as target locations for deploying Azure services instances. Azure offerings that can be deployed on top of custom locations include databases, such as SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc and Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server.
On Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters, a custom location represents an abstraction of a namespace within the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster. Custom locations create the granular RoleBindings and ClusterRoleBindings necessary for other Azure services to access the cluster.
Custom location permissions
Since the custom location is an Azure Resource Manager resource that supports Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC), an administrator or operator can determine which users have access to create resource instances on:
- A namespace within a Kubernetes cluster to target deployment of SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc or Azure Arc-enabled PostgreSQL server.
- The compute, storage, networking, and other vCenter or Azure Local resources to deploy and manage VMs.
For example, a cluster operator could create a custom location Contoso-Michigan-Healthcare-App representing a namespace on a Kubernetes cluster in your organization's Michigan Data Center. The operator can assign Azure RBAC permissions to application developers on this custom location so that they can deploy healthcare-related web applications. The developers can then deploy these applications to Contoso-Michigan-Healthcare-App without having to know details of the namespace and Kubernetes cluster.
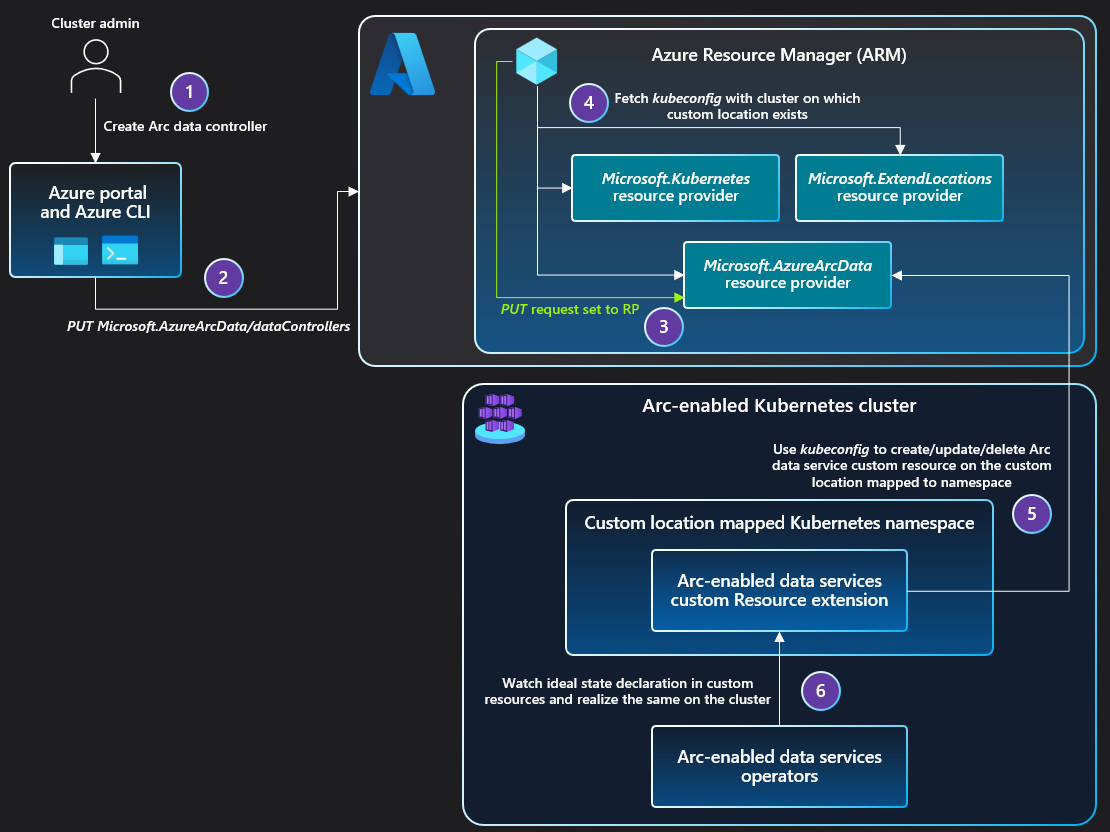
Architecture for Arc-enabled Kubernetes
When an administrator enables the custom locations feature on a cluster, a ClusterRoleBinding is created, authorizing the Microsoft Entra application used by the Custom Locations Resource Provider (RP). Once authorized, the Custom Locations RP can create ClusterRoleBindings or RoleBindings needed by other Azure RPs to create custom resources on this cluster. The cluster extensions installed on the cluster determine the list of RPs to authorize.
When the user creates a data service instance on the cluster:
- The PUT request is sent to Azure Resource Manager.
- The PUT request is forwarded to the Azure Arc-enabled Data Services RP.
- The RP fetches the
kubeconfigfile associated with the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster, on which the custom location exists.- The custom location is referenced as
extendedLocationin the original PUT request.
- The custom location is referenced as
- The Azure Arc-enabled Data Services RP uses the
kubeconfigto communicate with the cluster to create a custom resource of the Azure Arc-enabled Data Services type on the namespace mapped to the custom location.- The Azure Arc-enabled Data Services operator was deployed via cluster extension creation before the custom location existed.
- The Azure Arc-enabled Data Services operator reads the new custom resource created on the cluster and creates the data controller, translating into realization of the desired state on the cluster.
The sequence of steps to create the SQL managed instance or PostgreSQL instance are identical to the sequence of steps described above.
Next steps
- Use our quickstart to connect a Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc.
- Learn how to create a custom location on your Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.