What is Domain Name System (DNS)?
DNS is an industry-standard protocol providing computer name-to-IP address mapping and name resolution services to computers and users. DNS is the default name resolution service used in Windows networks. DNS is part of the TCP/IP protocol suite and all TCP/IP network connections are by default configured with the IP address of at least one DNS server in order to perform name resolution on the network.
Using DNS in Windows and Windows Server
In Windows Server, DNS is a server role that you can install by using Server Manager or Windows PowerShell commands. If you are installing a new Active Directory forest and domain, DNS is automatically installed with Active Directory as the Global Catalogue server for the forest and domain.
Typically, Windows Server DNS is deployed in support of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) uses DNS as its domain controller location mechanism. When any of the principal Active Directory operations is performed, such as authentication, updating, or searching, computers use DNS to locate Active Directory domain controllers. In addition, domain controllers use DNS to locate each other.
Windows Server DNS is also commonly deployed without Active Directory as a standard DNS solution. Using Windows Server DNS to host an organization's public lookup zones is one example of this usage.
The DNS Client service is included in all client and server versions of the Windows operating system, and is running by default upon operating system installation. When you configure a TCP/IP network connection with the IP address of a DNS server, the DNS Client queries the DNS server to discover domain controllers, and to resolve computer names to IP addresses. For example, when a network user with an Active Directory user account logs in to an Active Directory domain, the DNS Client service queries the DNS server to locate a domain controller for the Active Directory domain. When the DNS server responds to the query and provides the domain controller's IP address to the client, the client contacts the domain controller and the authentication process can begin.
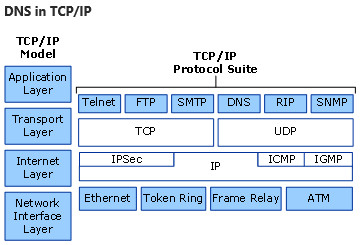
The Windows Server DNS Server and DNS Client services use the DNS protocol that is included in the TCP/IP protocol suite. DNS is part of the application layer of the TCP/IP reference model, as shown in the following illustration.
Get started
Get started with DNS in Windows Server using the Quickstart: Install and configure DNS Server on Windows Server.