Tables, matrices, and lists in Report Builder paginated reports
Applies to:
Microsoft Report Builder (SSRS)
Power BI Report Builder
Report Designer in SQL Server Data Tools
In Report Builder, tables, matrices, and lists are data regions that display paginated report data in cells that are organized into rows and columns. The cells typically contain text data such as text, dates, and numbers. But they can also contain gauges, charts, or report items such as images. Tables, matrices, and lists are frequently referred to as tablix data regions.
The table, matrix, and list templates are built on the tablix data region, which is a flexible grid that can display data in cells. In the table and matrix templates, cells are organized into rows and columns. Templates are variations of the underlying generic tablix data region. So you can display data in a combination of template formats and change the table, matrix, or list to include the features of another data region as you develop your report. For example, if you add a table and find it doesn't serve your needs, you can add column groups to make the table a matrix.
The table and matrix data regions can display complex data relationships by including nested tables, matrices, lists, charts, and gauges. Tables and matrices have a tabular layout, and their data comes from a single dataset, built on a single data source. The key difference between tables and matrices is that tables can include only row groups, but matrices have row groups and column groups.
Lists are different. They support a free layout that can include multiple peer tables or matrices, where each uses data from a different dataset. Lists can also be used for forms, such as invoices.
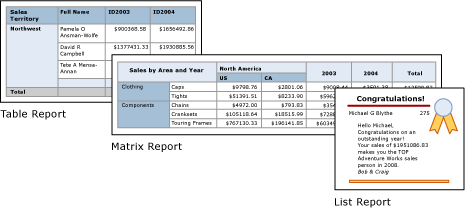
The following images show simple reports with a table, matrix, or list:
To get started with tables, matrices, and lists, see these tutorials:
- Tutorial: Create a basic table report (Report Builder)
- Tutorial: Create a matrix report (Report Builder)
- Tutorial: Create a free form report (Report Builder)
Note
You can publish tables, matrices, and lists separately from a report as report parts. For more information, see Report Parts (Report Builder and SSRS). However, report parts are deprecated for all releases of SQL Server Reporting Services after SQL Server Reporting Services 2019, and they're discontinued starting in SQL Server Reporting Services 2022 and Power BI Report Server.
Use a table
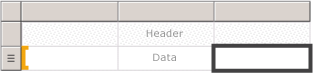
Use a table to display detail data, organize the data in row groups, or do both. The Table template contains three columns with a table header row and a details row for data. The following figure shows the initial Table template, selected on the design surface:
You can group data by a single field, by multiple fields, or by writing your own expression. You can create nested groups or independent, adjacent groups and display aggregated values for grouped data, or add totals to groups. For example, if your table has a row group called Category, you can add a subtotal for each group and a grand total for the report. To improve the appearance of the table and highlight data you want to emphasize, you can merge cells and apply formatting to data and table headings.
You can initially hide detail or grouped data and include drilldown toggles that let a user choose how much data to show.
For more information, see Tables in paginated reports (Report Builder).
Use a matrix
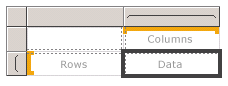
Use a matrix to display aggregated data summaries, grouped in rows and columns, similar to a PivotTable or crosstab. The number of unique values for each row and column group determines the number of rows and columns. The following figure shows the initial matrix template, selected on the design surface:
You can group data by multiple fields or expressions in row and column groups. At run time, when the report data and data regions combine, a matrix grows horizontally and vertically on the page as you add columns for column groups and rows for row groups. The matrix cells display aggregate values that are scoped to the intersection of the row and column groups to which the cell belongs. For example, you might have a matrix that has a row group called Category and two column groups called Territory and Year that display the sum of sales. The report displays two cells with sums of sales for each value in the Category group. The cells at the two intersections each are scoped. One cell is "Category and Territory" and the other is "Category and Year." The matrix can include nested and adjacent groups. Nested groups have a parent-child relationship, and adjacent groups have a peer relationship. You can add subtotals for any level of nested row and column groups within the matrix.
To make the matrix data more readable and highlight the data you want to emphasize, you can merge cells or split them horizontally and vertically. You can apply formatting to data and group headings.
You can also include drilldown toggles that initially hide detail data. The user can then select the toggles to display more or less detail as needed.
For more information, see Create a matrix in a paginated report (Report Builder).
Use a list
Use a list to create a free-form layout. You aren't limited to a grid layout, so you can place fields freely inside the list. You can use a list to design a form for displaying many dataset fields or as a container to display multiple data regions side by side for grouped data. For example, you can define a group for a list. You can add a table, chart, and image. You can display values in table and graphic form for each group value, as you might for an employee or patient record.
For more information, see Create invoices and forms with lists in a paginated report (Report Builder).
Prepare data
A table, matrix, and list data regions display data from a dataset. You can prepare the data in the query that retrieves the data for the dataset or by setting properties in the table, matrix, or list.
The query languages such as Transact-SQL, that you use to retrieve the data for the report datasets can prepare the data by applying filters to include only a subset of the data. This action replaces null values or blanks with constants that make the report more readable, and it sorts and groups data.
If you choose to prepare the data in the table, matrix, or list data region of a report, you set properties on the data region or cells within the data region. If you want to filter or sort the data, set the properties on the data region. For example, to sort the data you specify the columns to sort on and the sort direction. If you want to provide an alternative value for a field, you set the values of the cell text that displays the field. For example, to display blank when a field is empty or null, you use an expression to set the value.
For more information, see Prepare data for display in a tablix data region in a paginated report (Report Builder).
Build and configure a table, matrix, or list
When you add tables or matrices to your report, you can use the Table and Matrix Wizard. Or you can build them manually from the templates that Report Builder and Report Designer provide. Lists are built manually from the list template.
The wizard guides you through the steps to quickly build and configure a table or matrix. After you complete the wizard, or build your table yourself, you can further configure and refine them. The dialog boxes, available from the right-click menus on the data regions, make it easy to set the most commonly used properties:
- page breaks
- repeatability
- visibility of headers and footers
- display options
- filters
- sorting
The tablix data region provides a wealth of other properties, which you can set only in the Properties pane of Report Builder. For example, if you want to display a message when the dataset for a table, matrix, or list is empty, you specify the message text in the NoRowsMessage tablix property in the Properties pane.
Change between tablix templates
You aren't limited by your initial tablix template choice. As you add groups, totals, and labels, you might want to modify your tablix design. For example, you might start with a table and then delete the details row and add column groups. For more information, see Explore the flexibility of a tablix data region in a paginated report (Report Builder).
You can continue to develop a table, matrix, or list by adding any tablix feature. Tablix features include displaying detail data or aggregates for grouped data on rows and columns. You can create nested groups, independent adjacent groups, or recursive groups. You can filter and sort grouped data, and easily combine groups by including multiple group expressions in a group definition
You can add totals for a group or grand totals for the data region. You can hide rows or columns to simplify a report and enable the user to toggle the display of the hidden data, as in a drilldown report. For more information, see Control the tablix data region display on a paginated report page (Report Builder).
Work with tablix data regions
The following table provides articles with descriptions about working with the tablix data region:
| Article | Description |
|---|---|
| Tablix data region in a paginated report (Report Builder) | Explains key concepts related to the tablix data region: tablix, detail and grouped data, column and row groups, and static and dynamic rows and columns. |
| Add data to a tablix data region in a paginated report (Report Builder) | Provides information about adding detailed and grouped data, subtotals and totals, and labels to a tablix data region. |
| Control the tablix data region display on a paginated report page (Report Builder) | Describes properties for a tablix data region that you can modify to change the way it appears when you view it in a report. |
| Control row & column headings in a paginated report (Report Builder) | Describes how to control row and column headings when a table, matrix, or list data region span multiple pages horizontally or vertically. |
| Create recursive hierarchy groups in a paginated report (Report Builder) | Describes how to display recursive data where fields represent the relationship between parent and child in the dataset. |
| Groups in a Report Builder paginated report | Explains what groups are and when you use them and describes the groups available for the different tablix data regions. |