Connect to and manage MySQL in Microsoft Purview
This article outlines how to register MySQL, and how to authenticate and interact with MySQL in Microsoft Purview. For more information about Microsoft Purview, read the introductory article.
Supported capabilities
| Metadata Extraction | Full Scan | Incremental Scan | Scoped Scan | Classification | Labeling | Access Policy | Lineage | Data Sharing | Live view |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
The supported MySQL server versions are 5.7 to 8.x.
When scanning MySQL source, Microsoft Purview supports:
Extracting technical metadata including:
- Server
- Databases
- Tables including the columns
- Views including the columns
Fetching static lineage on assets relationships among tables and views.
When setting up scan, you can choose to scan an entire MySQL server, or scope the scan to a subset of databases matching the given name(s) or name pattern(s).
Known limitations
When object is deleted from the data source, currently the subsequent scan won't automatically remove the corresponding asset in Microsoft Purview.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- An active Microsoft Purview account.
- You need Data Source Administrator and Data Reader permissions to register a source and manage it in the Microsoft Purview governance portal. For more information about permissions, see Access control in Microsoft Purview.
Note
If your data store is not publicly accessible (if your data store limits access from on-premises network, private network or specific IPs, etc.), you will need to configure a self hosted integration runtime to connect to it.
- If your data source isn't publicly accessible, set up the latest self-hosted integration runtime.
- Choose the right integration runtime for your scenario:
- To use a self-hosted integration runtime:
- Follow the article to create and configure a self-hosted integration runtime.
- Ensure JDK 11 is installed on the machine where the self-hosted integration runtime is installed. Restart the machine after you newly install the JDK for it to take effect.
- Ensure that Visual C++ Redistributable (version Visual Studio 2012 Update 4 or newer) is installed on the machine where the self-hosted integration runtime is running. If you don't have this update installed, download it now.
- To use a kubernetes supported self-hosted integration runtime:
- To use a self-hosted integration runtime:
- Choose the right integration runtime for your scenario:
Required permissions for scan
The MySQL user must have the SELECT, SHOW VIEW and EXECUTE permissions for each target MySQL schema that contains metadata.
Register
This section describes how to register MySQL in Microsoft Purview using the Microsoft Purview governance portal.
Steps to register
To register a new MySQL source in Microsoft Purview Unified Catalog, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your Microsoft Purview account in the Microsoft Purview governance portal.
- Select Data Map on the left navigation.
- Select Register
- On Register sources, select MySQL. Select Continue.
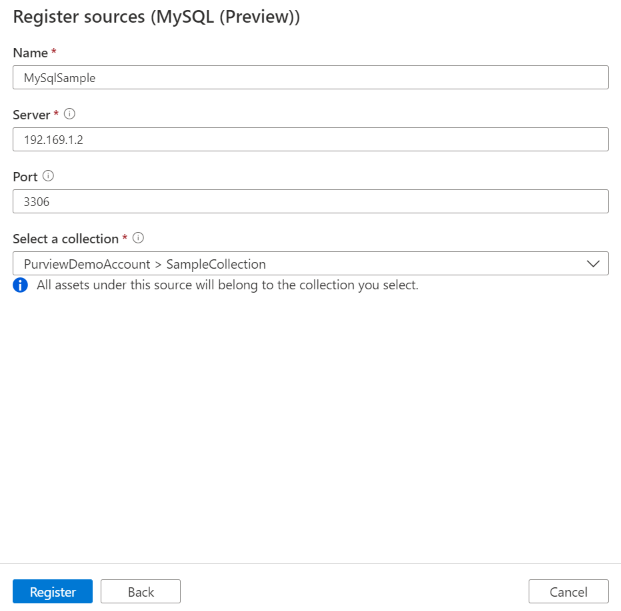
On the Register sources (MySQL) screen, follow these steps:
Enter a Name that the data source will be listed within the Catalog.
Enter the Server name to connect to a MySQL source. This can either be:
- A host name used to connect to the database server. For example:
MyDatabaseServer.com - An IP address. For example:
192.169.1.2
- A host name used to connect to the database server. For example:
Enter the Port used to connect to the database server (3306 by default for MySQL).
Select a collection from the list.
Finish to register the data source.
Scan
Follow the steps below to scan MySQL to automatically identify assets. For more information about scanning in general, see our introduction to scans and ingestion.
Authentication for a scan
The supported authentication type for a MySQL source is Basic authentication.
Create and run scan
To create and run a new scan, follow these steps:
If your server is publicly accessible, skip to step two. Otherwise, you'll need to make sure your self-hosted integration runtime is configured:
- In the Microsoft Purview governance portal, got to the Management Center, and select Integration runtimes.
- Make sure a self-hosted integration runtime is available. If one isn't set up, use the steps mentioned in prerequisites to set up a self-hosted integration runtime.
In the Microsoft Purview governance portal, navigate to Sources.
Select the registered MySQL source.
Select + New scan.
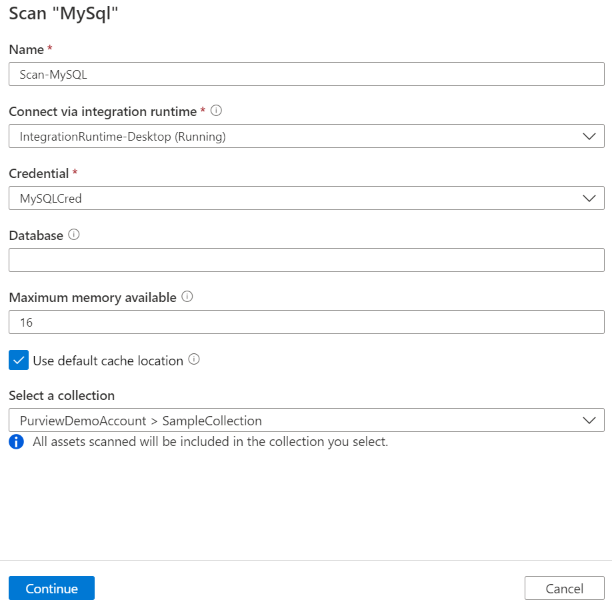
Provide the below details:
Name: The name of the scan
Connect via integration runtime: Select the Azure auto-resolved integration runtime if your server is publicly accessible, or your configured self-hosted integration runtime if it isn't publicly available.
Credential: Select the credential to connect to your data source. Make sure to:
- Select Basic Authentication while creating a credential.
- Provide the user name used to connect to the database server in the User name input field.
- Store the user password used to connect to the database server in the secret key.
Database: List subset of databases to import expressed as a semicolon separated list. For example,
database1;database2. All user databases are imported if the list is empty. All system databases (for example, SysAdmin) are ignored by default.Acceptable schema name patterns can be static names or contain wildcard %. For example:
A%;%B;%C%;D- Start with A or
- End with B or
- Contain C or
- Equal D
Usage of NOT and special characters aren't acceptable.
Maximum memory available (applicable when using self-hosted integration runtime): Maximum memory (in GB) available on customer's VM to be used by scanning processes. This is dependent on the size of MySQL source to be scanned.
Note
As a rule of thumb, please provide 1GB memory for every 1000 tables
Select Test connection to validate the settings (available when using Azure Integration Runtime).
Select Continue.
Choose your scan trigger. You can set up a schedule or ran the scan once.
Review your scan and select Save and Run.
View your scans and scan runs
To view existing scans:
- Go to the Microsoft Purview portal. On the left pane, select Data map.
- Select the data source. You can view a list of existing scans on that data source under Recent scans, or you can view all scans on the Scans tab.
- Select the scan that has results you want to view. The pane shows you all the previous scan runs, along with the status and metrics for each scan run.
- Select the run ID to check the scan run details.
Manage your scans
To edit, cancel, or delete a scan:
Go to the Microsoft Purview portal. On the left pane, select Data Map.
Select the data source. You can view a list of existing scans on that data source under Recent scans, or you can view all scans on the Scans tab.
Select the scan that you want to manage. You can then:
- Edit the scan by selecting Edit scan.
- Cancel an in-progress scan by selecting Cancel scan run.
- Delete your scan by selecting Delete scan.
Note
- Deleting your scan does not delete catalog assets created from previous scans.
Lineage
After scanning your MySQL source, you can browse Unified Catalog or search Unified Catalog to view the asset details.
Go to the asset -> lineage tab, you can see the asset relationship when applicable. Refer to the supported capabilities section on the supported MySQL lineage scenarios. For more information about lineage in general, see data lineage and lineage user guide.
Next steps
Now that you've registered your source, follow the below guides to learn more about Microsoft Purview and your data.