Stream data from Azure Storage Blob into Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 using Azure Stream Analytics
In this article, you learn how to use Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 as an output for an Azure Stream Analytics job. This article demonstrates a simple scenario that reads data from an Azure Storage blob (input) and writes the data to Data Lake Storage Gen1 (output).
Prerequisites
Before you begin this tutorial, you must have the following:
An Azure subscription. See Get Azure free trial.
Azure Storage account. You will use a blob container from this account to input data for a Stream Analytics job. For this tutorial, assume you have a storage account called storageforasa and a container within the account called storageforasacontainer. Once you have created the container, upload a sample data file to it.
A Data Lake Storage Gen1 account. Follow the instructions at Get started with Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 using the Azure portal. Let's assume you have a Data Lake Storage Gen1 account called myadlsg1.
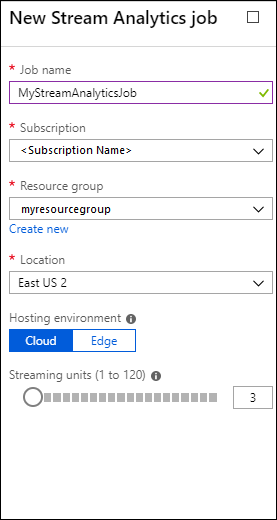
Create a Stream Analytics Job
You start by creating a Stream Analytics job that includes an input source and an output destination. For this tutorial, the source is an Azure blob container and the destination is Data Lake Storage Gen1.
Sign on to the Azure portal.
From the left pane, click Stream Analytics jobs, and then click Add.
Note
Make sure you create job in the same region as the storage account or you will incur additional cost of moving data between regions.
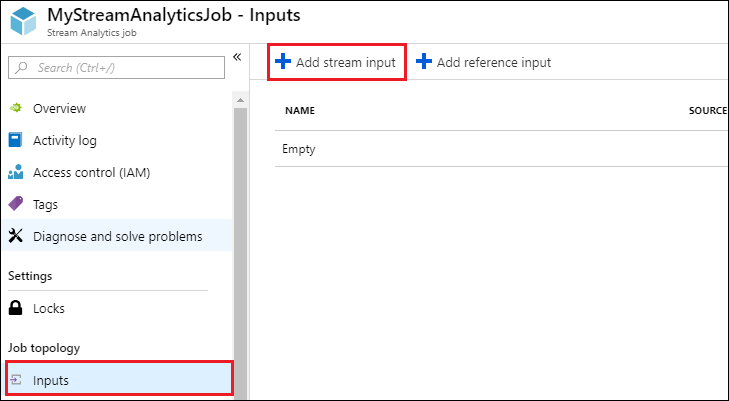
Create a Blob input for the job
Open the page for the Stream Analytics job, from the left pane click the Inputs tab, and then click Add.
On the New input blade, provide the following values.
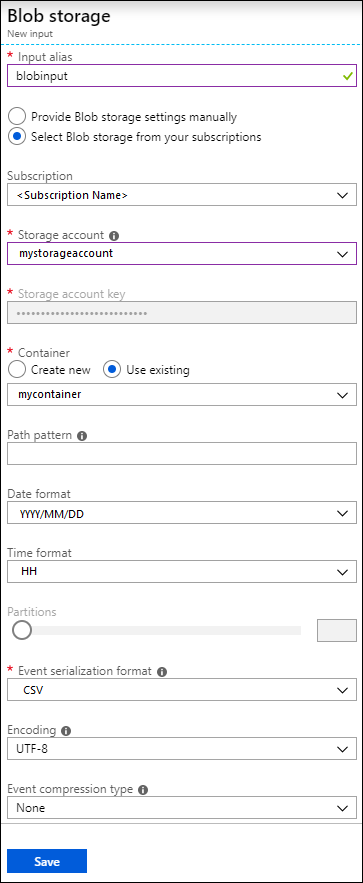
For Input alias, enter a unique name for the job input.
For Source type, select Data stream.
For Source, select Blob storage.
For Subscription, select Use blob storage from current subscription.
For Storage account, select the storage account that you created as part of the prerequisites.
For Container, select the container that you created in the selected storage account.
For Event serialization format, select CSV.
For Delimiter, select tab.
For Encoding, select UTF-8.
Click Create. The portal now adds the input and tests the connection to it.
Create a Data Lake Storage Gen1 output for the job
Open the page for the Stream Analytics job, click the Outputs tab, click Add, and select Data Lake Storage Gen1.
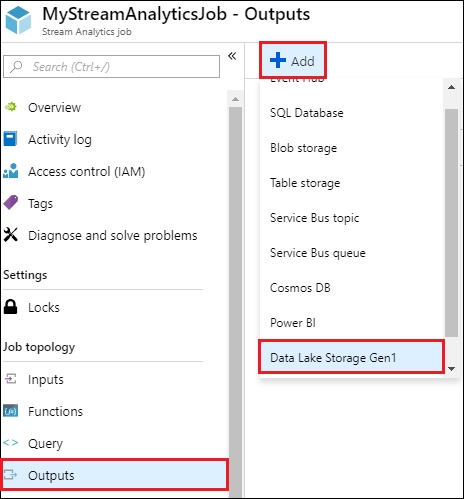
On the New output blade, provide the following values.
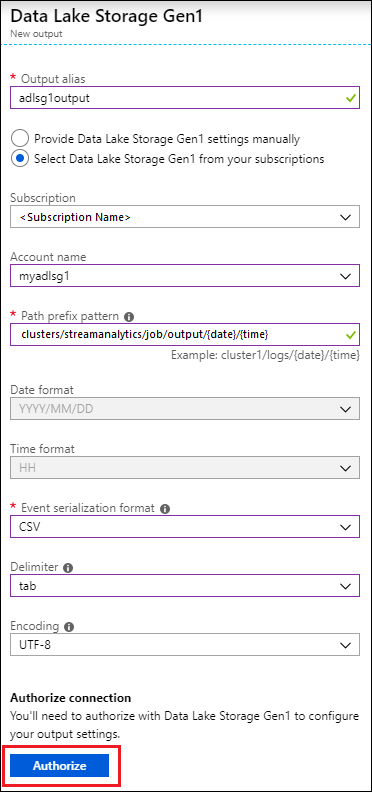
- For Output alias, enter a unique name for the job output. This is a friendly name used in queries to direct the query output to this Data Lake Storage Gen1 account.
- You will be prompted to authorize access to the Data Lake Storage Gen1 account. Click Authorize.
On the New output blade, continue to provide the following values.
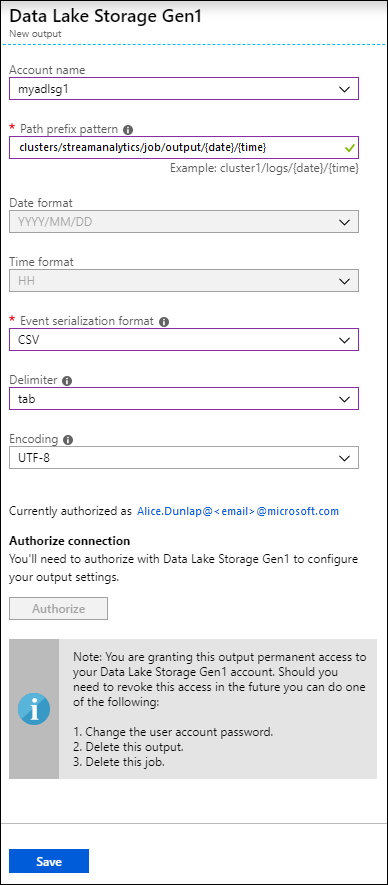
For Account name, select the Data Lake Storage Gen1 account you already created where you want the job output to be sent to.
For Path prefix pattern, enter a file path used to write your files within the specified Data Lake Storage Gen1 account.
For Date format, if you used a date token in the prefix path, you can select the date format in which your files are organized.
For Time format, if you used a time token in the prefix path, specify the time format in which your files are organized.
For Event serialization format, select CSV.
For Delimiter, select tab.
For Encoding, select UTF-8.
Click Create. The portal now adds the output and tests the connection to it.
Run the Stream Analytics job
To run a Stream Analytics job, you must run a query from the Query tab. For this tutorial, you can run the sample query by replacing the placeholders with the job input and output aliases, as shown in the screen capture below.
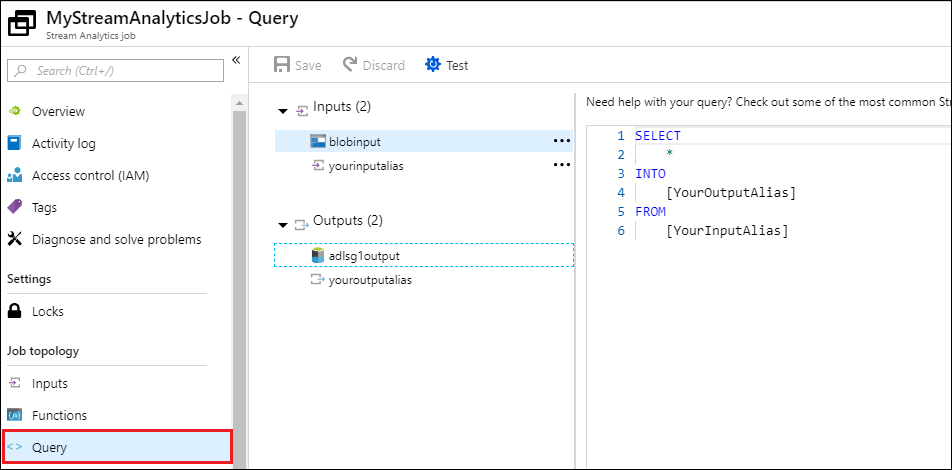
Click Save from the top of the screen, and then from the Overview tab, click Start. From the dialog box, select Custom Time, and then set the current date and time.
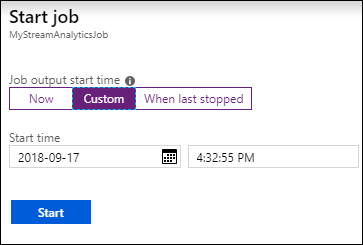
Click Start to start the job. It can take up to a couple minutes to start the job.
To trigger the job to pick the data from the blob, copy a sample data file to the blob container. You can get a sample data file from the Azure Data Lake Git Repository. For this tutorial, let's copy the file vehicle1_09142014.csv. You can use various clients, such as Azure Storage Explorer, to upload data to a blob container.
From the Overview tab, under Monitoring, see how the data was processed.
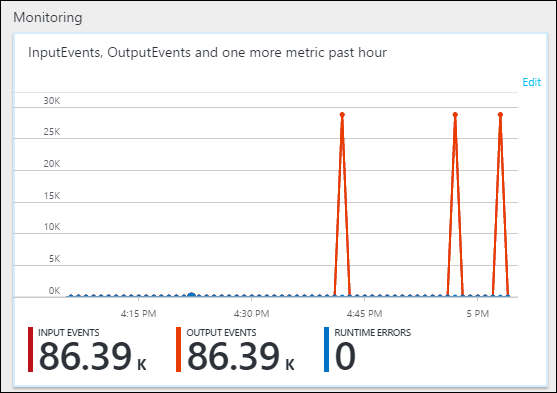
Finally, you can verify that the job output data is available in the Data Lake Storage Gen1 account.
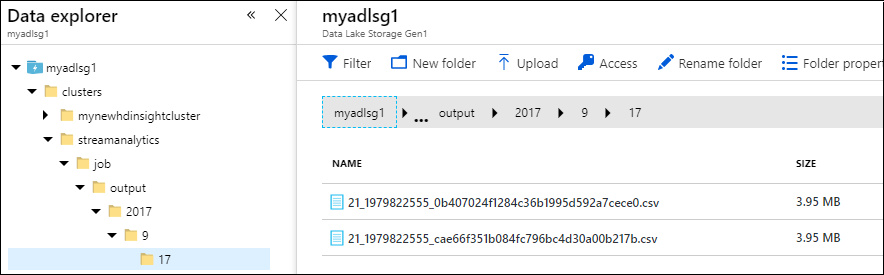
In the Data Explorer pane, notice that the output is written to a folder path as specified in the Data Lake Storage Gen1 output settings (
streamanalytics/job/output/{date}/{time}).