Task sequence steps to manage BIOS to UEFI conversion
Windows includes many security features that require UEFI-enabled devices. You might have newer Windows devices that support UEFI, but are using legacy BIOS. Previously, converting a device to UEFI required you to go to each device, repartition the hard disk, and reconfigure the firmware.
With Configuration Manager you can automate the following actions:
- Prepare a hard drive for BIOS to UEFI conversion
- Convert from BIOS to UEFI as part of the in-place upgrade process
- Collect UEFI information as part of hardware inventory
Hardware inventory collects UEFI information
The hardware inventory class (SMS_Firmware) and property (UEFI) are available to help you determine whether a computer starts in UEFI mode. When a computer is started in UEFI mode, the UEFI property is set to TRUE. Hardware inventory enables this class by default. For more information about hardware inventory, see How to configure hardware inventory.
Create a custom task sequence to prepare the hard drive
You can customize an OS deployment task sequence with the TSUEFIDrive variable. The Restart Computer step prepares a FAT32 partition on the hard drive for transition to UEFI. The following procedure provides an example of how you can create task sequence steps to do this action.
Prepare the FAT32 partition for the conversion to UEFI
In an existing task sequence to install an OS, add a new group with steps to do the BIOS to UEFI conversion.
Create a new task sequence group after the steps to capture files and settings, and before the steps to install the OS. For example, create a group after the Capture Files and Settings group named BIOS-to-UEFI.
On the Options tab of the new group, add a new task sequence variable as a condition. Set _SMSTSBootUEFI not equal true. With this condition, the task sequence only runs these steps on BIOS devices.
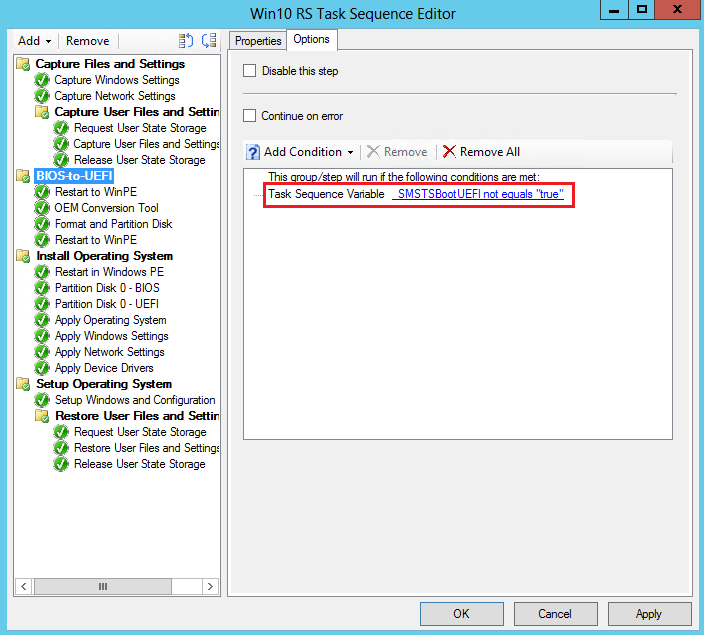
Under the new group, add the Restart Computer task sequence step. In Specify what to run after restart, select The boot image assigned to this task sequence is selected. This action restarts the computer in Windows PE.
On the Options tab, add a task sequence variable as a condition. Set _SMSTSInWinPE equals false. With this condition, the task sequence doesn't run this step if the computer is already in Windows PE.
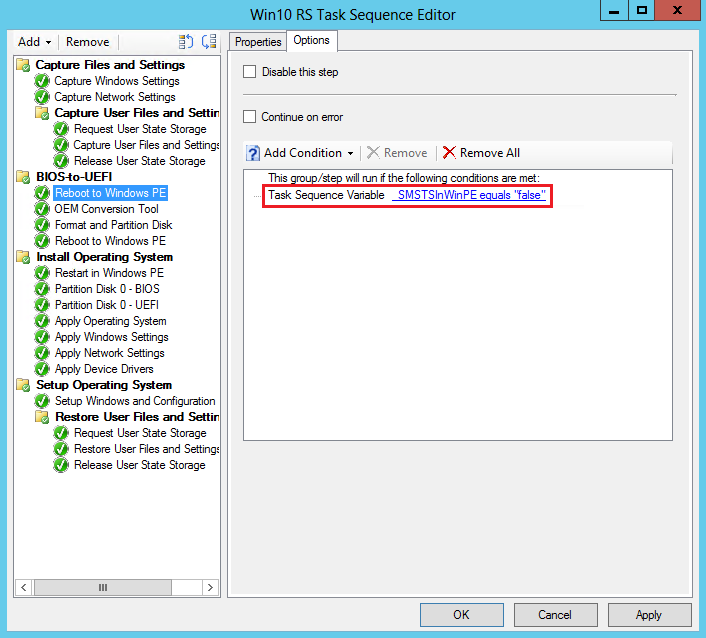
Add a step to start an OEM tool to convert the firmware from BIOS to UEFI. This step is typically Run Command Line, with the command to run the OEM tool.
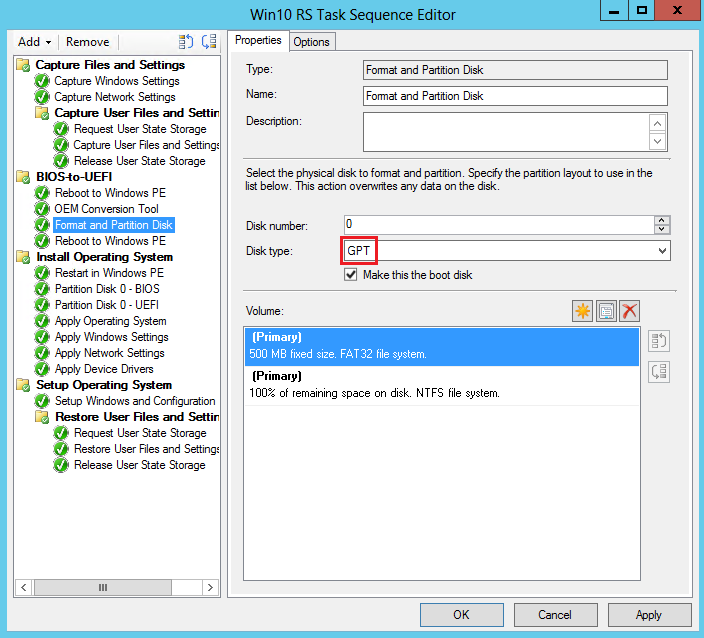
Add the Format and Partition Disk task sequence step. In this step, configure the following options:
Create the FAT32 partition to convert to UEFI before the OS is installed. For Disk type, choose GPT.
Go to the properties for the FAT32 partition. In the Variable field, enter
TSUEFIDrive. When the task sequence detects this variable, it prepares the partition for the UEFI transition before it restarts the computer.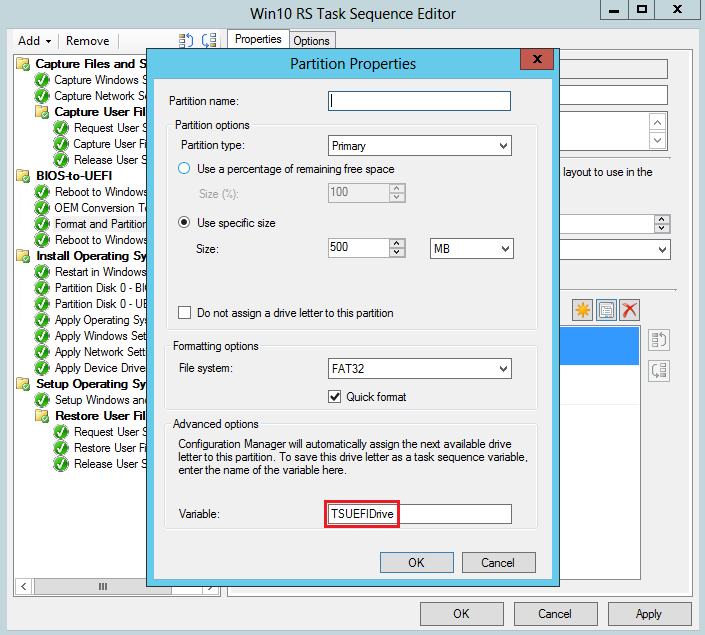
Create an NTFS partition that the task sequence uses to save its state and to store log files.
Add another Restart Computer task sequence step. In Specify what to run after restart, select The boot image assigned to this task sequence is selected to start the computer in Windows PE.
Tip
By default, the EFI partition size is 500 MB. In some environments, the boot image is too large to store on this partition. To work around this issue, increase the size of the EFI partition. For example, set it to 1 GB.
Convert from BIOS to UEFI during in-place upgrade
Windows includes a simple conversion tool, MBR2GPT. It automates the process to repartition the hard disk for UEFI-enabled hardware. You can integrate the conversion tool into the in-place upgrade process. Combine this tool with your upgrade task sequence and the OEM tool that converts the firmware from BIOS to UEFI.
Requirements
- A supported version of Windows 10 or later
- Computers that support UEFI
- OEM tool that converts the computer's firmware from BIOS to UEFI
Process to convert from BIOS to UEFI during an in-place upgrade task sequence
Edit the task sequence. In the Post-Processing group, make the following changes:
- Add the Run Command Line step. Specify the command line for the MBR2GPT tool. When run in the full OS, configure it to covert the disk from MBR to GPT without modifying or deleting data. In Command line, enter the following command:
MBR2GPT.exe /convert /disk:0 /AllowFullOS
Tip
You can also choose to run the MBR2GPT.EXE tool when in Windows PE instead of in the full OS. Add a step to restart the computer to Windows PE before the step to run the MBR2GPT.EXE tool. Then remove the
/AllowFullOSoption from the command line.For more information about the tool and available options, see MBR2GPT.EXE.
Add a step to run the OEM tool that converts the firmware from BIOS to UEFI. This step is typically Run Command Line, with a command line to run the OEM tool.
Add the Restart Computer step, and select The currently installed default operating system.
- Add the Run Command Line step. Specify the command line for the MBR2GPT tool. When run in the full OS, configure it to covert the disk from MBR to GPT without modifying or deleting data. In Command line, enter the following command:
Deploy the task sequence.