Partitioning Data (Visual Basic)
Partitioning in LINQ refers to the operation of dividing an input sequence into two sections, without rearranging the elements, and then returning one of the sections.
The following illustration shows the results of three different partitioning operations on a sequence of characters. The first operation returns the first three elements in the sequence. The second operation skips the first three elements and returns the remaining elements. The third operation skips the first two elements in the sequence and returns the next three elements.
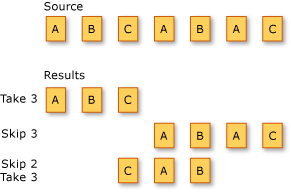
The standard query operator methods that partition sequences are listed in the following section.
Operators
| Operator Name | Description | Visual Basic Query Expression Syntax | More Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skip | Skips elements up to a specified position in a sequence. | Skip |
Enumerable.Skip Queryable.Skip |
| SkipWhile | Skips elements based on a predicate function until an element does not satisfy the condition. | Skip While |
Enumerable.SkipWhile Queryable.SkipWhile |
| Take | Takes elements up to a specified position in a sequence. | Take |
Enumerable.Take Queryable.Take |
| TakeWhile | Takes elements based on a predicate function until an element does not satisfy the condition. | Take While |
Enumerable.TakeWhile Queryable.TakeWhile |
| Chunk | Splits the elements of a sequence into chunks of a specified maximum size. | Enumerable.Chunk Queryable.Chunk |
Query Expression Syntax Examples
Skip
The following code example uses the Skip clause in Visual Basic to skip over the first four strings in an array of strings before returning the remaining strings in the array.
Dim words = {"an", "apple", "a", "day", "keeps", "the", "doctor", "away"}
Dim query = From word In words
Skip 4
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each str As String In query
sb.AppendLine(str)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' keeps
' the
' doctor
' away
SkipWhile
The following code example uses the Skip While clause in Visual Basic to skip over the strings in an array while the first letter of the string is "a". The remaining strings in the array are returned.
Dim words = {"an", "apple", "a", "day", "keeps", "the", "doctor", "away"}
Dim query = From word In words
Skip While word.Substring(0, 1) = "a"
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each str As String In query
sb.AppendLine(str)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' day
' keeps
' the
' doctor
' away
Take
The following code example uses the Take clause in Visual Basic to return the first two strings in an array of strings.
Dim words = {"an", "apple", "a", "day", "keeps", "the", "doctor", "away"}
Dim query = From word In words
Take 2
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each str As String In query
sb.AppendLine(str)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' an
' apple
TakeWhile
The following code example uses the Take While clause in Visual Basic to return strings from an array while the length of the string is five or less.
Dim words = {"an", "apple", "a", "day", "keeps", "the", "doctor", "away"}
Dim query = From word In words
Take While word.Length < 6
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each str As String In query
sb.AppendLine(str)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' an
' apple
' a
' day
' keeps
' the
