Debug on the Android Emulator
The Android Emulator, installed as part of the .NET Multi-Platform App UI development workload, can be run in various configurations to simulate different Android devices. Each one of these configurations is created as a virtual device. In this article, you'll learn how to launch the emulator from Visual Studio and run your app in a virtual device. For more information about how to create and configure a virtual device, see Managing virtual devices with the Android Device Manager.
Launching the Emulator
Near the top of Visual Studio, there's the Solution Configurations drop-down menu that can be used to select Debug or Release mode. Choosing Debug causes the debugger to attach to the application process running inside the emulator after the app starts. Choosing Release mode disables the debugger. When in release mode, you'll need to rely on app logging for debugging.
After you've chosen a virtual device from the Debug Target device drop-down menu, select either Debug or Release mode, then select the Play button to run the application:

After the emulator starts, Visual Studio deploys the app to the virtual device. An example screenshot of the Android Emulator is displayed below. In this example, the emulator is running the .NET MAUI template app.

When you're finished debugging and running your app, you can leave the emulator running. The first time a .NET MAUI app is run in the emulator, the .NET MAUI shared runtime for the targeted API level is installed, followed by the app. The runtime installation may take a few moments to install. If you leave the emulator running, later debugging sessions start faster as the runtime is already present on the device. If the device is restarted, the runtime will be redeployed to the device.
Fast boot
The Android Emulator includes a feature named Fast Boot which is enabled by default. This feature is configured by each device's emulator settings. With this feature enabled, a snapshot of the virtual device is saved when the emulator is closed. The snapshot is quickly restored the next time the device is started.
The first time a virtual device is started, a cold boot of the virtual device takes place without a speed improvement because a snapshot hasn't yet been created:
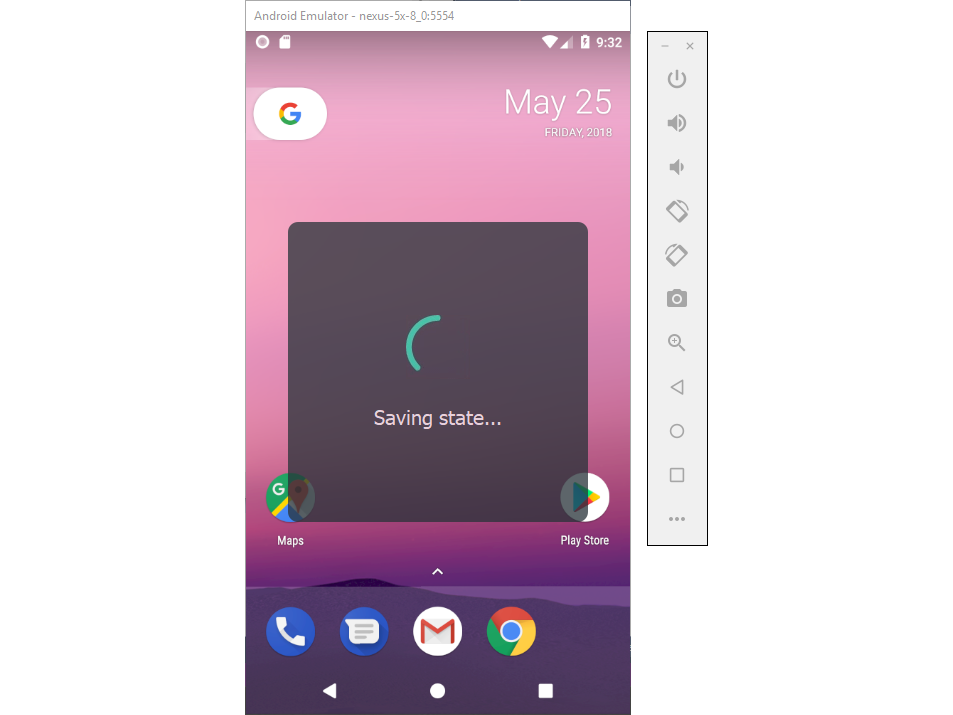
When you exit out of the emulator, Fast Boot saves the state of the emulator in a snapshot:
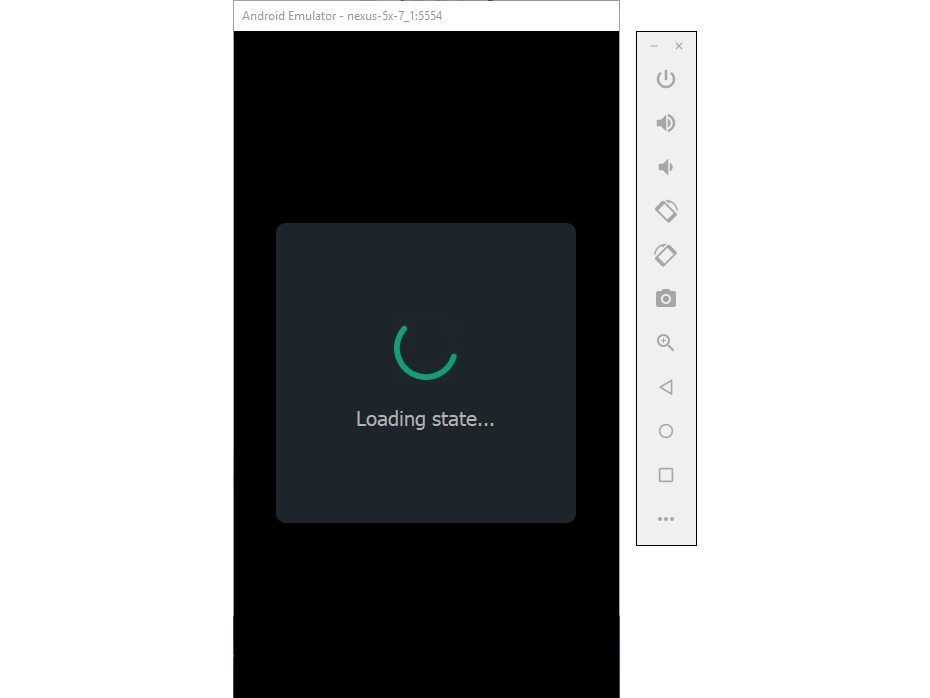
The next time the virtual device starts, it loads much faster because the emulator simply restores the state at which you closed the emulator.
Troubleshooting
For tips and workarounds for common emulator problems, see Android Emulator Troubleshooting.
For more information about using the Android Emulator, see the following Android Developer articles:
