Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on Linux with Saltstack
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Server
- Microsoft Defender for Servers
Want to experience Defender for Endpoint? Sign up for a free trial.
This article describes how to deploy Defender for Endpoint on Linux using Saltstack. A successful deployment requires the completion of all of the steps in this article.
Important
This article contains information about third-party tools. This is provided to help complete integration scenarios, however, Microsoft does not provide troubleshooting support for third-party tools.
Contact the third-party vendor for support.
Prerequisites and system requirements
Before you get started, see the main Defender for Endpoint on Linux page for a description of prerequisites and system requirements for the current software version.
In addition, for Saltstack deployment, you need to be familiar with Saltstack administration, have Saltstack installed, configure the Master and Minions, and know how to apply states. Saltstack has many ways to complete the same task. These instructions assume availability of supported Saltstack modules, such as apt and unarchive to help deploy the package. Your organization might use a different workflow. For more information, see Saltstack documentation.
Here are a few important points:
- Saltstack is installed on at least one computer (Saltstack calls the computer as the master).
- The Saltstack master accepted the managed nodes (Saltstack calls the nodes as minions) connections.
- The Saltstack minions are able to resolve communication to the Saltstack master (by default the minions try to communicate with a machine named salt).
- Run the following ping test:
sudo salt '*' test.ping - The Saltstack master has a file server location where the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint files can be distributed from (by default Saltstack uses the
/srv/saltfolder as the default distribution point)
Download the onboarding package
Warning
Repackaging the Defender for Endpoint installation package is not a supported scenario. Doing so can negatively impact the integrity of the product and lead to adverse results, including but not limited to triggering tampering alerts and updates failing to apply.
In Microsoft Defender portal, go to Settings > Endpoints > Device management > Onboarding.
In the first drop-down menu, select Linux Server as the operating system. In the second drop-down menu, select Your preferred Linux configuration management tool as the deployment method.
Select Download onboarding package. Save the file as
WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingPackage.zip.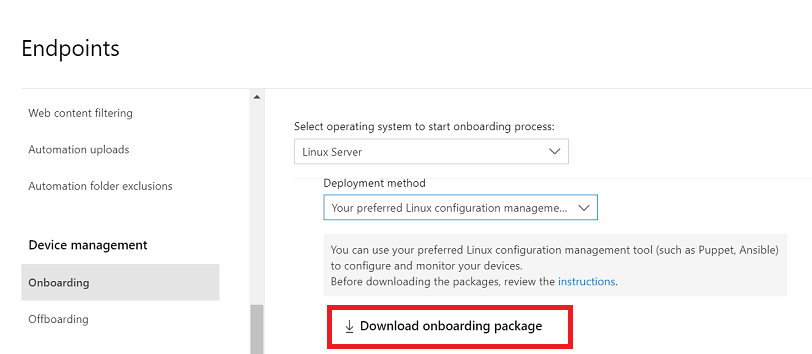
On the SaltStack Master, extract the contents of the archive to the SaltStack Server's folder (typically
/srv/salt):unzip WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingPackage.zip -d /srv/salt/mdeArchive: WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingPackage.zip inflating: /srv/salt/mde/mdatp_onboard.json
Create Saltstack state files
There are two ways you can create the Saltstack state files:
Use the installer Script (recommended): With this method, the script automates deployment by installing the agent, onboarding the device to the Microsoft Defender portal, and configuring the repositories to pick the correct agent compatible with your Linux distribution.
Manually configure the repositories: With this method, repositories must be configured manually along with selecting agent version compatible with your Linux distribution. This method gives you more granular control over the deployment process.
Create Saltstack state files using the installer script
Pull the installer bash script from Microsoft GitHub Repository, or use the following command to download it:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat/refs/heads/master/linux/installation/mde_installer.sh /srv/salt/mde/Create the state file
/srv/salt/install_mdatp.slswith the following content. The same can be downloaded from GitHub#Download the mde_installer.sh: https://github.com/microsoft/mdatp-xplat/blob/master/linux/installation/mde_installer.sh install_mdatp_package: cmd.run: - name: /srv/salt/mde/mde_installer.sh --install --onboard /srv/salt/mde/mdatp_onboard.json - shell: /bin/bash - unless: 'pgrep -f mde_installer.sh'
Note
The installer script also supports other parameters such as channel (insiders-fast, insiders-slow, prod (default)), real-time protection, version, etc. To select from the list of available options, check help through the following command:
./mde_installer.sh --help
Create Saltstack state files by manually configuring repositories
In this step, you create a SaltState state file in your configuration repository (typically /srv/salt) that applies the necessary states to deploy and onboard Defender for Endpoint. Then, you add the Defender for Endpoint repository and key: install_mdatp.sls.
Note
Defender for Endpoint on Linux can be deployed from one of the following channels:
- insiders-fast, denoted as
[channel] - insiders-slow, denoted as
[channel] - prod, denoted as
[channel]using the version name (see Linux Software Repository for Microsoft Products)
Each channel corresponds to a Linux software repository. The choice of the channel determines the type and frequency of updates that are offered to your device. Devices in insiders-fast are the first ones to receive updates and new features, followed later by insiders-slow, and lastly by prod.
In order to preview new features and provide early feedback, it's recommended that you configure some devices in your enterprise to use either insiders-fast or insiders-slow.
Warning
Switching the channel after the initial installation requires the product to be reinstalled. To switch the product channel: uninstall the existing package, reconfigure your device to use the new channel, and follow the steps in this document to install the package from the new location.
Note your distribution and version and identify the closest entry for it under
https://packages.microsoft.com/config/[distro]/.In the following commands, replace [distro] and [version] with your information.
Note
For Oracle Linux and Amazon Linux 2, replace [distro] with "rhel." For Amazon Linux 2, replace [version] with "7". For Oracle utilize, replace [version] with the version of Oracle Linux.
cat /srv/salt/install_mdatp.slsadd_ms_repo: pkgrepo.managed: - humanname: Microsoft Defender Repository {% if grains['os_family'] == 'Debian' %} - name: deb [arch=amd64,armhf,arm64] https://packages.microsoft.com/[distro]/[version]/[channel] [codename] main - dist: [codename] - file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft-[channel].list - key_url: https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc - refresh: true {% elif grains['os_family'] == 'RedHat' %} - name: packages-microsoft-[channel] - file: microsoft-[channel] - baseurl: https://packages.microsoft.com/[distro]/[version]/[channel]/ - gpgkey: https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc - gpgcheck: true {% endif %}Add the package installed state to
install_mdatp.slsafter theadd_ms_repostate as previously defined.install_mdatp_package: pkg.installed: - name: matp - required: add_ms_repoAdd the onboarding file deployment to
install_mdatp.slsafter theinstall_mdatp_packageas previously defined.copy_mde_onboarding_file: file.managed: - name: /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/mdatp_onboard.json - source: salt://mde/mdatp_onboard.json - required: install_mdatp_packageThe completed install state file should look similar to this output:
add_ms_repo: pkgrepo.managed: - humanname: Microsoft Defender Repository {% if grains['os_family'] == 'Debian' %} - name: deb [arch=amd64,armhf,arm64] https://packages.microsoft.com/[distro]/[version]/prod [codename] main - dist: [codename] - file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft-[channel].list - key_url: https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc - refresh: true {% elif grains['os_family'] == 'RedHat' %} - name: packages-microsoft-[channel] - file: microsoft-[channel] - baseurl: https://packages.microsoft.com/[distro]/[version]/[channel]/ - gpgkey: https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc - gpgcheck: true {% endif %} install_mdatp_package: pkg.installed: - name: mdatp - required: add_ms_repo copy_mde_onboarding_file: file.managed: - name: /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/mdatp_onboard.json - source: salt://mde/mdatp_onboard.json - required: install_mdatp_packageCreate a SaltState state file in your configuration repository (typically
/srv/salt) that applies the necessary states to offboard and remove Defender for Endpoint. Before using the offboarding state file, you need to download the offboarding package from the Microsoft Defender portal and extract it in the same way you did the onboarding package. The downloaded offboarding package is only valid for a limited period of time.Create an Uninstall state file
uninstall_mdapt.slsand add the state to remove themdatp_onboard.jsonfile.cat /srv/salt/uninstall_mdatp.slsremove_mde_onboarding_file: file.absent: - name: /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/mdatp_onboard.jsonAdd the offboarding file deployment to the
uninstall_mdatp.slsfile after theremove_mde_onboarding_filestate defined in the previous section.offboard_mde: file.managed: - name: /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/mdatp_offboard.json - source: salt://mde/mdatp_offboard.jsonAdd the removal of the MDATP package to the
uninstall_mdatp.slsfile after theoffboard_mdestate defined in the previous section.remove_mde_packages: pkg.removed: - name: mdatpThe complete uninstall state file should look similar to the following output:
remove_mde_onboarding_file: file.absent: - name: /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/mdatp_onboard.json offboard_mde: file.managed: - name: /etc/opt/microsoft/mdatp/mdatp_offboard.json - source: salt://mde/offboard/mdatp_offboard.json remove_mde_packages: pkg.removed: - name: mdatp
Deploy Defender on Endpoint using the state files created earlier
This step applies to both the installer script or manual configuration method. In this step, you apply the state to the minions. The following command applies the state to machines with the name that begins with mdetest.
Installation:
salt 'mdetest*' state.apply install_mdatpImportant
When the product starts for the first time, it downloads the latest antimalware definitions. Depending on your Internet connection, this can take up to a few minutes.
Validation/configuration:
salt 'mdetest*' cmd.run 'mdatp connectivity test'salt 'mdetest*' cmd.run 'mdatp health'Uninstallation:
salt 'mdetest*' state.apply uninstall_mdatp
Troubleshoot installation issues
To troubleshoot issues:
For information on how to find the log that's generated automatically when an installation error occurs, see Log installation issues.
For information about common installation issues, see Installation issues.
If the health of the device is
false, see Defender for Endpoint agent health issues.For product performance issues, see Troubleshoot performance issues.
For proxy and connectivity issues, see Troubleshoot cloud connectivity issues.
To get support from Microsoft, open a support ticket, and provide the log files created by using the client analyzer.
How to configure policies for Microsoft Defender on Linux
You can configure antivirus or EDR settings on your endpoints using any of the following methods:
- See Set preferences for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on Linux.
- See security settings management to configure settings in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Operating system upgrades
When upgrading your operating system to a new major version, you must first uninstall Defender for Endpoint on Linux, install the upgrade, and finally reconfigure Defender for Endpoint on your Linux device.
Reference
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.