Authenticate Azure Spring Apps with Azure Key Vault in GitHub Actions
Note
The Basic, Standard, and Enterprise plans will be deprecated starting from mid-March, 2025, with a 3 year retirement period. We recommend transitioning to Azure Container Apps. For more information, see the Azure Spring Apps retirement announcement.
The Standard consumption and dedicated plan will be deprecated starting September 30, 2024, with a complete shutdown after six months. We recommend transitioning to Azure Container Apps. For more information, see Migrate Azure Spring Apps Standard consumption and dedicated plan to Azure Container Apps.
This article applies to: ✅ Java ✅ C#
This article applies to: ✅ Basic/Standard ✅ Enterprise
This article shows you how to use Key Vault with a CI/CD workflow for Azure Spring Apps with GitHub Actions.
Key vault is a secure place to store keys. Enterprise users need to store credentials for CI/CD environments in scope that they control. The key to get credentials in the key vault should be limited to resource scope. It has access to only the key vault scope, not the entire Azure scope. It's like a key that can only open a strong box not a master key that can open all doors in a building. It's a way to get a key with another key, which is useful in a CICD workflow.
Generate Credential
To generate a key to access the key vault, execute command below on your local machine:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role contributor --scopes /subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE_GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/<KEY_VAULT> --json-auth
The scope specified by the --scopes parameter limits the key access to the resource. It can only access the strong box.
With results:
{
"clientId": "<GUID>",
"clientSecret": "<GUID>",
"subscriptionId": "<GUID>",
"tenantId": "<GUID>",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}
Then save the results to GitHub secrets as described in Set up your GitHub repository and authenticate with Azure.
Add Access Policies for the Credential
The credential you created above can get only general information about the Key Vault, not the contents it stores. To get secrets stored in the Key Vault, you need set access policies for the credential.
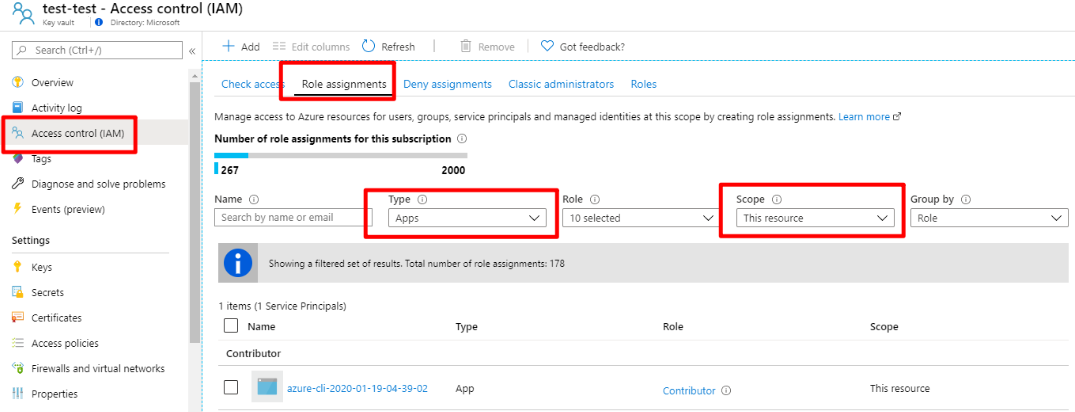
Go to the Key Vault dashboard in Azure portal, select the Access control menu, then open the Role assignments tab. Select Apps for Type and This resource for scope. You should see the credential you created in previous step:
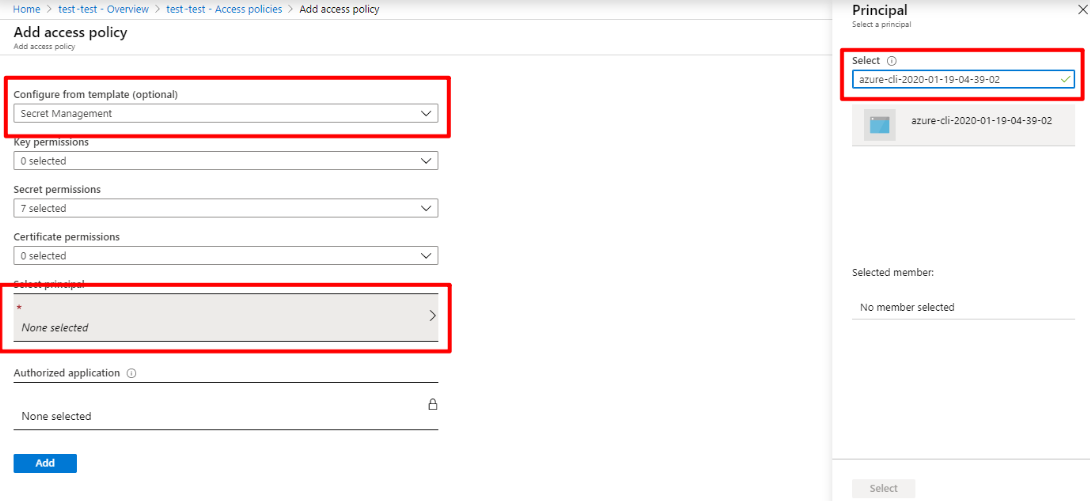
Copy the credential name, for example, azure-cli-2020-01-19-04-39-02. Open the Access policies menu, then select the Add Access Policy link. Select Secret Management for Template, then select Principal. Paste the credential name in Principal/Select input box:
Select the Add button in the Add access policy dialog, then select Save.
Generate full-scope Azure Credential
This is the master key to open all doors in the building. The procedure is similar to the previous step, but here we change the scope to generate the master key:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role contributor --scopes /subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION_ID> --json-auth
Again, results:
{
"clientId": "<GUID>",
"clientSecret": "<GUID>",
"subscriptionId": "<GUID>",
"tenantId": "<GUID>",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}
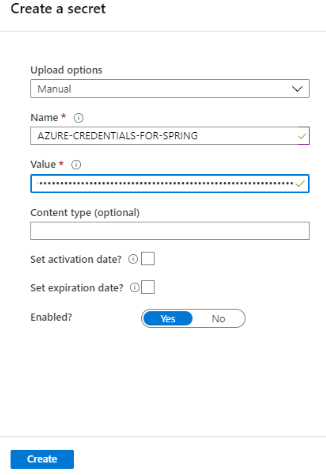
Copy the entire JSON string. Go back to Key Vault dashboard. Open the Secrets menu, then select the Generate/Import button. Input the secret name, such as AZURE-CREDENTIALS-FOR-SPRING. Paste the JSON credential string to the Value input box. You may notice the value input box is a one-line text field, rather than a multi-line text area. You can paste the complete JSON string there.
Combine credentials in GitHub Actions
Set the credentials used when the CICD pipeline executes:
on: [push]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: azure/login@v1
with:
creds: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CREDENTIALS }} # Strong box key you generated in the first step
- uses: Azure/get-keyvault-secrets@v1.0
with:
keyvault: "<Your Key Vault Name>"
secrets: "AZURE-CREDENTIALS-FOR-SPRING" # Master key to open all doors in the building
id: keyvaultaction
- uses: azure/login@v1
with:
creds: ${{ steps.keyvaultaction.outputs.AZURE-CREDENTIALS-FOR-SPRING }}
- name: Azure CLI script
uses: azure/CLI@v1
with:
azcliversion: 2.0.75
inlineScript: |
az extension add --name spring # Spring CLI commands from here
az spring list