Use Service Connector in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is one of the compute services supported by Service Connector. This article aims to help you understand:
- What operations are made on the cluster when creating a service connection.
- How to use the Kubernetes resources created by Service Connector.
- How to troubleshoot and view Service Connector logs in an AKS cluster.
Prerequisites
- This guide assumes that you already know the basic concepts of Service Connector.
Operations performed by Service Connector on the AKS cluster
Depending on the different target services and authentication types selected when creating a service connection, Service Connector makes different operations on the AKS cluster. The following lists the possible operations made by Service Connector.
Adding the Service Connector Kubernetes extension
A Kubernetes extension named sc-extension is added to the cluster the first time a service connection is created. Later on, the extension helps create Kubernetes resources in user's cluster, whenever a service connection request comes to Service Connector. You can find the extension in your AKS cluster in the Azure portal, in the Extensions + applications menu.
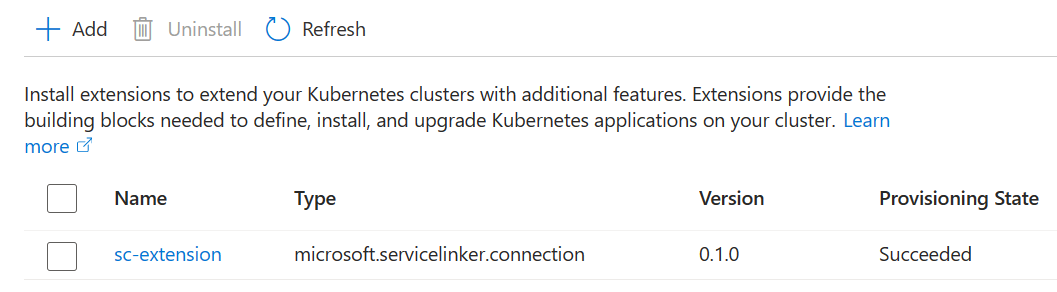
The extension is also where the cluster connections metadata are stored. Uninstalling the extension makes all the connections in the cluster unavailable. The extension operator is hosted in the cluster namespace sc-system.
Creating the Kubernetes resources
Service Connector creates some Kubernetes resources to the namespace the user specified when creating a service connection. The Kubernetes resources store the connection information, which is needed by the user's workload definitions or application code to talk to target services. Depending on different authentication types, different Kubernetes resources are created. For the Connection String and Service Principal auth types, a Kubernetes secret is created. For the Workload Identity auth type, a Kubernetes service account is also created in addition to a Kubernetes secret.
You can find the Kubernetes resources created by Service Connector for each service connection on the Azure portal in your Kubernetes resource, in the Service Connector menu.
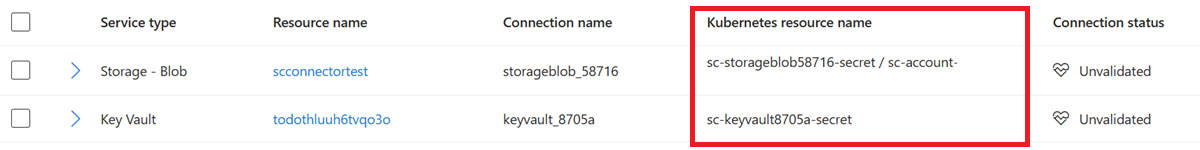
Deleting a service connection doesn't delete the associated Kubernetes resource. If necessary, remove your resource manually, using for example the kubectl delete command.
Enabling the azureKeyvaultSecretsProvider add-on
If target service is Azure Key Vault and the Secret Store CSI Driver is enabled when creating a service connection, Service Connector enables the azureKeyvaultSecretsProvider add-on for the cluster.
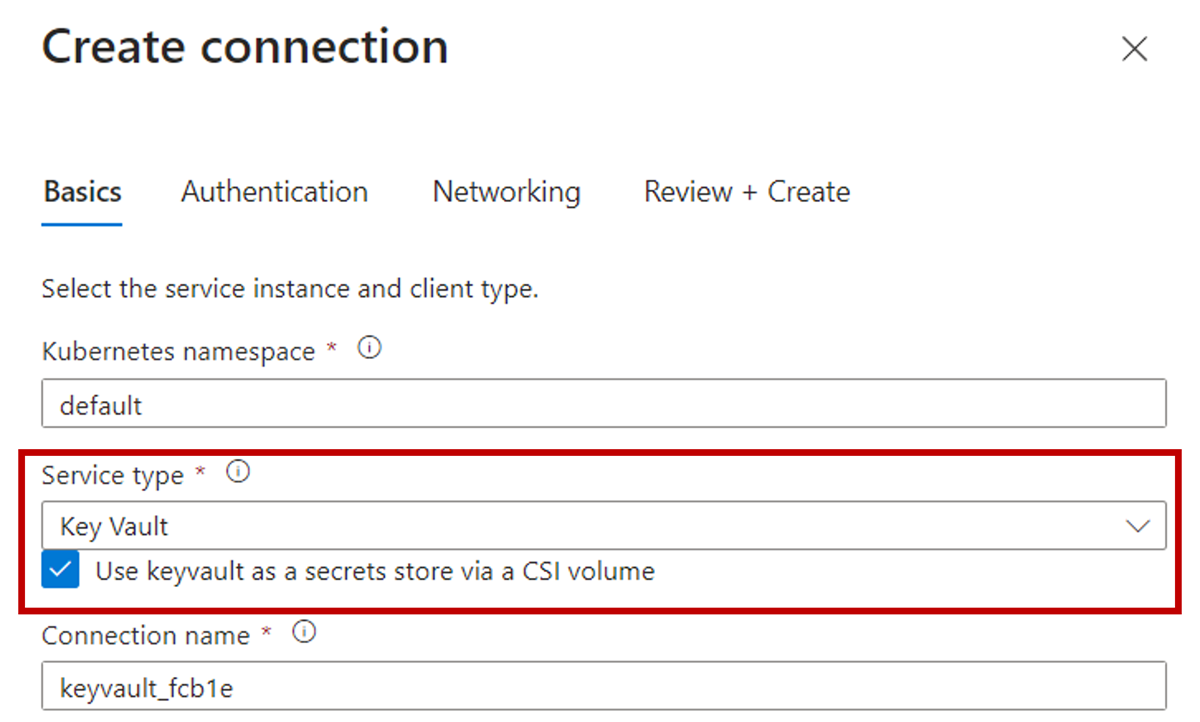
Follow the Connect to Azure Key Vault using CSI driver tutorialto set up a connection to Azure Key Vault using Secret Store CSI driver.
Enabling workload identity and OpenID Connect (OIDC) issuer
If the authentication type is Workload Identity when creating a service connection, Service Connector enables workload identity and OIDC issuer for the cluster.
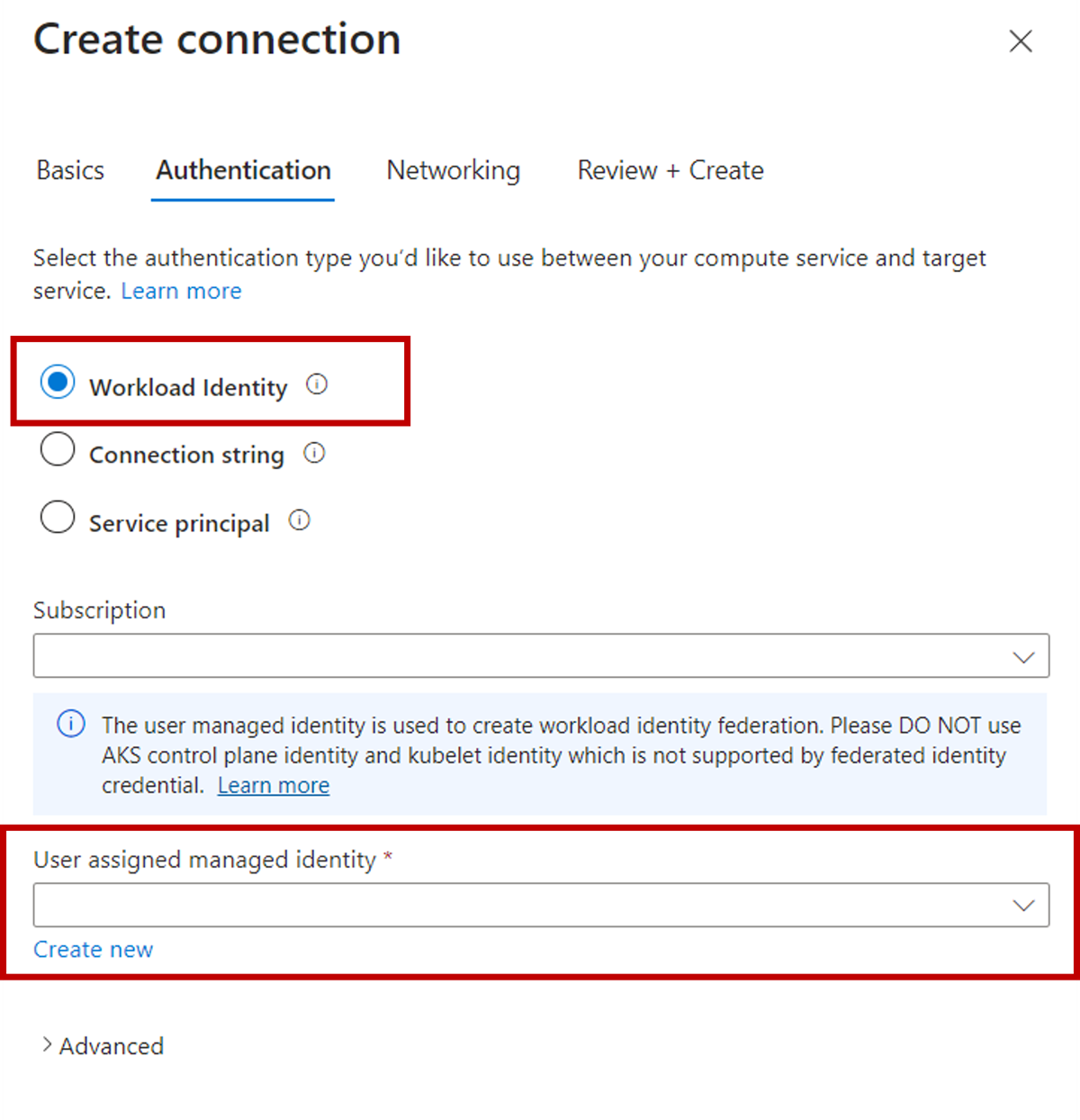
When the authentication type is Workload Identity, a user-assigned managed identity is needed to create the federated identity credential. Learn more from what are workload identities, or follow the tutorialto set up a connection to Azure Storage using workload identity.
Use the Kubernetes resources created by Service Connector
Various Kubernetes resources are created by Service Connector depending on the target service type and authentication type. The following sections show how to use the Kubernetes resources created by Service Connector in your cluster workloads definition and application code.
Kubernetes secret
A Kubernetes secret is created when the authentication type is set to either Connection String or Service Principal. Your cluster workload definition can reference the secret directly. The following snippet provides an example.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
namespace: default
name: sc-sample-job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: raw-linux
image: alpine
command: ['printenv']
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: <SecretCreatedByServiceConnector>
restartPolicy: OnFailure
Your application code can consume the connection string in the secret from an environment variable. Check the following sample code to learn more about the environment variable names and how to use them in your application code to authenticate to different target services.
Kubernetes service account
A Kubernetes service account and a secret are created when the authentication type is set to Workload Identity. Your cluster workload definition can reference the service account and secret to authenticate through workload identity. The following snippet provides an example.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
namespace: default
name: sc-sample-job
labels:
azure.workload.identity/use: "true"
spec:
template:
spec:
serviceAccountName: <ServiceAccountCreatedByServiceConnector>
containers:
- name: raw-linux
image: alpine
command: ['printenv']
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: <SecretCreatedByServiceConnector>
restartPolicy: OnFailure
Check the following tutorial to learn how to connect to Azure Storage using workload identity.
Troubleshoot and view logs
If an error occurs and can't be resolved by retrying when creating a service connection, the following methods help gather more information for troubleshooting.
Check Service Connector Kubernetes extension
The Service Connector Kubernetes extension is built on top of Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster extensions. Use the following commands to check for any errors that occurred during the extension installation or update process.
Install the
k8s-extensionAzure CLI extension.az extension add --name k8s-extensionRetrieve the status of the Service Connector extension. Check the
statusesproperty in the command output to identify any errors.az k8s-extension show \ --resource-group MyClusterResourceGroup \ --cluster-name MyCluster \ --cluster-type managedClusters \ --name sc-extension
Check Kubernetes cluster logs
If an error occurs during the extension installation and the error message in the statuses property doesn't provide sufficient information, you can further investigate by checking the Kubernetes logs with the followings steps.
Connect to your AKS cluster.
az aks get-credentials \ --resource-group MyClusterResourceGroup \ --name MyClusterThe Service Connector extension is installed in the
sc-systemnamespace using a Helm chart. Check the namespace and the Helm release using the following commands.Check the namespace exists.
kubectl get nsCheck the helm release status.
helm list -n sc-system
During the extension installation or update, a Kubernetes job called
sc-jobcreates the Kubernetes resources for the service connection. A job execution failure typically causes the extension to fail. Check the job status by running the following commands. Ifsc-jobdoesn't exist in thesc-systemnamespace, it should have been executed successfully. This job is designed to be automatically deleted after successful execution.Check the job exists.
kubectl get job -n sc-systemGet the job status.
kubectl describe job/sc-job -n sc-systemView the job logs.
kubectl logs job/sc-job -n sc-system
Common errors and mitigations
Extension creation error
Error message:
Unable to get a response from the agent in time.
Mitigation:
Refer to extension creation errors
Helm errors
Error messages:
Timed out waiting for resource readinessUnable to download the Helm chart from the repo URLHelm chart rendering failed with given valuesResource already exists in your clusterOperation is already in progress for Helm
Mitigation:
Refer to Helm errors
Conflict
Error message:
Operation returned an invalid status code: Conflict.
Reason:
This error typically occurs when attempting to create a service connection while the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster is in an updating state. The service connection update conflicts with the ongoing update. This error also occurs when your subscription is not registered with the Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration resource provider.
Mitigation:
Ensure your cluster is in a "Succeeded" state and retry the creation.
Run the following command to make sure your subscription is registered with the
Microsoft.KubernetesConfigurationresource provider.az provider register -n Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration
Unauthorized resource access
Error message:
You do not have permission to perform ... If access was recently granted, please refresh your credentials.
Reason:
Service Connector requires permissions to operate the Azure resources you want to connect to, in order to perform connection operations on your behalf. This error indicates a lack of necessary permissions on some Azure resources.
Mitigation:
Check the permissions on the Azure resources specified in the error message. Obtain the required permissions and retry the creation.
Missing subscription registration
Error message:
The subscription is not registered to use namespace 'Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration'
Reason:
Service Connector requires the subscription to be registered with Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration, which is the resource provider for Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster extensions.
Mitigation:
Register the Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration resource provider by running the following command. For more information on resource provider registration errors, please refer to Resolve errors for resource provider registration.
az provider register -n Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration
Next step
Learn how to integrate different target services and read about their configuration settings and authentication methods.