Quickstart: Use .NET (C#) to connect and query data in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
This quickstart demonstrates how to connect to an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance using a C# application. It shows how to use SQL statements to query, insert, update, and delete data in the database. The steps in this article assume that you are familiar with developing using C#, and that you are new to working with Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Prerequisites
For this quickstart you need:
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- Create an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server, if you do not have one.
- Use the empty postgres database available on the server or create a new database.
- Install the .NET SDK for your platform (Windows, Ubuntu Linux, or macOS) for your platform.
- Install Visual Studio to build your project.
- Install Npgsql NuGet package in Visual Studio.
Get connection information
Get the connection information needed to connect to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. You need the fully qualified server name and login credentials.
Using the Azure portal:
From the left-hand menu in Azure portal, click All resources, and then search for the server you have created.
Click the server name.
In the resource menu, select Overview.
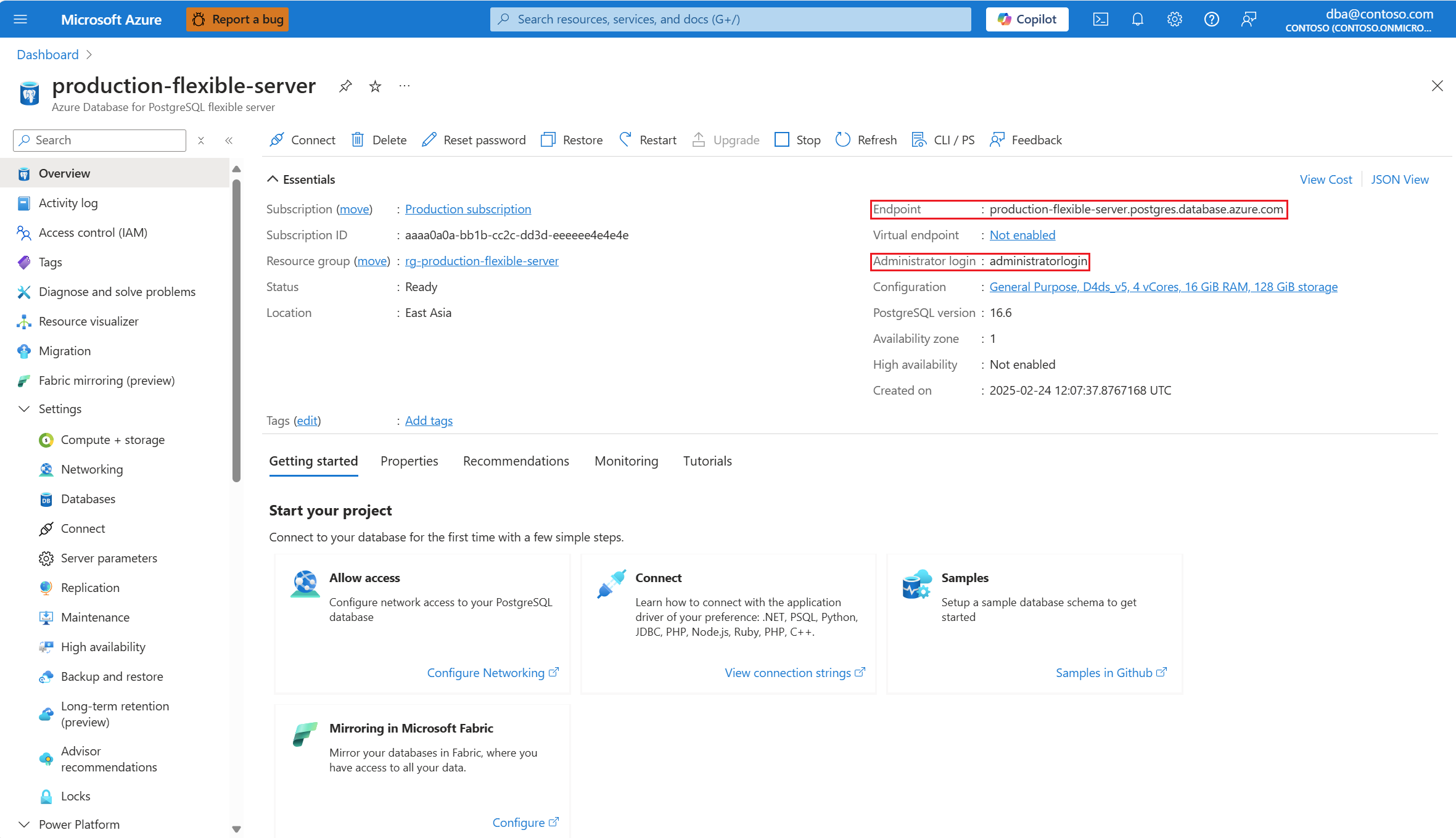
Copy the values shown as Endpoint and Administrator login.
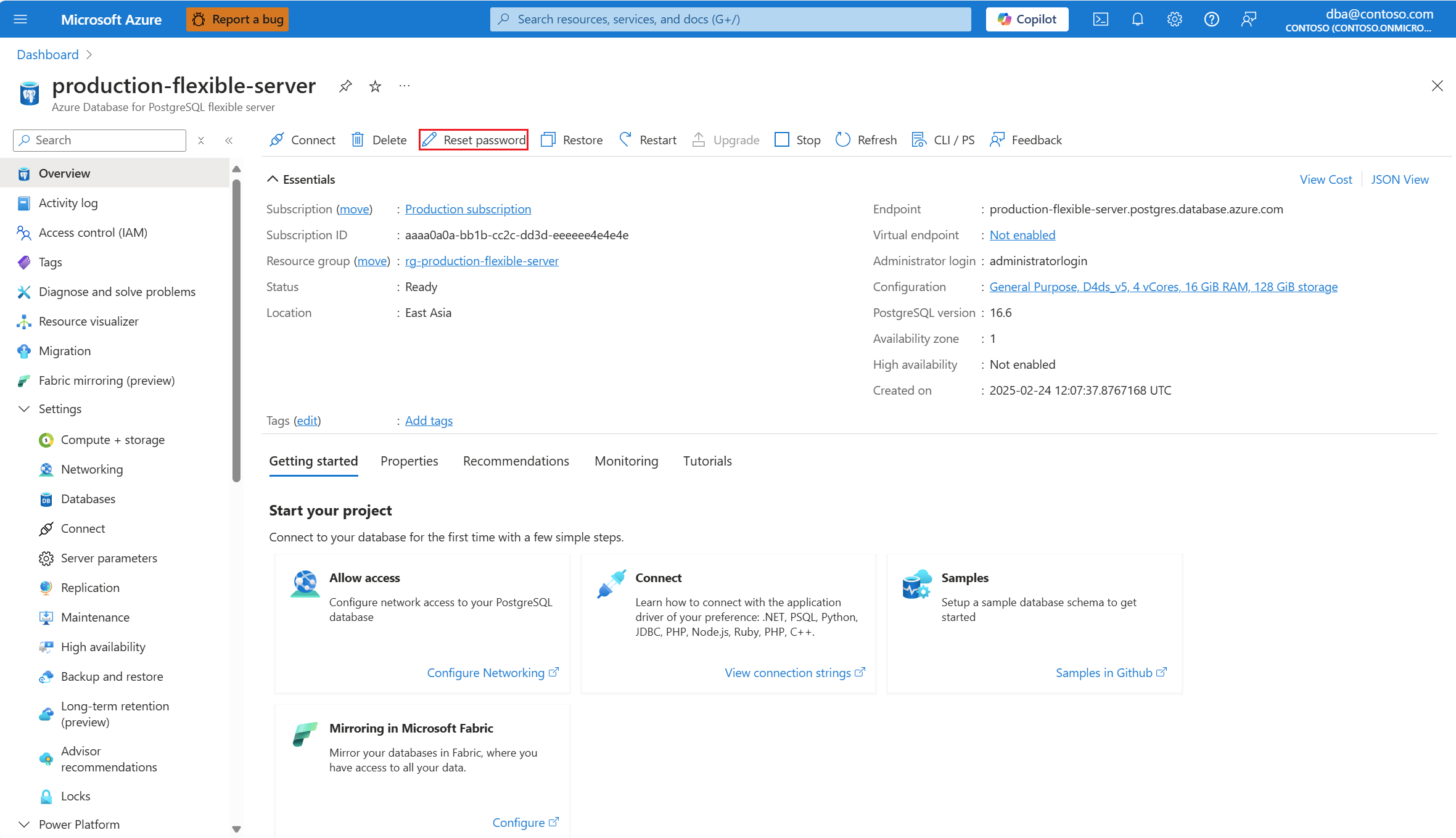
If you forget the password of the administrator login, you can reset it using the Reset password button.
Step 1: Connect and insert data
Use the following code to connect and load the data using CREATE TABLE and INSERT INTO SQL statements. The code uses NpgsqlCommand class with method:
- Open() to establish a connection to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server database.
- CreateCommand() sets the CommandText property.
- ExecuteNonQuery() method to run the database commands.
Important
Replace the Host, DBName, User, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using Npgsql;
namespace Driver
{
public class AzurePostgresCreate
{
// Obtain connection string information from the portal
//
private static string Host = "mydemoserver.postgres.database.azure.com";
private static string User = "mylogin";
private static string DBname = "postgres";
private static string Password = "<server_admin_password>";
private static string Port = "5432";
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Build connection string using parameters from portal
//
string connString =
String.Format(
"Server={0};Username={1};Database={2};Port={3};Password={4};SSLMode=Prefer",
Host,
User,
DBname,
Port,
Password);
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString))
{
Console.Out.WriteLine("Opening connection");
conn.Open();
using (var command = new NpgsqlCommand("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS inventory", conn))
{
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Finished dropping table (if existed)");
}
using (var command = new NpgsqlCommand("CREATE TABLE inventory(id serial PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), quantity INTEGER)", conn))
{
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Finished creating table");
}
using (var command = new NpgsqlCommand("INSERT INTO inventory (name, quantity) VALUES (@n1, @q1), (@n2, @q2), (@n3, @q3)", conn))
{
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("n1", "banana");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("q1", 150);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("n2", "orange");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("q2", 154);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("n3", "apple");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("q3", 100);
int nRows = command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.Out.WriteLine(String.Format("Number of rows inserted={0}", nRows));
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Having any issues? Let us know.
Step 2: Read data
Use the following code to connect and read the data using a SELECT SQL statement. The code uses NpgsqlCommand class with method:
- Open() to establish a connection to PostgreSQL.
- CreateCommand() and ExecuteReader() to run the database commands.
- Read() to advance to the record in the results.
- GetInt32() and GetString() to parse the values in the record.
Important
Replace the Host, DBName, User, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using Npgsql;
namespace Driver
{
public class AzurePostgresRead
{
// Obtain connection string information from the portal
//
private static string Host = "mydemoserver.postgres.database.azure.com";
private static string User = "mylogin";
private static string DBname = "postgres";
private static string Password = "<server_admin_password>";
private static string Port = "5432";
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Build connection string using parameters from portal
//
string connString =
String.Format(
"Server={0}; User Id={1}; Database={2}; Port={3}; Password={4};SSLMode=Prefer",
Host,
User,
DBname,
Port,
Password);
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString))
{
Console.Out.WriteLine("Opening connection");
conn.Open();
using (var command = new NpgsqlCommand("SELECT * FROM inventory", conn))
{
var reader = command.ExecuteReader();
while (reader.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine(
string.Format(
"Reading from table=({0}, {1}, {2})",
reader.GetInt32(0).ToString(),
reader.GetString(1),
reader.GetInt32(2).ToString()
)
);
}
reader.Close();
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Having any issues? Let us know.
Step 3: Update data
Use the following code to connect and update the data using an UPDATE SQL statement. The code uses NpgsqlCommand class with method:
- Open() to establish a connection to Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- CreateCommand(), sets the CommandText property.
- ExecuteNonQuery() method to run the database commands.
Important
Replace the Host, DBName, User, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using Npgsql;
namespace Driver
{
public class AzurePostgresUpdate
{
// Obtain connection string information from the portal
//
private static string Host = "mydemoserver.postgres.database.azure.com";
private static string User = "mylogin";
private static string DBname = "postgres";
private static string Password = "<server_admin_password>";
private static string Port = "5432";
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Build connection string using parameters from portal
//
string connString =
String.Format(
"Server={0}; User Id={1}; Database={2}; Port={3}; Password={4};SSLMode=Prefer",
Host,
User,
DBname,
Port,
Password);
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString))
{
Console.Out.WriteLine("Opening connection");
conn.Open();
using (var command = new NpgsqlCommand("UPDATE inventory SET quantity = @q WHERE name = @n", conn))
{
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("n", "banana");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("q", 200);
int nRows = command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.Out.WriteLine(String.Format("Number of rows updated={0}", nRows));
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Having any issues? Let us know.
Step 4: Delete data
Use the following code to connect and delete data using a DELETE SQL statement.
The code uses NpgsqlCommand class with method Open() to establish a connection to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server database. Then, the code uses the CreateCommand() method, sets the CommandText property, and calls the method ExecuteNonQuery() to run the database commands.
Important
Replace the Host, DBName, User, and Password parameters with the values that you specified when you created the server and database.
using System;
using Npgsql;
namespace Driver
{
public class AzurePostgresDelete
{
// Obtain connection string information from the portal
//
private static string Host = "mydemoserver.postgres.database.azure.com";
private static string User = "mylogin@mydemoserver";
private static string DBname = "postgres";
private static string Password = "<server_admin_password>";
private static string Port = "5432";
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Build connection string using parameters from portal
//
string connString =
String.Format(
"Server={0}; User Id={1}; Database={2}; Port={3}; Password={4};SSLMode=Prefer",
Host,
User,
DBname,
Port,
Password);
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString))
{
Console.Out.WriteLine("Opening connection");
conn.Open();
using (var command = new NpgsqlCommand("DELETE FROM inventory WHERE name = @n", conn))
{
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("n", "orange");
int nRows = command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.Out.WriteLine(String.Format("Number of rows deleted={0}", nRows));
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press RETURN to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Clean up resources
To clean up all resources used during this quickstart, delete the resource group using the following command:
az group delete \
--name $AZ_RESOURCE_GROUP \
--yes
Related content
- Manage Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
- Quickstart: Use Python to connect and query data from an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- Quickstart: Use Java to connect and query data from an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- Quickstart: Use Go language to connect and query data from an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- Quickstart: Use PHP to connect and query data from an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- Quickstart: Use Azure CLI to connect and query data from an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- Quickstart: Import data from Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server in Power BI.