Preprocess Text
This article describes a component in Azure Machine Learning designer.
Use the Preprocess Text component to clean and simplify text. It supports these common text processing operations:
- Removal of stop-words
- Using regular expressions to search for and replace specific target strings
- Lemmatization, which converts multiple related words to a single canonical form
- Case normalization
- Removal of certain classes of characters, such as numbers, special characters, and sequences of repeated characters such as "aaaa"
- Identification and removal of emails and URLs
The Preprocess Text component currently only supports English.
Configure Text Preprocessing
Add the Preprocess Text component to your pipeline in Azure Machine Learning. You can find this component under Text Analytics.
Connect a dataset that has at least one column containing text.
Select the language from the Language dropdown list.
Text column to clean: Select the column that you want to preprocess.
Remove stop words: Select this option if you want to apply a predefined stopword list to the text column.
Stopword lists are language-dependent and customizable.
Lemmatization: Select this option if you want words to be represented in their canonical form. This option is useful for reducing the number of unique occurrences of otherwise similar text tokens.
The lemmatization process is highly language-dependent..
Detect sentences: Select this option if you want the component to insert a sentence boundary mark when performing analysis.
This component uses a series of three pipe characters
|||to represent the sentence terminator.Perform optional find-and-replace operations using regular expressions. The regular expression will be processed at first, ahead of all other built-in options.
- Custom regular expression: Define the text you're searching for.
- Custom replacement string: Define a single replacement value.
Normalize case to lowercase: Select this option if you want to convert ASCII uppercase characters to their lowercase forms.
If characters aren't normalized, the same word in uppercase and lowercase letters is considered two different words.
You can also remove the following types of characters or character sequences from the processed output text:
Remove numbers: Select this option to remove all numeric characters for the specified language. Identification numbers are domain-dependent and language dependent. If numeric characters are an integral part of a known word, the number might not be removed. Learn more in Technical notes.
Remove special characters: Use this option to remove any non-alphanumeric special characters.
Remove duplicate characters: Select this option to remove extra characters in any sequences that repeat for more than twice. For example, a sequence like "aaaaa" would be reduced to "aa".
Remove email addresses: Select this option to remove any sequence of the format
<string>@<string>.Remove URLs: Select this option to remove any sequence that includes the following URL prefixes:
http,https,ftp,www
Expand verb contractions: This option applies only to languages that use verb contractions; currently, English only.
For example, by selecting this option, you could replace the phrase "wouldn't stay there" with "would not stay there".
Normalize backslashes to slashes: Select this option to map all instances of
\\to/.Split tokens on special characters: Select this option if you want to break words on characters such as
&,-, and so forth. This option can also reduce the special characters when it repeats more than twice.For example, the string
MS---WORDwould be separated into three tokens,MS,-, andWORD.Submit the pipeline.
Technical notes
The preprocess-text component in Studio(classic) and designer use different language models. The designer uses a multi-task CNN trained model from spaCy. Different models give different tokenizer and part-of-speech tagger, which leads to different results.
Following are some examples:
| Configuration | Output result |
|---|---|
| With all options selected Explanation: For the cases like '3test' in the 'WC-3 3test 4test', the designer remove the whole word '3test', since in this context, the part-of-speech tagger specifies this token '3test' as numeral, and according to the part-of-speech, the component removes it. |
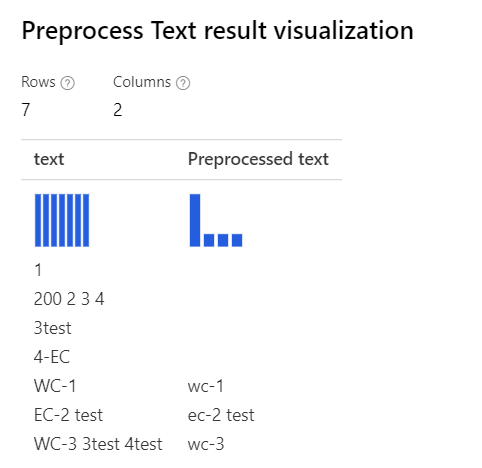
|
With only Removing number selected Explanation: For the cases like '3test', '4-EC', the designer tokenizer dose not split these cases, and treats them as the whole tokens. So it won't remove the numbers in these words. |

|
You can also use regular expression to output customized results:
| Configuration | Output result |
|---|---|
| With all options selected Custom regular expression: (\s+)*(-|\d+)(\s+)* Custom replacement string: \1 \2 \3 |

|
With only Removing number selected Custom regular expression: (\s+)*(-|\d+)(\s+)* Custom replacement string: \1 \2 \3 |
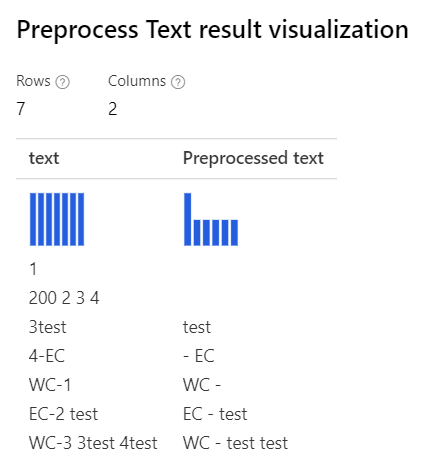
|
Next steps
See the set of components available to Azure Machine Learning.