Configure MQTT broker authentication
Important
This page includes instructions for managing Azure IoT Operations components using Kubernetes deployment manifests, which is in preview. This feature is provided with several limitations, and shouldn't be used for production workloads.
See the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews for legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
An MQTT broker supports multiple authentication methods for clients. You can configure each listener port to have its own authentication settings with a BrokerAuthentication resource. For a list of the available settings, see the Broker Authentication API reference.
Link BrokerListener and BrokerAuthentication
The following rules apply to the relationship between BrokerListener and BrokerAuthentication resources:
- Each BrokerListener resource can have multiple ports. You can link each port to a BrokerAuthentication resource.
- Each BrokerAuthentication resource can support multiple authentication methods at once.
- Ports that don't link a BrokerAuthentication resource have authentication disabled.
To link a BrokerListener port to a BrokerAuthentication resource, specify the authenticationRef field in the ports setting of the BrokerListener resource. To learn more, see BrokerListener resource.
Default BrokerAuthentication resource
Azure IoT Operations deploys a default BrokerAuthentication resource named default linked with the default listener in the azure-iot-operations namespace. It uses only Kubernetes service account tokens (SATs) for authentication.
Important
The SAT authentication method in the default BrokerAuthentication resource is required for components in IoT Operations to function correctly. Avoid updating or deleting the default BrokerAuthentication resource.
In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
Select the Authentication tab.
From the authentication policy list, select the default policy name.
To add new authentication methods, select Add method.
Authentication flow
The order of the specified authentication methods determines how the MQTT broker authenticates clients. The MQTT broker tries to authenticate the client's credentials by using the first specified method and iterates through the specified methods until it finds a match or reaches the end.
For each method, the MQTT broker first checks if the client's credentials are relevant for that method. For example, SAT authentication requires a username starting with K8S-SAT, and X.509 authentication requires a client certificate. If the client's credentials are relevant, the MQTT broker then verifies if they're valid. For more information, see the Configure authentication method section.
For custom authentication, the MQTT broker treats failure to communicate with the custom authentication server as credentials not relevant. This behavior lets the MQTT broker fall back to other methods if the custom authentication server is unreachable.
The authentication flow ends when:
- One of these conditions is true:
- The client's credentials are relevant and valid for one of the methods.
- The client's credentials aren't relevant for any of the methods.
- The client's credentials are relevant but invalid for any of the methods.
- The MQTT broker either grants or denies access to the client based on the outcome of the authentication flow.
For example:
apiVersion: mqttbroker.iotoperations.azure.com/v1
kind: BrokerAuthentication
metadata:
name: default
namespace: azure-iot-operations
spec:
authenticationMethods:
- method: Custom
customSettings:
# ...
- method: ServiceAccountToken
serviceAccountTokenSettings:
# ...
The earlier example specifies custom and SAT. When a client connects, the MQTT broker attempts to authenticate the client by using the specified methods in the order custom and then SAT.
- The MQTT broker checks if the client's credentials are valid for custom authentication. Because custom authentication relies on an external server to determine validity of credentials, the broker considers all credentials relevant to custom auth and forwards them to the custom authentication server.
- If the custom authentication server responds with a
PassorFailresult, the authentication flow ends. If the custom authentication server isn't available, the MQTT broker falls back to the remaining specified methods, with SAT being next. - The MQTT broker tries to authenticate the credentials as SAT credentials.
If the custom authentication server is unavailable and all subsequent methods determine that the provided credentials aren't relevant, the broker denies the client connection.
Configure authentication method
You can add authentication methods such as X.509, SAT, or custom to authentication policies.
To add an authentication method to a policy:
In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
Select the Authentication tab.
Choose an existing authentication policy or create a new one.
Add a new method by selecting Add method.
Choose the method type from the dropdown list, and then select Add details to configure the method.
To learn more about each of the authentication options, see the next sections for each method.
For more information about how to enable secure settings by configuring an Azure Key Vault instance and enabling workload identities, see Enable secure settings in Azure IoT Operations deployment.
X.509
Tip
For an end-to-end example of how to configure X.509 authentication, see Tutorial: TLS, X.509 client authentication, and attribute-based access control (ABAC) authorization.
With X.509 authentication, the MQTT broker uses a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) certificate to validate client certificates. This trusted CA can be a root or intermediate CA. The broker checks the client certificate chain against the trusted CA certificate. If the chain is valid, the client is authenticated.
To use X.509 authentication with a trusted CA certificate, you must meet the following requirements:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol: Because X.509 relies on TLS client certificates, TLS must be enabled for ports by using X.509 authentication.
- Key algorithms: Both EC and RSA keys are supported, but all certificates in the chain must use the same key algorithm.
- Format: The CA certificate must be in Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format.
Tip
PEM format is a common format for certificates and keys. PEM files are Base64-encoded ASCII files with headers like -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- and -----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----.
If you have a certificate in another format, you can convert it to PEM by using OpenSSL. For more information, see Convert a certificate into the appropriate format.
Get a trusted CA certificate
In a production setup, the CA certificate is provided by an organization's public key infrastructure (PKI) or a public certificate authority.
For testing, create a self-signed CA certificate with OpenSSL. For example, run the following command to generate a self-signed CA certificate with an RSA key, a distinguished name CN=Contoso Root CA Cert, and a validity of 365 days:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout ca-key.pem -out ca.pem -days 365 -nodes -subj "/CN=Contoso Root CA Cert"
The same command with the Step CLI, which is a convenient tool for managing certificates, is:
step certificate create "Contoso Root CA Cert" ca.pem ca-key.pem --profile root-ca --kty RSA --size 4096 --no-password --insecure
--not-after 8760h
These commands create a CA certificate, ca.pem, and a private key, ca-key.pem, in PEM format. You can import the CA certificate ca.pem into the MQTT broker for X.509 authentication.
Import a trusted CA certificate
To get started with X.509 authentication, import the trusted CA certificate into a ConfigMap in the azure-iot-operations namespace. To import a trusted CA certificate ca.pem into a ConfigMap named client-ca, run:
kubectl create configmap client-ca --from-file=ca.pem -n azure-iot-operations
In this example, the CA certificate is imported under the key ca.pem. The MQTT broker trusts all CA certificates in the ConfigMap, so you can use anything for the name of the key.
To check that the root CA certificate is properly imported, run kubectl describe configmap. The result shows the same Base64 encoding of the PEM certificate file.
kubectl describe configmap client-ca -n azure-iot-operations
Name: client-ca
Namespace: azure-iot-operations
Data
====
ca.pem:
----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFDjCCAvagAwIBAgIRAKQWo1+S13GTwqZSUYLPemswDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAw
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
BinaryData
====
Configure X.509 authentication method
After the trusted CA certificate is imported, enable X.509 client authentication by adding it as an authentication method in a BrokerAuthentication resource. Ensure that this resource is linked to a TLS-enabled listener port.
In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
Select the Authentication tab.
Choose an existing authentication policy or create a new one.
Add a new method by selecting Add method.
Choose the method type X.509 from the dropdown list. Then select Add details to configure the method.
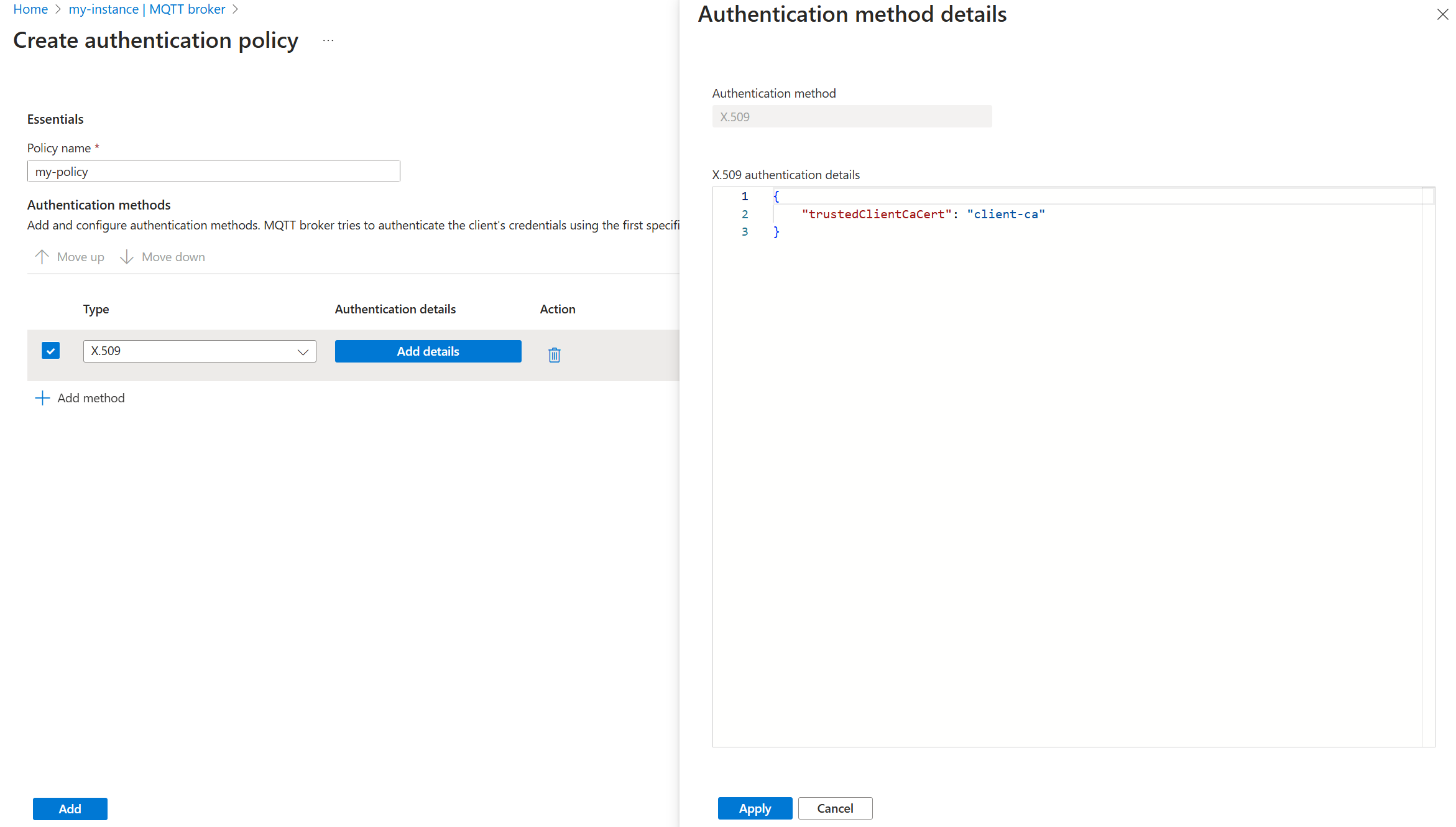
On the X.509 authentication details pane, specify the trusted CA certificate ConfigMap name by using JSON format.
{ "trustedClientCaCert": "<TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP>" }Replace
<TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP>with the name of the ConfigMap that contains the trusted CA certificate. For example, use"trustedClientCaCert": "client-ca".Optionally, add authorization attributes for clients by using X.509 certificates. To learn more, see Certificate attributes for authorization.
Select Apply to save the changes.
Optional: Certificate attributes for authorization
You can specify X.509 attributes in the BrokerAuthentication resource for authorizing clients based on their certificate properties. The attributes are defined in the authorizationAttributes field.
For example:
In the Azure portal, when you configure the X.509 authentication method, add the authorization attributes in the X.509 authentication details pane in JSON format.
{
"trustedClientCaCert": "<TRUSTED_CA_CONFIGMAP>",
"authorizationAttributes": {
"root": {
"subject": "CN = Contoso Root CA Cert, OU = Engineering, C = US",
"attributes": {
"organization": "contoso"
}
},
"intermediate": {
"subject": "CN = Contoso Intermediate CA",
"attributes": {
"city": "seattle",
"foo": "bar"
}
},
"smartfan": {
"subject": "CN = smart-fan",
"attributes": {
"building": "17"
}
}
}
}
In this example, every client that has a certificate issued by the root CA with distinguished name CN = Contoso Root CA Cert, OU = Engineering, C = US or the intermediate CA with distinguished name CN = Contoso Intermediate CA receives the attributes listed. In addition, the smart-fan client certificate receives attributes specific to it.
The matching for attributes always starts from the leaf client certificate and then goes along the chain. The attribute assignment stops after the first match. In the previous example, even if smart-fan has the intermediate certificate CN = Contoso Intermediate CA, it doesn't get the associated attributes.
You can apply authorization rules to clients by using X.509 certificates with these attributes. To learn more, see Authorize clients that use X.509 authentication.
Enable X.509 authentication for a listener port
After you import the trusted CA certificate and configure the BrokerAuthentication resource, link it to a TLS-enabled listener port. This step is important because X.509 authentication relies on TLS for client certificate validation.
To get a TLS-enabled listener port, see Enable TLS manual certificate management for a port and Enable TLS automatic certificate management for a port.
Note
Enabling TLS on a broker listener port means that the broker uses a server certificate for TLS encryption. When clients connect to this port, they must trust the server certificate by having the CA certificate that signed it in their trust store. This process is known as trust distribution or trust bundling. It's important to understand the difference between client validation and server validation:
- Client validation: The MQTT broker (server) checks the client certificate against the trusted CA certificate specified in the
trustedClientCaCertfield for X.509 client authentication. - Server validation: Clients (like Mosquitto or MQTTX) check the MQTT broker's server certificate against the trusted CA certificate in their trust store. For Mosquitto clients, use the
--cafileparameter to specify the CA certificate file. For MQTTX, add the CA certificate to the trust store in the settings.
After you enable X.509 authentication, ensure that clients trust the broker's server certificate by having the server-side CA certificate in their trust store. Don't confuse trusting the server-side CA certificate with the client-side CA certificate used for client authentication that's specified in the trustedClientCaCert field.
For a full example, see Tutorial: TLS, X.509 client authentication, and attribute-based access control (ABAC) authorization.
Connect Mosquitto client to MQTT broker with X.509 client certificate
A client like Mosquitto needs two files to be able to connect to the MQTT broker with TLS and X.509 client authentication:
- The
--certparameter specifies the client certificate PEM file. This file should also include any intermediate certificates to help the MQTT broker build the complete certificate chain. - The
--keyparameter specifies the client private key PEM file.
In cases where the MQTT broker is using a self-signed CA certificate to issue its TLS server certificate, the --cafile parameter is needed. This file contains the CA certificate (also known as trust bundle), which the Mosquitto client uses to validate the broker's server certificate when it connects over TLS. If the issuer of the MQTT broker's server certificate is part of the system root store (such as well-known public CAs), the --cafile parameter can be omitted.
For example:
mosquitto_pub -q 1 -t hello -d -V mqttv5 -m world -i thermostat \
-h "<BROKER_HOST>" \
--cert thermostat_cert.pem \
--key thermostat_key.pem \
--cafile ca.pem
Understand MQTT broker X.509 client authentication flow
Follow these steps for client authentication:
- When X.509 client authentication is turned on, connecting clients must present a client certificate and any intermediate certificates to let the MQTT broker build a certificate chain rooted to one of its configured trusted certificates.
- The load balancer directs the communication to one of the frontend brokers.
- After the frontend broker receives the client certificate, it tries to build a certificate chain that's rooted to one of the configured certificates. If the frontend broker successfully builds a chain and the presented chain is verified, it finishes the TLS handshake. The connecting client is able to send MQTT packets to the frontend through the TLS channel.
- The TLS channel is open, but the client authentication or authorization isn't finished yet.
- The client then sends a CONNECT packet to the MQTT broker.
- The CONNECT packet is routed to a frontend again.
- The frontend collects all credentials the client presented so far, like authentication data from the CONNECT packet, and the client certificate chain presented during the TLS handshake.
- The frontend sends these credentials to the authentication service. The authentication service checks the certificate chain once again and collects the subject names of all the certificates in the chain.
- The authentication service uses its configured authorization rules to determine what attributes the connecting clients have. These attributes determine what operations the client can run, including the CONNECT packet itself.
- Authentication service returns the decision to the frontend broker.
- The frontend broker knows the client attributes and if it's allowed to connect. If so, then the MQTT connection is completed and the client can continue to send and receive MQTT packets as determined by its authorization rules.
Kubernetes service account tokens
Kubernetes SATs are JSON web tokens associated with Kubernetes service accounts. Clients present SATs to the MQTT broker to authenticate themselves.
The MQTT broker uses bound service account tokens that are described in the What GKE users need to know about Kubernetes' new service account tokens post. Here are the main features from the post:
Bound tokens launched in Kubernetes 1.13 and became the default format in 1.21. Bound tokens address all of the limited functionality of legacy tokens, and more:
- The tokens are hard to steal and misuse. They're time-bound, audience-bound, and object-bound.
- They adopt a standardized format. OpenID Connect (OIDC), with full OIDC Discovery, makes it easier for service providers to accept them.
- They're distributed to pods more securely by using a new Kubelet projected volume type.
The broker verifies tokens by using the Kubernetes Token Review API. Enable the Kubernetes TokenRequestProjection feature to specify audiences (default since 1.21). If this feature isn't enabled, you can't use SATs.
Create a service account
To create SATs, first create a service account. The following command creates a service account called mqtt-client:
kubectl create serviceaccount mqtt-client -n azure-iot-operations
Optional: Add attributes for authorization
Clients authenticating via SAT can optionally have their service accounts annotated with attributes to be used with authorization policies. To distinguish these annotations from others, they begin with aio-broker-auth/ prefix.
You can annotate a service account by using kubectl annotate:
kubectl annotate serviceaccount <SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME> aio-broker-auth/<ATTRIBUTE>=<VALUE> -n azure-iot-operations
Or you can add the annotations to the service account manifest file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: <SERVICE_ACCOUNT_NAME>
namespace: azure-iot-operations
annotations:
aio-broker-auth/<ATTRIBUTE_1>: <VALUE_1>
aio-broker-auth/<ATTRIBUTE_2>: <VALUE_2>
To learn more, see Authorize clients that use Kubernetes service account tokens.
Enable SAT authentication
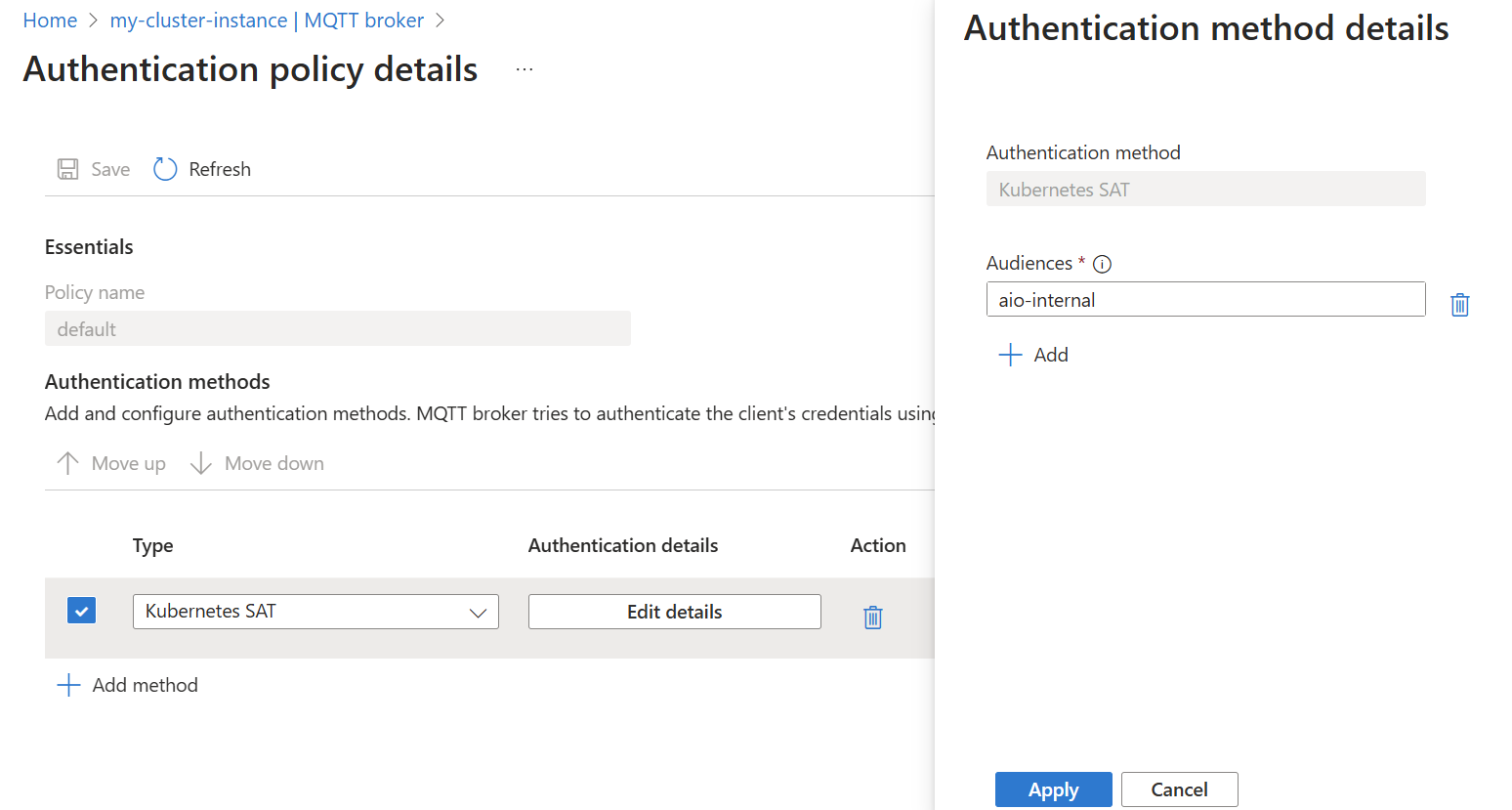
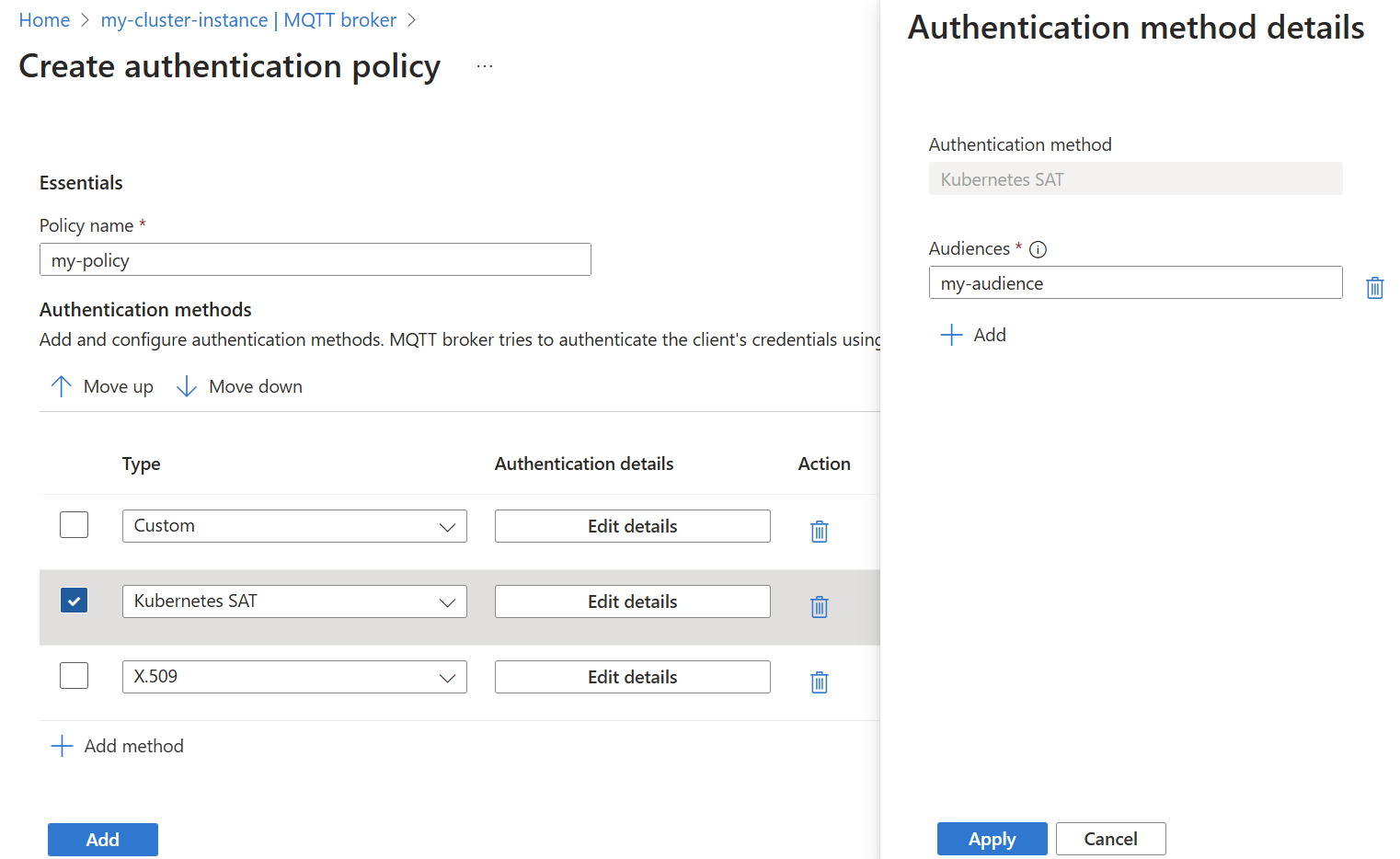
Modify the authenticationMethods setting in a BrokerAuthentication resource to specify ServiceAccountToken as a valid authentication method. The audiences parameter specifies the list of valid audiences for tokens. Choose unique values that identify the MQTT broker service. You must specify at least one audience, and all SATs must match one of the specified audiences.
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
- Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
- Select the Authentication tab.
- Choose an existing authentication policy or create a new one.
- Add a new method by selecting Add method.
- Choose the method type Kubernetes SAT from the dropdown list. Then select Add details to configure the method.
Test SAT authentication
SAT authentication uses the MQTT v5 enhanced authentication fields. A client must set the enhanced authentication method to K8S-SAT and the enhanced authentication data to the token.
For example, use Mosquitto (some fields omitted for brevity):
mosquitto_pub ... -D CONNECT authentication-method 'K8S-SAT' -D CONNECT authentication-data <TOKEN>
Here, <TOKEN> is the service account token. To get a test token, run:
kubectl create token <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> -n azure-iot-operations --audience <AUDIENCE>
Here, <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> is the name of the service account you created, and <AUDIENCE> is one of the audiences configured in the BrokerAuthentication resource.
For an example on how to configure a Kubernetes pod to use SAT authentication, see Connect to the default listener inside the cluster.
In the pod configuration, the serviceAccountName field must match the service account associated with the token being used. The serviceAccountToken.audience field must be one of the audiences configured in the BrokerAuthentication resource.
Refresh service account tokens
Service account tokens are valid for a limited time and configured with expirationSeconds. However, Kubernetes automatically refreshes the token before it expires. The token is refreshed in the background, and the client doesn't need to do anything other than to fetch it again.
For example, if the client is a pod that uses the token mounted as a volume, like in the test SAT authentication example, the latest token is available at the same path /var/run/secrets/tokens/broker-sat. When the client makes a new connection, the client can fetch the latest token and use it to authenticate. The client should also have a mechanism to handle MQTT unauthorized errors by fetching the latest token and retrying the connection.
Custom authentication
Extend client authentication beyond the provided authentication methods with custom authentication. It's pluggable because the service can be anything as long as it adheres to the API.
When a client connects to the MQTT broker with custom authentication enabled, the broker sends an HTTPS request to a custom authentication server with the client's credentials. The server then responds with either approval or denial, including the client's authorization attributes.
Create custom authentication service
The custom authentication server is implemented and deployed separately from the MQTT broker.
A sample custom authentication server and instructions are available on GitHub. Use this sample as a template and a starting point for implementing your own custom authentication logic.
API
The API between the MQTT broker and the custom authentication server follows the API specification for custom authentication. The OpenAPI specification is available on GitHub.
HTTPS with TLS encryption is required
The MQTT broker sends requests containing sensitive client credentials to the custom authentication server. To protect these credentials, communication between the MQTT broker and custom authentication server must be encrypted with TLS.
The custom authentication server must present a server certificate, and the MQTT broker must have a trusted root CA certificate for validating the server certificate. Optionally, the custom authentication server might require the MQTT broker to present a client certificate to authenticate itself.
Enable custom authentication for a listener
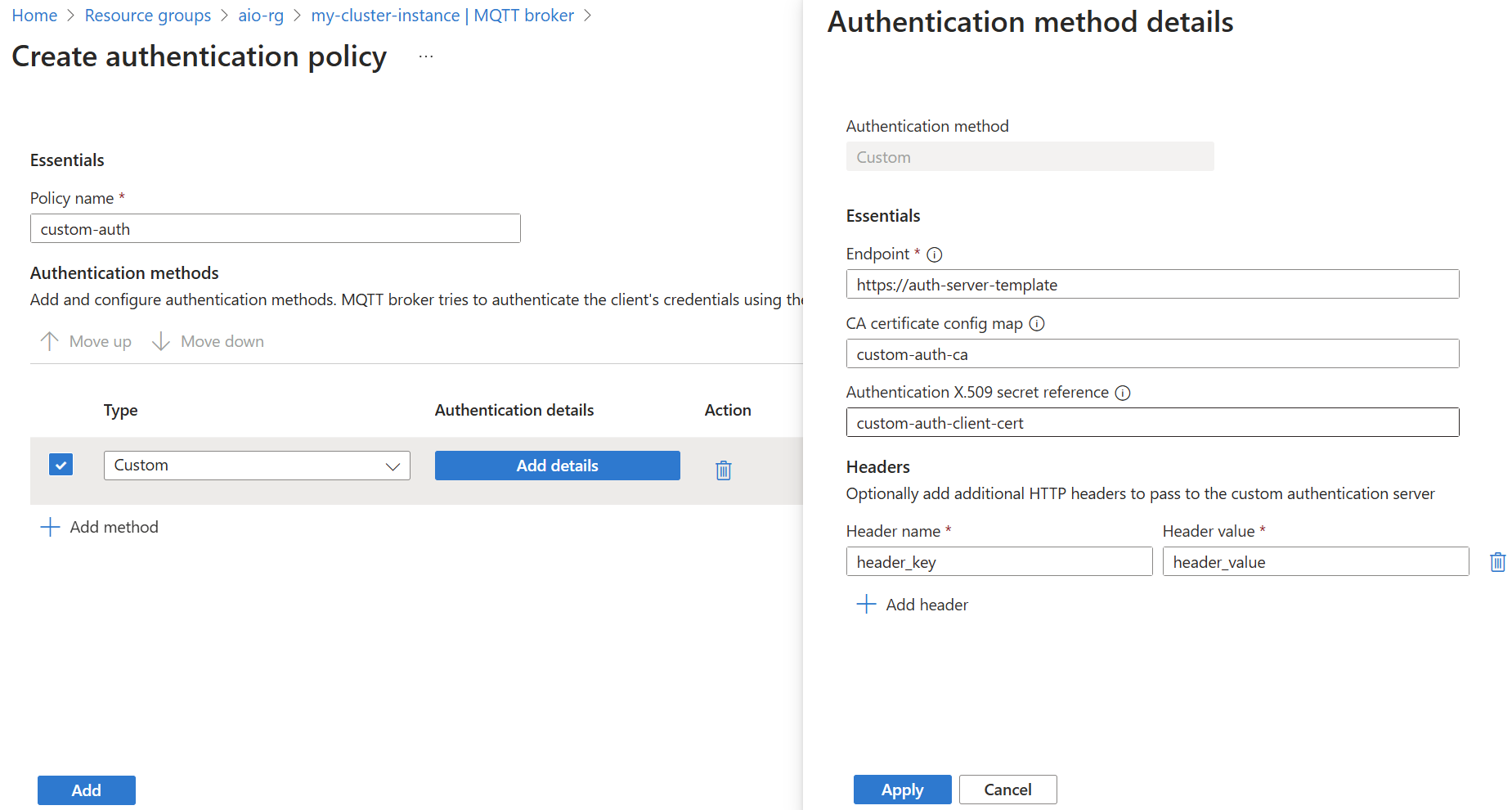
Modify the Authentication methods setting in a BrokerAuthentication resource to specify Custom as a valid authentication method. Then, specify the parameters required to communicate with a custom authentication server.
In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
Select the Authentication tab.
Choose an existing authentication policy or create a new one.
Add a new method by selecting Add method.
Choose the method type Custom from the dropdown list. Then select Add details to configure the method.
Disable authentication
For testing, you can disable authentication for a broker listener port. We don't recommend that you disable authentication for production environments.
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
- Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
- Select the broker listener you want to edit from the list.
- On the port where you want to disable authentication, select None in the authentication dropdown.
Clients disconnect after credentials expire
The MQTT broker disconnects clients when their credentials expire. Disconnect after credential expiration applies to all clients that connect to the MQTT broker frontends, such as:
- Clients authenticated with SATs disconnect when their SAT expires.
- Clients authenticated with X.509 disconnect when their client certificate expires.
- Clients authenticated with custom authentication disconnect based on the expiry time returned from the custom authentication server.
On disconnect, the client's network connection is closed. The client doesn't receive an MQTT DISCONNECT packet, but the broker logs a message that it disconnected the client.
MQTT v5 clients authenticated with SATs and custom authentication can reauthenticate with a new credential before their initial credential expires. X.509 clients can't reauthenticate and must reestablish the connection because authentication is done at the TLS layer.
Clients can reauthenticate by sending an MQTT v5 AUTH packet with reason ReAuth.
SAT clients send an AUTH client with the fields method: K8S-SAT and data: <token>. Custom authentication clients set the method and data field as required by the custom authentication server.
Successful reauthentication updates the client's credential expiry with the expiry time of its new credential. The broker responds with a Success AUTH packet. Failed authentication because of transient issues, such as the custom authentication server being unavailable, causes the broker to respond with a ContinueAuthentication AUTH packet. The client can try again later. Other authentication failures cause the broker to send a DISCONNECT packet and close the client's network connection.