IoT Hub support for virtual networks with Azure Private Link
By default, IoT Hub's hostnames map to a public endpoint with a publicly routable IP address over the internet. Different customers share this IoT Hub public endpoint, and IoT devices in wide-area networks and on-premises networks can all access it.
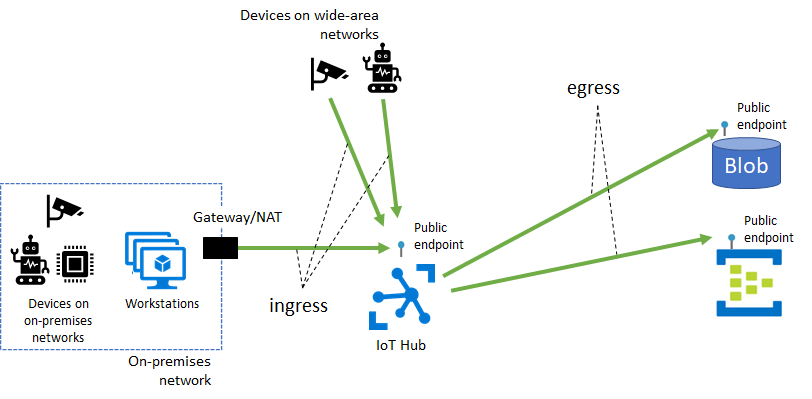
Some IoT Hub features, including message routing, file upload, and bulk device import/export, also require connectivity from IoT Hub to a customer-owned Azure resource over its public endpoint. These connectivity paths make up the egress traffic from IoT Hub to customer resources.
You might want to restrict connectivity to your Azure resources (including IoT Hub) through a VNet that you own and operate for several reasons, including:
Introducing network isolation for your IoT hub by preventing connectivity exposure to the public internet.
Enabling a private connectivity experience from your on-premises network assets, which ensures that your data and traffic is transmitted directly to Azure backbone network.
Preventing exfiltration attacks from sensitive on-premises networks.
Following established Azure-wide connectivity patterns using private endpoints.
This article describes how to achieve these goals using Azure Private Link for ingress connectivity to IoT Hub and using trusted Microsoft services exception for egress connectivity from IoT Hub to other Azure resources.
Ingress connectivity to IoT Hub using Azure Private Link
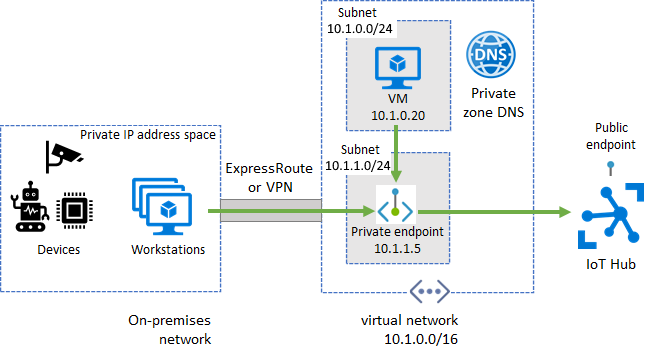
A private endpoint is a private IP address allocated inside a customer-owned VNet through which an Azure resource is reachable. With Azure Private Link, you can set up a private endpoint for your IoT hub to allow services inside your VNet to reach IoT Hub without requiring traffic to be sent to IoT Hub's public endpoint. Similarly, your on-premises devices can use Virtual Private Network (VPN) or ExpressRoute peering to gain connectivity to your VNet and your IoT hub (via its private endpoint). As a result, you can restrict or completely block off connectivity to your IoT hub's public endpoints by using IoT Hub IP filter or the public network access toggle. This approach keeps connectivity to your hub using the private endpoint for devices. The main focus of this setup is for devices inside an on-premises network. This setup isn't advised for devices deployed in a wide-area network.
Before proceeding ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
You've created an Azure VNet with a subnet in which the private endpoint will be created.
For devices that operate in on-premises networks, set up Virtual Private Network (VPN) or ExpressRoute private peering into your Azure VNet.
Set up a private endpoint for IoT Hub ingress
Private endpoint works for IoT Hub device APIs (like device-to-cloud messages) and service APIs (like creating and updating devices).
In the Azure portal, navigate to your IoT hub.
Select Networking > Private access, and then select Create a private endpoint.
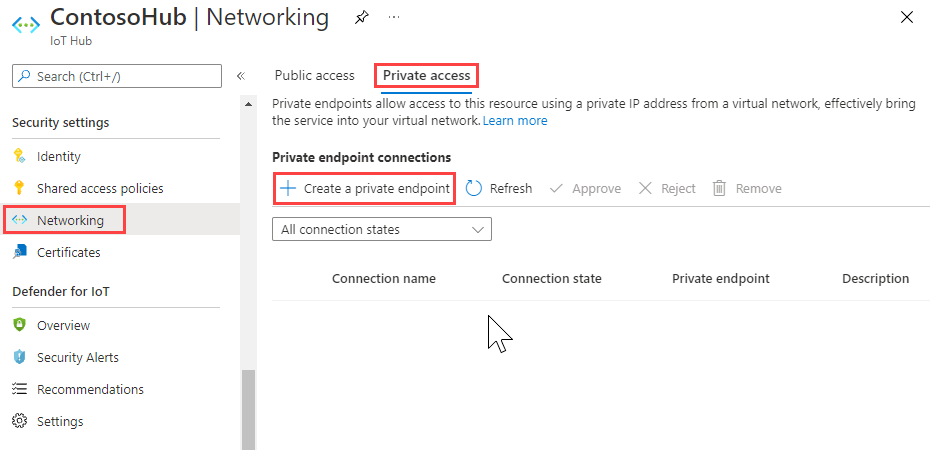
Provide the subscription, resource group, name, and region to create the new private endpoint. Ideally, a private endpoint should be created in the same region as your hub.
Select Next: Resource, and provide the subscription for your IoT Hub resource, and select "Microsoft.Devices/IotHubs" as resource type, your IoT hub name as resource, and iotHub as target subresource.
Select Next: Configuration and provide your virtual network and subnet to create the private endpoint in. Select the option to integrate with Azure private DNS zone, if desired.
Select Next: Tags, and optionally provide any tags for your resource.
Select Review + create to create your private link resource.
Built-in Event Hubs compatible endpoint
The built-in Event Hubs compatible endpoint can also be accessed over private endpoint. When private link is configured, you should see another private endpoint connection for the built-in endpoint. It's the one with servicebus.windows.net in the FQDN.
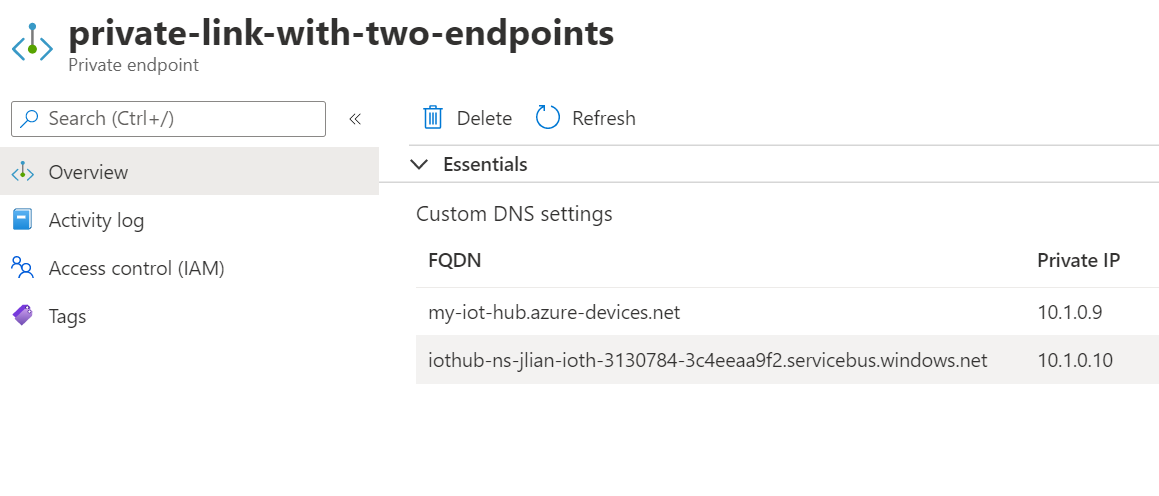
IoT Hub's IP filter can optionally control public access to the built-in endpoint.
To completely block public network access to your IoT hub, turn off public network access or use IP filter to block all IP and select the option to apply rules to the built-in endpoint.
Pricing for Private Link
For pricing details, see Azure Private Link pricing.
Egress connectivity from IoT Hub to other Azure resources
IoT Hub can connect to your Azure blob storage, event hub, service bus resources for message routing, file upload, and bulk device import/export over the resources' public endpoint. Binding your resource to a VNet blocks connectivity to the resource by default. As a result, this configuration prevents IoT hubs from sending data to your resources. To fix this issue, enable connectivity from your IoT Hub resource to your storage account, event hub, or service bus resources via the trusted Microsoft service option.
To allow other services to find your IoT hub as a trusted Microsoft service, your hub must use a managed identity. Once a managed identity is provisioned, grant permission to your hub's managed identity to access your custom endpoint. Follow the article Managed identities support in IoT Hub to provision a managed identity with Azure role-based access control (RBAC) permission, and add the custom endpoint to your IoT hub. Make sure you turn on the trusted Microsoft first party exception to allow your IoT hubs access to the custom endpoint if you have the firewall configurations in place.
Pricing for trusted Microsoft service option
Trusted Microsoft first party services exception feature is free of charge. Charges for the provisioned storage accounts, event hubs, or service bus resources apply separately.
Next steps
Use the following links to learn more about IoT Hub features: