Table API and SQL in Apache Flink® clusters on HDInsight on AKS
Note
We will retire Azure HDInsight on AKS on January 31, 2025. Before January 31, 2025, you will need to migrate your workloads to Microsoft Fabric or an equivalent Azure product to avoid abrupt termination of your workloads. The remaining clusters on your subscription will be stopped and removed from the host.
Only basic support will be available until the retirement date.
Important
This feature is currently in preview. The Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews include more legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, in preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability. For information about this specific preview, see Azure HDInsight on AKS preview information. For questions or feature suggestions, please submit a request on AskHDInsight with the details and follow us for more updates on Azure HDInsight Community.
Apache Flink features two relational APIs - the Table API and SQL - for unified stream and batch processing. The Table API is a language-integrated query API that allows the composition of queries from relational operators such as selection, filter, and join intuitively. Flink’s SQL support is based on Apache Calcite, which implements the SQL standard.
The Table API and SQL interfaces integrate seamlessly with each other and Flink’s DataStream API. You can easily switch between all APIs and libraries, which build upon them.
Apache Flink SQL
Like other SQL engines, Flink queries operate on top of tables. It differs from a traditional database because Flink doesn't manage data at rest locally; instead, its queries operate continuously over external tables.
Flink data processing pipelines begin with source tables and end with sink tables. Source tables produce rows operated over during the query execution; they're the tables referenced in the FROM clause of a query. Connectors can be of type HDInsight Kafka, HDInsight HBase, Azure Event Hubs, databases, filesystems, or any other system whose connector lies in the classpath.
Using Flink SQL Client in HDInsight on AKS clusters
You can refer this article on how to use CLI from Secure Shell on Azure portal. Here are some quick samples of how to get started.
To start the SQL client
./bin/sql-client.shTo pass an initialization sql file to run along with sql-client
./sql-client.sh -i /path/to/init_file.sqlTo set a configuration in sql-client
SET execution.runtime-mode = streaming; SET sql-client.execution.result-mode = table; SET sql-client.execution.max-table-result.rows = 10000;
SQL DDL
Flink SQL supports the following CREATE statements
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE CATALOG
Following is an example syntax to define a source table using jdbc connector to connect to MSSQL, with id, name as columns in a CREATE TABLE Statement
CREATE TABLE student_information (
id BIGINT,
name STRING,
address STRING,
grade STRING,
PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'jdbc',
'url' = 'jdbc:sqlserver://servername.database.windows.net;database=dbname;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=true;create=false;loginTimeout=30',
'table-name' = 'students',
'username' = 'username',
'password' = 'password'
);
CREATE DATABASE :
CREATE DATABASE students;
CREATE CATALOG:
CREATE CATALOG myhive WITH ('type'='hive');
You can run Continuous Queries on Top of these tables
SELECT id,
COUNT(*) as student_count
FROM student_information
GROUP BY grade;
Write out to Sink Table from Source Table:
INSERT INTO grade_counts
SELECT id,
COUNT(*) as student_count
FROM student_information
GROUP BY grade;
Adding Dependencies
JAR statements are used to add user jars into the classpath or remove user jars from the classpath or show added jars in the classpath in the runtime.
Flink SQL supports the following JAR statements:
- ADD JAR
- SHOW JARS
- REMOVE JAR
Flink SQL> ADD JAR '/path/hello.jar';
[INFO] Execute statement succeed.
Flink SQL> ADD JAR 'hdfs:///udf/common-udf.jar';
[INFO] Execute statement succeed.
Flink SQL> SHOW JARS;
+----------------------------+
| jars |
+----------------------------+
| /path/hello.jar |
| hdfs:///udf/common-udf.jar |
+----------------------------+
Flink SQL> REMOVE JAR '/path/hello.jar';
[INFO] The specified jar is removed from session classloader.
Hive Metastore in Apache Flink® clusters on HDInsight on AKS
Catalogs provide metadata, such as databases, tables, partitions, views, and functions and information needed to access data stored in a database or other external systems.
In HDInsight on AKS, Flink we support two catalog options:
GenericInMemoryCatalog
The GenericInMemoryCatalog is an in-memory implementation of a catalog. All the objects are available only for the lifetime of the sql session.
HiveCatalog
The HiveCatalog serves two purposes; as persistent storage for pure Flink metadata, and as an interface for reading and writing existing Hive metadata.
Note
HDInsight on AKS clusters comes with an integrated option of Hive Metastore for Apache Flink. You can opt for Hive Metastore during cluster creation
How to Create and Register Flink Databases to Catalogs
You can refer this article on how to use CLI and get started with Flink SQL Client from Secure Shell on Azure portal.
Start
sql-client.shsession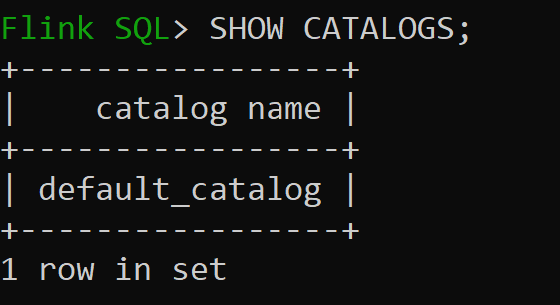
Default_catalog is the default in-memory catalog
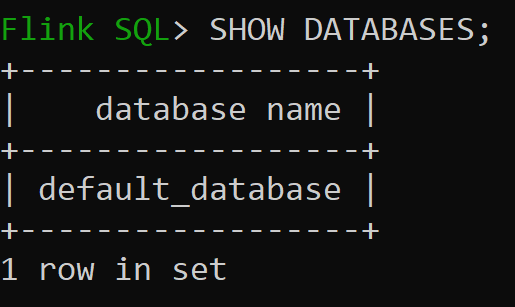
Let us now check default database of in-memory catalog
Let us create Hive Catalog of version 3.1.2 and use it
CREATE CATALOG myhive WITH ('type'='hive'); USE CATALOG myhive;Note
HDInsight on AKS supports Hive 3.1.2 and Hadoop 3.3.2. The
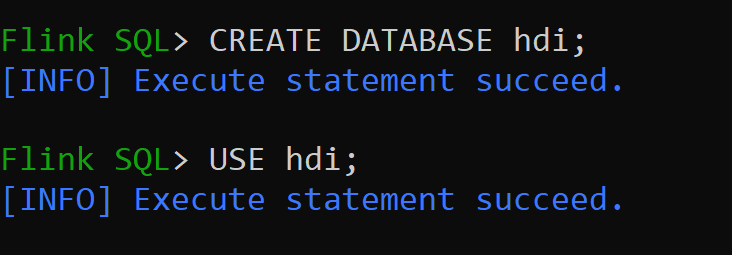
hive-conf-diris set to location/opt/hive-confLet us create Database in hive catalog and make it default for the session (unless changed).
How to Create and Register Hive Tables to Hive Catalog
Follow the instructions on How to Create and Register Flink Databases to Catalog
Let us create Flink Table of connector type Hive without Partition
CREATE TABLE hive_table(x int, days STRING) WITH ( 'connector' = 'hive', 'sink.partition-commit.delay'='1 s', 'sink.partition-commit.policy.kind'='metastore,success-file');Insert Data into hive_table
INSERT INTO hive_table SELECT 2, '10'; INSERT INTO hive_table SELECT 3, '20';Read data from hive_table
Flink SQL> SELECT * FROM hive_table; 2023-07-24 09:46:22,225 INFO org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileInputFormat[] - Total input files to process : 3 +----+-------------+--------------------------------+ | op | x | days | +----+-------------+--------------------------------+ | +I | 3 | 20 | | +I | 2 | 10 | | +I | 1 | 5 | +----+-------------+--------------------------------+ Received a total of 3 rowsNote
Hive Warehouse Directory is located in the designated container of storage account chosen during Apache Flink cluster creation, can be found at directory hive/warehouse/
Lets create Flink Table of connector type hive with Partition
CREATE TABLE partitioned_hive_table(x int, days STRING) PARTITIONED BY (days) WITH ( 'connector' = 'hive', 'sink.partition-commit.delay'='1 s', 'sink.partition-commit.policy.kind'='metastore,success-file');
Important
There is a known limitation in Apache Flink. The last ‘n’ columns are chosen for partitions, irrespective of user defined partition column. FLINK-32596 The partition key will be wrong when use Flink dialect to create Hive table.
Reference
- Apache Flink Table API & SQL
- Apache, Apache Flink, Flink, and associated open source project names are trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).