Push delivery with HTTP
This article builds on the What is Azure Event Grid? article to provide essential information before you start using Event Grid’s pull and push delivery over HTTP. It covers fundamental concepts, resource models, and message delivery modes supported. At the end of this document, you find useful links to articles that guide you on how to use Event Grid and to articles that offer in-depth conceptual information.
Important
This document helps you get started with Event Grid capabilities that use the HTTP protocol. This article is suitable for users who need to integrate applications on the cloud. If you require to communicate IoT device data, see Overview of the MQTT Support in Azure Event Grid.
Core concepts
CloudEvents
Event Grid conforms to CNCF’s open standard CloudEvents 1.0 specification using the HTTP protocol binding with JSON format. It means that your solutions publish and consume event messages using a format like the following example:
{
"specversion" : "1.0",
"type" : "com.yourcompany.order.created",
"source" : "https://yourcompany.com/orders/",
"subject" : "O-28964",
"id" : "A234-1234-1234",
"time" : "2018-04-05T17:31:00Z",
"comexampleextension1" : "value",
"comexampleothervalue" : 5,
"datacontenttype" : "application/json",
"data" : {
"orderId" : "O-28964",
"URL" : "https://com.yourcompany/orders/O-28964"
}
}
What is an event?
An event is the smallest amount of information that fully describes something that happened in a system. We often refer to an event as shown above as a discrete event because it represents a distinct, self-standing fact about a system that provides an insight that can be actionable. Examples include: com.yourcompany.Orders.OrderCreated, org.yourorg.GeneralLedger.AccountChanged, io.solutionname.Auth.MaximumNumberOfUserLoginAttemptsReached.
Note
We interchangeably use the terms discrete events, cloudevents, or just events to refer to those messages that inform about a change of a system state.
For more information on events, see the Event Grid Terminology.
Another kind of event
The user community also refers to events to those type of messages that carry a data point, such as a single reading from a device or a single click on a web application page. That kind of event is usually analyzed over a time window or event stream size to derive insights and take an action. In Event Grid’s documentation, we refer to that kind of event as data point, streaming data, or telemetry. They're a kind of data that Event Grid’s MQTT support and Azure Event Hubs usually handle.
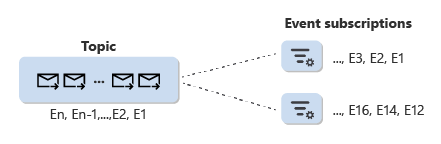
Topics and event subscriptions
Events published to Event Grid land on a topic, which is a resource that logically contains all events. An event subscription is a configuration resource associated with a single topic. Among other things, you use an event subscription to set event selection criteria to define the event collection available to a subscriber out of the total set of events present in a topic.
Push delivery
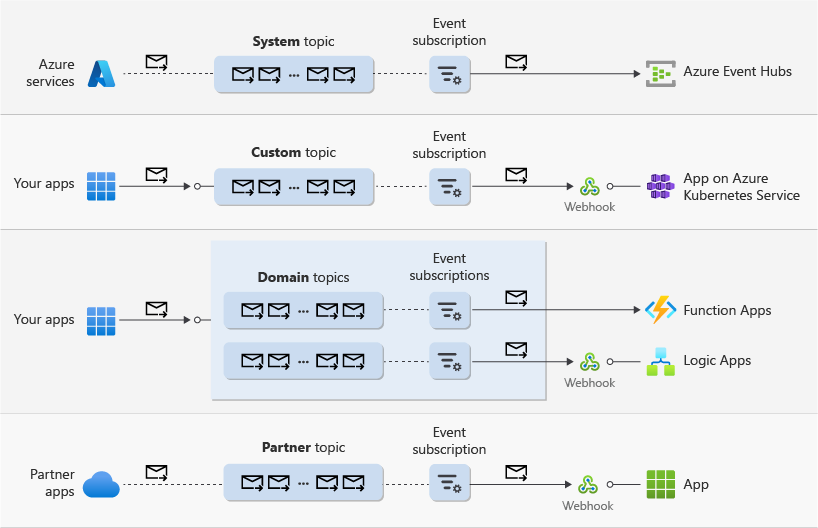
Push delivery is supported for the following resources. Click on the links to learn more about each of them.
- System topics. Use system topics to receive (system) events from Azure services.
- Custom topics. Use custom topics when you want to publish your application’s events.
- Domains. Domains represent a group of domain topics typically associated with a single application that requires sending events to different group of users, organizations, or applications. A common approach is to associate a domain topic with a group of target applications or users of an organization within the same tenant. An organization can be a team, a division in company, a company, etc.
- Partner topics. Use partner topics when you want to consume events from third-party partners.
Configure an event subscription on a system, custom, or partner topic to specify a filtering criteria for events and to set a destination to one of the supported event handlers.
The following diagram illustrates the resources that support push delivery with some of the supported event handlers.
Note
If you are interested to know more about push delivery on Event Grid namespaces, see [namespace-push-delivery-overview.md].
Next steps
The following articles provide you with information on how to use Event Grid or provide you with additional information on concepts.
- Learn about System Topics
- Learn about Partner Topics
- Learn about Event Domains
- Learn about event handlers
- Learn about event filtering
- Publish and subscribe using custom topics.
- Subscribe to storage events
- Subscribe to partner events
Other useful links
- Control plane and data plane SDKs
- Data plane SDKs announcement with a plethora of information, samples, and links
- Quotas and limits