Custom delivery properties
Event subscriptions allow you to set up HTTP headers that are included in delivered events. This capability allows you to set custom headers that are required by a destination. You can set up to 10 headers when creating an event subscription. Each header value shouldn't be greater than 4,096 (4K) bytes.
You can set custom headers on the events that are delivered to the following destinations:
- Webhooks
- Azure Service Bus topics and queues
- Azure Event Hubs
- Azure Functions
- Azure Relay Hybrid Connections
When creating an event subscription in the Azure portal, you can use the Delivery Properties tab to set custom HTTP headers. This page lets you set fixed and dynamic header values.
Setting static header values
To set headers with a fixed value, provide the name of the header and its value in the corresponding fields:
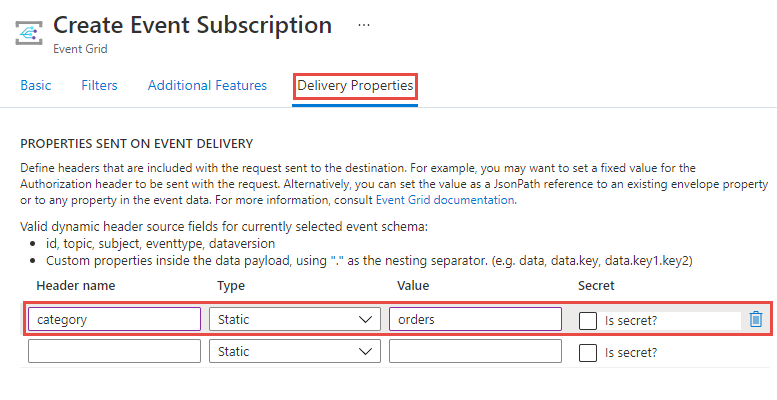
You might want to check Is secret? when you're providing sensitive data. The visibility of sensitive data on the Azure portal depends on the user's RBAC permission.
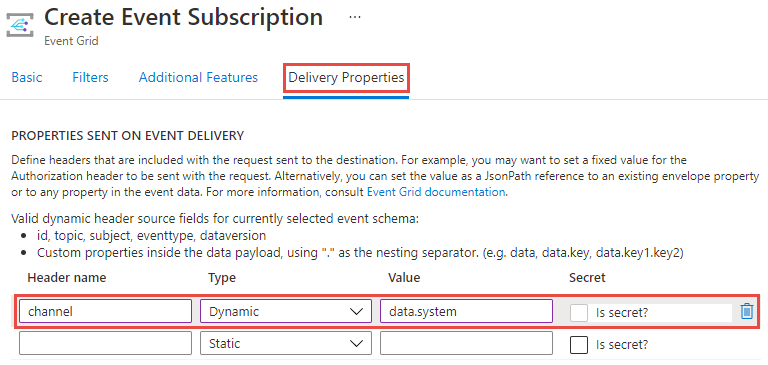
Setting dynamic header values
You can set the value of a header based on a property in an incoming event. Use JsonPath syntax to refer to an incoming event's property value to be used as the value for a header in outgoing requests. Only JSON values of string, number and boolean are supported. For example, to set the value of a header named Channel using the value of the incoming event property system in the event data, configure your event subscription in the following way:
Use Azure CLI
Use the --delivery-attribute-mapping parameter when creating a subscription using the az eventgrid event-subscription create command. Here's an example:
az eventgrid event-subscription create -n es1 \
--source-resource-id /subscriptions/{SubID}/resourceGroups/{RG}/providers/Microsoft.EventGrid/topics/topic1
--endpoint-type storagequeue \
--endpoint /subscriptions/{SubID}/resourceGroups/TestRG/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/sa1/queueservices/default/queues/q1 \
--enable-advanced-filtering-on-arrays true
--delivery-attribute-mapping staticproperty1 static somestaticvalue2 true
--delivery-attribute-mapping staticproperty2 static somestaticvalue3 false
--delivery-attribute-mapping dynamicproperty1 dynamic data.key1
Examples
This section gives you a few examples of using delivery properties.
Setting the Authorization header with a bearer token (non-normative example)
Set a value to an Authorization header to identify the request with your Webhook handler. An Authorization header can be set if you aren't protecting your Webhook with Microsoft Entra ID.
| Header name | Header type | Header value |
|---|---|---|
Authorization |
Static | BEARER SlAV32hkKG... |
Outgoing requests should now contain the header set on the event subscription:
POST /home.html HTTP/1.1
Host: acme.com
Authorization: BEARER SlAV32hkKG...
Note
Defining authorization headers is a sensible option when your destination is a Webhook. It should not be used for functions subscribed with a resource id, Service Bus, Event Hubs, and Hybrid Connections as those destinations support their own authentication schemes when used with Event Grid.
Service Bus example
Azure Service Bus supports the use of following message properties when sending single messages.
| Header name | Header type |
|---|---|
MessageId |
Dynamic |
PartitionKey |
Static or dynamic |
SessionId |
Static or dynamic |
CorrelationId |
Static or dynamic |
Label |
Static or dynamic |
ReplyTo |
Static or dynamic |
ReplyToSessionId |
Static or dynamic |
To |
Static or dynamic |
ViaPartitionKey |
Static or dynamic |
Note
- The default value of
MessageIdis the internal ID of the Event Grid event. You can override it. For example,data.field. - You can only set either
SessionIdorMessageId.
You can also specify custom properties when sending messages to Service Bus queues or topics. Don't use the aeg- prefix as it's used by system properties in message headers. For a list of message header properties, see Service Bus as an event handler
Event Hubs example
If you need to publish events to a specific partition within an event hub, set the PartitionKey property on your event subscription to specify the partition key that identifies the target event hub partition.
| Header name | Header type |
|---|---|
PartitionKey |
Static or dynamic |
You can also specify custom properties when sending messages to an event hub. Don't use the aeg- prefix for the property name as it's used by system properties in message headers. For a list of message header properties, see Event Hubs as an event handler
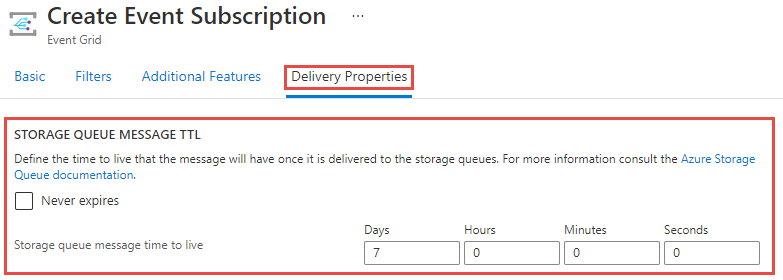
Configure time to live on outgoing events to Azure Storage Queues
For the Azure Storage Queues destination, you can only configure the time-to-live the outgoing message will have once it has been delivered to an Azure Storage queue. If no time is provided, the message's default time to live is 7 days. You can also set the event to never expire.
Next steps
For more information about event delivery, see the following article: