Securely govern your cloud estate
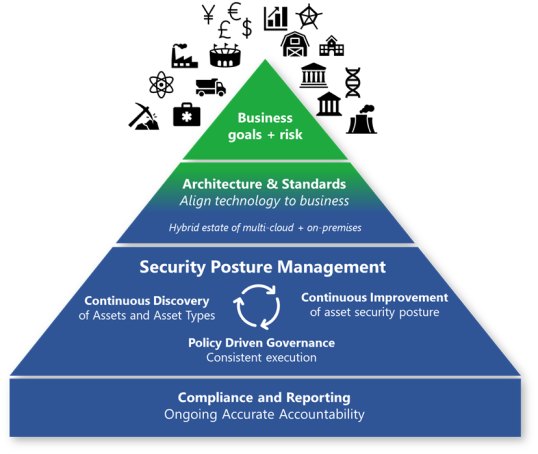
Security governance connects your business priorities with technical implementations, such as architecture, standards, and policies. Governance teams provide oversight and monitoring to sustain and improve security posture over time. These teams also report compliance that regulatory bodies require.
Business goals and risk provide the most effective guidance for security. This approach ensures that security efforts are concentrated on the organization’s key priorities. Additionally, it helps risk owners by using familiar language and processes within the risk management framework.
This article is a supporting guide to the Govern methodology. It provides areas of security optimization for you to consider as you move through that phase in your journey.
Security posture modernization
Using only problem reporting isn't an effective strategy for maintaining your security posture. In the cloud era, governance requires an active approach that continuously collaborates with other teams. Security posture management is an emerging and essential function. This role addresses the critical question of environmental security. It encompasses key areas such as vulnerability management and security compliance reporting.
In an on-premises environment, security governance relies on the periodic data that's available about the environment. This approach often results in outdated information. Cloud technology revolutionizes this process by providing on-demand visibility into the current security posture and asset coverage. This real-time insight transforms governance into a more dynamic organization. It fosters closer collaboration with other security teams to monitor security standards, provide guidance, and enhance processes.
In its ideal state, governance drives continuous improvement throughout the organization. This ongoing process engages all parts of the organization to ensure constant security advancements.
The following are key principles for security governance:
Continuous discovery of assets and asset types: A static inventory isn't possible in a dynamic cloud environment. Your organization must focus on the continuous discovery of assets and asset types. In the cloud, new types of services are added regularly. Workload owners dynamically adjust the number of application and service instances as needed, which creates a constantly changing environment. This situation makes inventory management a continuously evolving discipline. Governance teams need to continuously identify asset types and instances to keep up with this pace of change.
Continuous improvement of asset security posture: Governance teams should focus on improving and enforcing standards to keep up with the cloud and attackers. Information technology (IT) organizations must react quickly to new threats and adapt accordingly. Attackers constantly evolve their techniques, while defenses continuously improve and might need to be updated. You can’t always incorporate all necessary security measures in the initial setup.
Policy-driven governance: This governance ensures consistent implementation because you define policies once and apply them automatically across resources. This process limits wasted time and effort on repeated manual tasks. It's often implemented by using Azure Policy or non-Microsoft policy automation frameworks.
To maintain agility, best practices guidance is often iterative. It digests small pieces of information from multiple sources to create the whole picture and continuously make small adjustments.
Azure facilitation
Microsoft Defender for Cloud can help you continuously discover and automatically manage virtual machines in your environment through automatic data collection provisioning.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud apps can help you continuously discover and govern first-party and non-Microsoft software as a service apps that are used in your environments.
Incident preparedness and response
Security governance is critical for maintaining your preparedness. To strictly enforce standards, robust governance mechanisms and practices must support the implementation of preparedness and response mechanisms and operational practices. Consider the following recommendations to help govern incident preparedness and response standards:
Incident preparedness governance
Automate governance: Use tooling to automate governance as much as possible. You can use tooling to manage policies for infrastructure deployments, implement hardening measures, protect data, and maintain identity and access management standards. By automating the governance of these security measures, you can ensure that all resources in your environment are compliant with your own security standards and all compliance frameworks that are required for your business. For more information, see Enforce cloud governance policies.
Adhere to security baselines from Microsoft: Understand the security recommendations from Microsoft for the services in your cloud estate, which are available as security baselines. These baselines can help you ensure that your existing deployments are properly secured and that new deployments are correctly configured from the start. This approach reduces the risk of misconfigurations.
Incident response governance
Governance of the incident response plan: The incident response plan should be maintained with the same care as the other critical documents in your estate. Your incident response plan should be:
Version controlled to ensure that teams are working off of the most recent version, and that the versioning can be audited.
Stored in highly available and secure storage.
Reviewed regularly and updated when changes to the environment require it.
Governance of incident response training: Training materials for incident response should be version-controlled for auditability and to ensure that the most recent version is being used at any given time. They should also be reviewed regularly and updated when updates to the incident response plan are made.
Azure facilitation
Azure Policy is a policy management solution that you can use to help enforce organizational standards and to assess compliance at-scale. To automate policy enforcement for many Azure services, take advantage of built-in policy definitions.
Defender for Cloud provides security policies that can automate compliance with your security standards.
Confidentiality governance
Effective governance is crucial for maintaining security and compliance in enterprise cloud environments. Governance includes the policies, procedures, and controls that ensure data is managed securely and in accordance with regulatory requirements. It provides a framework for decision-making, accountability, and continuous improvement, which is essential for protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust. This framework is crucial for upholding the principle of confidentiality from the CIA Triad. It helps you ensure that sensitive data is accessible only to authorized users and processes.
Technical policies: These policies include access control policies, data encryption policies, and data masking or tokenization policies. The goal of these policies is to create a secure environment by maintaining data confidentiality through stringent access controls and robust encryption methods.
Written policies: Written policies serve as the governing framework for the entire enterprise environment. They establish the requirements and parameters for data handling, access, and protection. These documents ensure consistency and compliance across the organization and provide clear guidelines for employees and IT staff. Written policies also serve as a reference point for audits and assessments, which helps identify and address any gaps in security practices.
Data loss protection: Continuous monitoring and auditing of data loss prevention (DLP) measures should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with confidentiality requirements. This process includes regularly reviewing and updating DLP policies, conducting security assessments, and responding to any incidents that might compromise data confidentiality. Establish DLP programmatically across the organization to ensure a consistent and scalable approach to protecting sensitive data.
Monitor compliance and methods of enforcement
It’s critical to monitor compliance and enforce policies to maintain the principle of confidentiality in enterprise cloud environments. These actions are essential for robust security standards. These processes ensure that all security measures are consistently applied and effective to help protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches. Regular assessments, automated monitoring, and comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure adherence to established policies and procedures.
Regular audits and assessments: Conduct regular security audits and assessments to ensure that policies are being followed and identify areas for improvement. These audits should cover regulatory, industry, and organizational standards and requirements, and might involve third-party assessors to provide an unbiased evaluation. An approved assessment and inspection program helps maintain high standards of security and compliance, and ensures that all aspects of data confidentiality are thoroughly reviewed and addressed.
Automated compliance monitoring: Tools like Azure Policy automate the monitoring of compliance with security policies and provide real-time insights and alerts. This functionality helps ensure continuous adherence to security standards. Automated monitoring helps you detect and respond to policy violations quickly, which reduces the risk of data breaches. It also ensures continuous compliance by regularly checking configurations and access controls against established policies.
Training and awareness programs: Educate employees about data confidentiality policies and best practices to foster a security-conscious culture. Regular training sessions and awareness programs help ensure that all staff members understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining data confidentiality. These programs should be updated regularly to reflect changes in policies and emerging threats. This strategy ensures that employees are always equipped with the latest knowledge and skills.
Integrity governance
To maintain your integrity protections effectively, you need a well-designed governance strategy. This strategy should ensure that all policies and procedures are documented and enforced, and that all systems are continuously audited for compliance.
The guidance described previously in the Confidentiality governance section also applies to the principle of integrity. The following recommendations are specific to integrity:
Automated data quality governance: Consider using an off-the-shelf solution to govern your data. Use a prebuilt solution to relieve your data governance team's burden of manual quality validation. This strategy also reduces the risk of unauthorized access and alterations to data during the validation process.
Automated system integrity governance: Consider using a centralized, unified tool to automate your system integrity governance. For example, Azure Arc allows you to govern systems across multiple clouds, on-premises data centers, and edge sites. By using a system like this, you can simplify your governance responsibilities and reduce operational burden.
Azure facilitation
- Microsoft Purview Data Quality allows users to assess data quality by using no-code/low-code rules, including out-of-the-box (OOB) rules and AI-generated rules. These rules are applied at the column level and then aggregated to provide scores for data assets, data products, and business domains. This approach ensures comprehensive visibility of data quality across each domain.
Availability governance
The architecture designs that you standardize in your cloud estate require governance to ensure that they aren't deviated from and that your availability isn't compromised by nonconforming design patterns. Likewise, your disaster recovery plans must also be governed to ensure that they're well-maintained.
Availability design governance
- Maintain standardized design patterns: Codify and strictly enforce infrastructure and application design patterns. Govern the maintenance of design standards to ensure that they remain up-to-date and protected from unauthorized access or alteration. Treat these standards with the same care as other policies. When possible, automate the enforcement of maintaining design patterns. For example, you can enable policies to control which types of resources can be deployed and specify the regions where deployments are permitted.
Disaster recovery governance
Governance of the disaster recovery plans: Treat disaster recovery plans with the same level of importance as incident response plans. Disaster recovery plans should be:
Version-controlled to ensure that teams are always working with the most recent version and that versioning can be audited for accuracy and compliance.
Stored in highly available and secure storage.
Reviewed regularly and updated when changes to the environment are needed.
Governance of disaster recovery drills: Disaster recovery drills aren't only for training on the plans but also serve as learning opportunities to improve the plan itself. They can also help refine operational or design standards. Meticulous record keeping of disaster recovery drills helps identify areas for improvement and ensures compliance with auditing requirements for disaster preparedness. By storing these records in the same repository as the plans, you can help keep everything organized and secure.
Sustaining secure governance
Modern Service Management (MSM)
Modern Service Management (MSM) is a set of practices and tools designed to manage and optimize IT services in a cloud environment. The goal of MSM is to align IT services with business needs. This approach ensures efficient service delivery while maintaining high standards of security and compliance. MSM provides a structured approach to managing complex cloud environments. MSM also allows organizations to respond quickly to changes, mitigate risks, and ensure continuous improvement. Additionally, MSM is relevant to the principle of confidentiality because it includes tools and practices that enforce data protection and monitor access controls.
Unified security management: MSM tools provide comprehensive security management by integrating various security functions to provide a holistic view of the cloud environment. This approach helps enforce security policies and detects and responds to threats in real-time.
Policy management and compliance: MSM facilitates the creation, enforcement, and monitoring of policies across the cloud environment. It ensures that all resources comply with organizational standards and regulatory requirements. Additionally, it provides real-time insights and alerts.
Continuous monitoring and improvement: MSM emphasizes continuous monitoring of the cloud environment to identify and address potential issues proactively. This approach supports ongoing optimization and improvement of IT services, which ensures that they remain aligned with business objectives.