Feature interoperability with SQL Server FCI & DNN
Applies to:
SQL Server on Azure VM
Tip
There are many methods to deploy an availability group. Simplify your deployment and eliminate the need for an Azure Load Balancer or distributed network name (DNN) for your Always On availability group by creating your SQL Server virtual machines (VMs) in multiple subnets within the same Azure virtual network. If you've already created your availability group in a single subnet, you can migrate it to a multi-subnet environment.
There are certain SQL Server features that rely on a hard-coded virtual network name (VNN). As such, when using the distributed network name (DNN) resource with your failover cluster instance and SQL Server on Azure VMs, there are some additional considerations.
In this article, learn how to configure the network alias when using the DNN resource, as well as which SQL Server features require additional consideration.
Create network alias (FCI)
Some server-side components rely on a hard-coded VNN value, and require a network alias that maps the VNN to the DNN DNS name to function properly. Follow the steps in Create a server alias to create an alias that maps the VNN to the DNN DNS name.
For a default instance, you can map the VNN to the DNN DNS name directly, such that VNN = DNN DNS name.
For example, if VNN name is FCI1, instance name is MSSQLSERVER, and the DNN is FCI1DNN (clients previously connected to FCI, and now they connect to FCI1DNN) then map the VNN FCI1 to the DNN FCI1DNN.
For a named instance the network alias mapping should be done for the full instance, such that VNN\Instance = DNN\Instance.
For example, if VNN name is FCI1, instance name is instA, and the DNN is FCI1DNN (clients previously connected to FCI1\instA, and now they connect to FCI1DNN\instaA) then map the VNN FCI1\instaA to the DNN FCI1DNN\instaA.
Client drivers
For ODBC, OLEDB, ADO.NET, JDBC, PHP, and Node.js drivers, users need to explicitly specify the DNN DNS name as the server name in the connection string. To ensure rapid connectivity upon failover, add MultiSubnetFailover=True to the connection string if the SQL client supports it.
Tools
Users of SQL Server Management Studio, sqlcmd, Azure Data Studio, and SQL Server Data Tools need to explicitly specify the DNN DNS name as the server name in the connection string.
Availability groups and FCI
You can configure an Always On availability group by using a failover cluster instance as one of the replicas. In this configuration, the mirroring endpoint URL for the FCI replica needs to use the FCI DNN. Likewise, if the FCI is used as a read-only replica, the read-only routing to the FCI replica needs to use the FCI DNN.
The format for the mirroring endpoint is: ENDPOINT_URL = 'TCP://<DNN DNS name>:<mirroring endpoint port>'.
For example, if your DNN DNS name is dnnlsnr, and 5022 is the port of the FCI's mirroring endpoint, the Transact-SQL (T-SQL) code snippet to create the endpoint URL looks like:
ENDPOINT_URL = 'TCP://dnnlsnr:5022'
Likewise, the format for the read-only routing URL is: TCP://<DNN DNS name>:<SQL Server instance port>.
For example, if your DNN DNS name is dnnlsnr, and 1444 is the port used by the read-only target SQL Server FCI, the T-SQL code snippet to create the read-only routing URL looks like:
READ_ONLY_ROUTING_URL = 'TCP://dnnlsnr:1444'
You can omit the port in the URL if it is the default 1433 port. For a named instance, configure a static port for the named instance and specify it in the read-only routing URL.
Replication
Replication has three components: Publisher, Distributor, Subscriber. Any of these components can be a failover cluster instance. Because the FCI VNN is heavily used in replication configuration, both explicitly and implicitly, a network alias that maps the VNN to the DNN might be necessary for replication to work.
Keep using the VNN name as the FCI name within replication, but create a network alias in the following remote situations before you configure replication:
| Replication component (FCI with DNN) | Remote component | Network alias map | Server with network map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Publisher | Distributor | Publisher VNN to Publisher DNN | Distributor |
| Distributor | Subscriber | Distributor VNN to Distributor DNN | Subscriber |
| Distributor | Publisher | Distributor VNN to Distributor DNN | Publisher |
| Subscriber | Distributor | Subscriber VNN to Subscriber DNN | Distributor |
For example, assume you have a Publisher that's configured as an FCI using DNN in a replication topology, and the Distributor is remote. In this case, create a network alias on the Distributor server to map the Publisher VNN to the Publisher DNN:
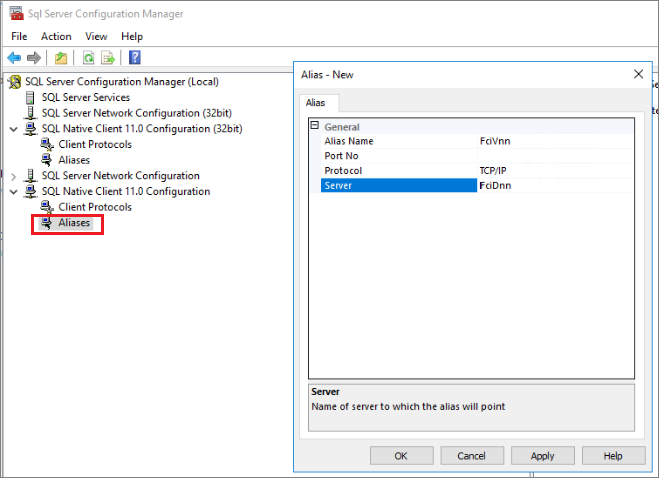
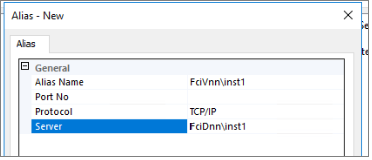
Use the full instance name for a named instance, like the following image example:
Database mirroring
You can configure database mirroring with an FCI as either database mirroring partner. Configure it by using Transact-SQL (T-SQL) rather than the SQL Server Management Studio GUI. Using T-SQL will ensure that the database mirroring endpoint is created using the DNN instead of the VNN.
For example, if your DNN DNS name is dnnlsnr, and the database mirroring endpoint is 7022, the following T-SQL code snippet configures the database mirroring partner:
ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks
SET PARTNER =
'TCP://dnnlsnr:7022'
GO
For client access, the Failover Partner property can handle database mirroring failover, but not FCI failover.
MSDTC
The FCI can participate in distributed transactions coordinated by Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC). Clustered MSDTC and local MSDTC are supported with FCI DNN. In Azure, an Azure Load Balancer is necessary for a clustered MSDTC deployment.
Tip
The DNN defined in the FCI does not replace the Azure Load Balancer requirement for the clustered MSDTC.
FileStream
Though FileStream is supported for a database in an FCI, accessing FileStream or FileTable by using File System APIs with DNN is not supported.
Linked servers
Using a linked server with an FCI DNN is supported. Either use the DNN directly to configure a linked server, or use a network alias to map the VNN to the DNN.
For example, to create a linked server with DNN DNS name dnnlsnr for named instance insta1, use the following Transact-SQL (T-SQL) command:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver
@server = N'dnnlsnr\inst1',
@srvproduct=N'SQL Server' ;
GO
Alternatively, you can create the linked server using the virtual network name (VNN) instead, but you will then need to define a network alias to map the VNN to the DNN.
For example, for instance name insta1, VNN name vnnname, and DNN name dnnlsnr, use the following Transact-SQL (T-SQL) command to create a linked server using the VNN:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver
@server = N'vnnname\inst1',
@srvproduct=N'SQL Server' ;
GO
Then, create a network alias to map vnnname\insta1 to dnnlsnr\insta1.
Frequently asked questions
Which SQL Server version brings DNN support?
SQL Server 2019 CU2 and later.
What is the expected failover time when DNN is used?
For DNN, the failover time will be just the FCI failover time, without any time added (like probe time when you're using Azure Load Balancer).
Is there any version requirement for SQL clients to support DNN with OLEDB and ODBC?
We recommend
MultiSubnetFailover=Trueconnection string support for DNN. It's available starting with SQL Server 2012 (11.x).Are any SQL Server configuration changes required for me to use DNN?
SQL Server does not require any configuration change to use DNN, but some SQL Server features might require more consideration.
Does DNN support multiple-subnet clusters?
Yes. The cluster binds the DNN in DNS with the physical IP addresses of all nodes in the cluster regardless of the subnet. The SQL client tries all IP addresses of the DNS name regardless of the subnet.
Next steps
To learn more, see: