To fail over, you first have to switch the replication modes SQL Server instance by using Transact-SQL (T-SQL).
Then, you can fail over and switch roles by using PowerShell.
Switch replication mode (Failover to SQL MI)
Replication between SQL Server and SQL Managed Instance is asynchronous by default. If you're failing over from SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance, before you fail over your database, switch the link to synchronous mode on SQL Server by using Transact-SQL (T-SQL).
Note
- Skip this step if you're failing over from SQL Managed Instance to SQL Server 2022.
- Synchronous replication across large network distances might slow down transactions on the primary replica.
Run the following T-SQL script on SQL Server to change the replication mode of the distributed availability group from async to sync. Replace:
<DAGName> with the name of the distributed availability group (used to create the link).<AGName> with the name of the availability group created on SQL Server (used to create the link).<ManagedInstanceName> with the name of your managed instance.
-- Run on SQL Server
-- Sets the distributed availability group to a synchronous commit.
-- ManagedInstanceName example: 'sqlmi1'
USE master
GO
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [<DAGName>]
MODIFY
AVAILABILITY GROUP ON
'<AGName>' WITH
(AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT),
'<ManagedInstanceName>' WITH
(AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT);
To confirm that you've changed the link's replication mode successfully, use the following dynamic management view. Results indicate the SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT state.
-- Run on SQL Server
-- Verifies the state of the distributed availability group
SELECT
ag.name, ag.is_distributed, ar.replica_server_name,
ar.availability_mode_desc, ars.connected_state_desc, ars.role_desc,
ars.operational_state_desc, ars.synchronization_health_desc
FROM
sys.availability_groups ag
join sys.availability_replicas ar
on ag.group_id=ar.group_id
left join sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states ars
on ars.replica_id=ar.replica_id
WHERE
ag.is_distributed=1
Now that you've switched SQL Server to synchronous commit mode, replication between the two instances is synchronous. If you need to reverse this state, follow the same steps and set the AVAILABILITY_MODE to ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT.
Check LSN values on both SQL Server and SQL Managed Instance
To complete the failover or migration, confirm that replication to the secondary is finished. For this, ensure the log sequence numbers (LSNs) in the log records for both SQL Server and SQL Managed Instance are the same.
Initially, it's expected that the LSN on the primary is higher than the LSN on the secondary. Network latency can cause replication to lag somewhat behind the primary. Because the workload has been stopped on the primary, the LSNs will match and stop changing after some time.
Use the following T-SQL query on SQL Server to read the LSN of the last recorded transaction log. Replace:
<DatabaseName> with your database name and look for the last hardened LSN number.
-- Run on SQL Server
-- Obtain the last hardened LSN for the database on SQL Server.
SELECT
ag.name AS [Replication group],
db.name AS [Database name],
drs.database_id AS [Database ID],
drs.group_id,
drs.replica_id,
drs.synchronization_state_desc AS [Sync state],
drs.end_of_log_lsn AS [End of log LSN],
drs.last_hardened_lsn AS [Last hardened LSN]
FROM
sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states drs
inner join sys.databases db on db.database_id = drs.database_id
inner join sys.availability_groups ag on drs.group_id = ag.group_id
WHERE
ag.is_distributed = 1 and db.name = '<DatabaseName>'
Use the following T-SQL query on SQL Managed Instance to read the last hardened LSN for your database. Replace <DatabaseName> with your database name.
This query works on a General Purpose SQL Managed Instance. For a Business Critical SQL Managed Instance, uncomment and drs.is_primary_replica = 1 at the end of the script. On the Business Critical service tier, this filter ensures that details are only read from the primary replica.
-- Run on SQL managed instance
-- Obtain the LSN for the database on SQL Managed Instance.
SELECT
db.name AS [Database name],
drs.database_id AS [Database ID],
drs.group_id,
drs.replica_id,
drs.synchronization_state_desc AS [Sync state],
drs.end_of_log_lsn AS [End of log LSN],
drs.last_hardened_lsn AS [Last hardened LSN]
FROM
sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states drs
inner join sys.databases db on db.database_id = drs.database_id
WHERE
db.name = '<DatabaseName>'
-- for Business Critical, add the following as well
-- AND drs.is_primary_replica = 1
Alternatively, you could also use the Get-AzSqlInstanceLink PowerShell or az sql mi link show Azure CLI command to fetch the LastHardenedLsn property for your link on SQL Managed Instance to provide the same information as the previous T-SQL query.
Important
Verify once again that your workload is stopped on the primary. Check that LSNs on both SQL Server and SQL Managed Instance match, and that they remain matched and unchanged for some time. Stable LSNs on both instances indicate the tail log has been replicated to the secondary and the workload is effectively stopped.
Fail over a database
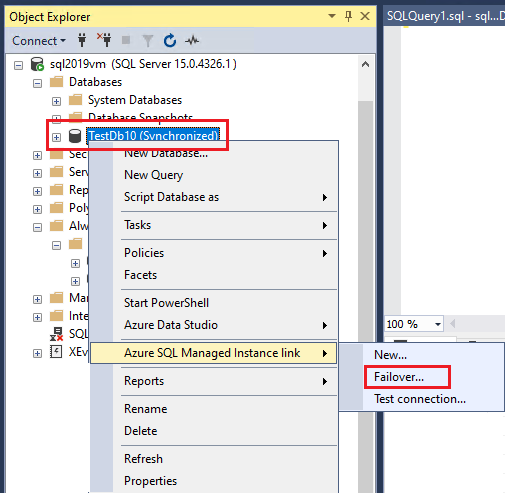
If you want to use PowerShell to fail over a database between SQL Server 2022 and SQL Managed Instance while still maintaining the link, or to perform a failover with data loss for any version of SQL Server, use the Failover between SQL Server and Managed Instance wizard in SSMS to generate the script for your environment. You can perform a planned failover from either the primary or the secondary replica. To do a forced failover, connect to the secondary replica.
To break the link and stop replication when you fail over or migrate your database regardless of SQL Server version, use the Remove-AzSqlInstanceLink PowerShell or az sql mi link delete Azure CLI command.
Caution
- Before failing over, stop the workload on the source database to allow the replicated database to completely catch up and failover without data loss. If you perform a forced failover, or if you break the link before LSNs match, you might lose data.
- Failing over a database in SQL Server 2019 and earlier versions breaks and removes the link between the two replicas. You can't fail back to the initial primary.
The following sample script breaks the link and ends replication between your replicas, making the database read/write on both instances. Replace:
<ManagedInstanceName> with the name of your managed instance.<DAGName> with the name of the link you're failing over (output of the property Name from Get-AzSqlInstanceLink command executed earlier above).
# Run in Azure Cloud Shell (select PowerShell console)
# =============================================================================
# POWERSHELL SCRIPT TO FAIL OVER OR MIGRATE DATABASE TO AZURE
# ===== Enter user variables here ====
# Enter your managed instance name – for example, "sqlmi1"
$ManagedInstanceName = "<ManagedInstanceName>"
$LinkName = "<DAGName>"
# ==== Do not customize the following cmdlet ====
# Find out the resource group name
$ResourceGroup = (Get-AzSqlInstance -InstanceName $ManagedInstanceName).ResourceGroupName
# Failover the specified link
Remove-AzSqlInstanceLink -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroup |
-InstanceName $ManagedInstanceName -Name $LinkName -Force
When failover succeeds, the link is dropped and no longer exists. The SQL Server database and SQL Managed Instance database can both execute read/write workloads as they're now completely independent.
Important
After successful fail over to SQL Managed Instance, manually repoint your application(s) connection string to the SQL managed instance FQDN to complete the migration or fail over process and continue running in Azure.
After the link is dropped, you can keep the availability group on SQL Server, but you must drop the distributed availability group to remove link metadata from SQL Server. This additional step is only necessary when failing over by using PowerShell since SSMS performs this action for you.
To drop your distributed availability group, replace the following value and then run the sample T-SQL code:
<DAGName> with the name of the distributed availability group on SQL Server (used to create the link).
-- Run on SQL Server
USE MASTER
GO
DROP AVAILABILITY GROUP <DAGName>
GO
Azure SQL Managed Instance