Understand Azure NetApp Files application volume groups
In managing data and optimizing storage solutions, understanding how an application volume group functions is crucial.
An application volume group is a framework designed to streamline the deployment of application volumes. It acts as a cohesive entity, bringing together related volumes to enhance efficiency, manageability, ease of administration, and volume placement relative to compute resources.
Application volume group provides technical improvements to simplify and standardize the volume deployment process for your application, ensuring optimal placement in the regional or zonal infrastructure and in accordance with best practices for the selected application or workload.
Application volume group deploys volumes in a single atomic operation using a predefined naming convention that allows you to easily identify the specific purpose of the volumes in the application volume group.
Key components
Learning about the key components of application volume groups is essential to understanding application volume groups.
Volumes
The fundamental building blocks within an application volume group are individual volumes. These volumes store application data and are organized based on specific characteristics and usage patterns.
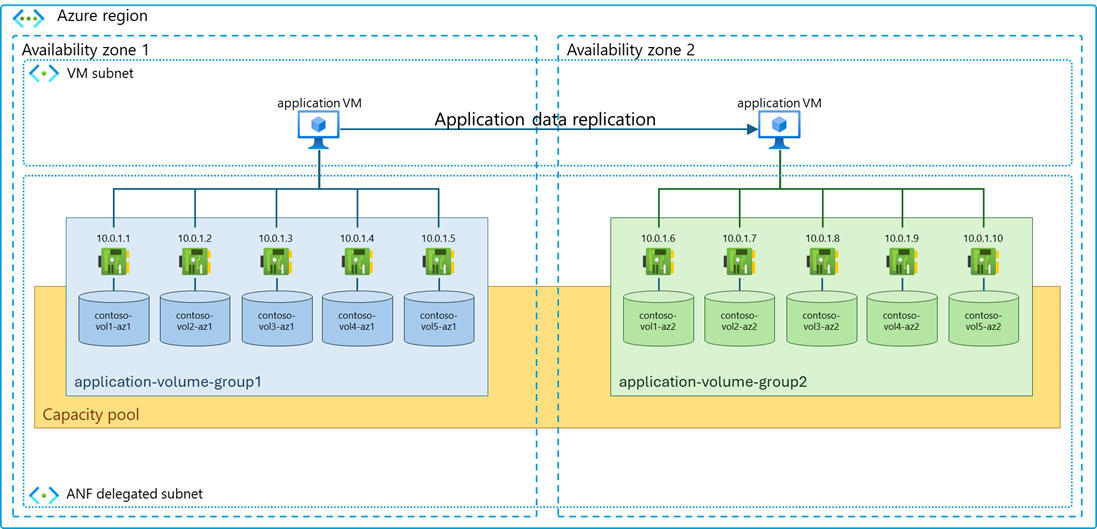
The following diagram captures an example layout of volumes deployed by an application volume group, which includes application volume groups provisioned in a secondary availability zone.
Volumes are assigned names by application volume group according to a template and based on user input describing the purpose and deployment type.
Grouping logic
Application volume group employs a logical grouping algorithm, allowing administrators to categorize and deploy volumes based on shared attributes such as application type and application specific identifiers. The algorithm is designed to take into consideration which volumes can and can't share storage endpoints. This logic ensures that application load is spread over available resources for optimal results.
Volume placement
Volumes are placed following best practices and in optimal infrastructure locations ensuring the best application performance from small to large scale deployments. Infrastructure locations are determined based on the selected availability zone and available network and storage capacity; volumes that require the highest throughput and lowest latency (such as database log volumes) are spread across available storage endpoints to mitigate network contention.
Policies
Application volume group operates under predefined policies that govern the placement of the grouped volumes. These policies can include performance optimization, data protection mechanisms, and scalability rules, which can't be followed using individual volume deployment.
Performance optimization
Within the application volume group, volumes are placed on underlying storage resources to optimize performance for the application. By considering factors such as workload characteristics, data access patterns, and performance SLA requirements, administrators can ensure that volumes are provisioned on storage resources with the appropriate performance capabilities to meet the demands of high-performance applications.
Availability and redundancy
Volume placement within the application volume group enables administrators to enhance availability and redundancy for critical application data. By distributing volumes across multiple storage resources, administrators can mitigate the risk of data loss or downtime due to hardware failures, network disruptions, or other infrastructure issues. Redundant configurations, such as replicating data across availability zones or geographically dispersed regions, further enhance data resilience and ensure business continuity.
Data locality and latency optimization
Volume placement within the application volume group allows you to optimize data locality and minimize latency for applications with stringent performance requirements. By deploying volumes closer to compute resources, administrators can reduce data access latency and improve application responsiveness particularly for latency-sensitive workloads such as database applications.
Cost optimization
Volume placement strategies within the application volume group enable you to optimize storage costs by matching workload requirements with appropriate storage tiers. You can leverage tiered storage offerings within Azure NetApp Files, such as Standard and Premium tiers, to balance performance and cost-effectiveness for different application workloads. By placing volumes on the most cost-effective storage tier that meets performance requirements, you can maximize resource utilization and minimize operational expenses. Volumes can be moved to different performance tiers at any moment and without service interruptions to align performance and cost with changing requirements.
Flexibility
After deployment, volume sizes and throughput settings can be adjusted like any other volume at any time without service interruption. This is a key attribute of Azure NetApp Files.
Compliance and data residency
Volume placement within the application volume group enables organizations to address compliance and data residency requirements by specifying the geographical location or Azure region where data should be stored. You can ensure that volumes are provisioned in compliance with regulatory mandates or organizational policies governing data sovereignty, privacy, and residency, thereby mitigating compliance risks and ensuring data governance.
Customer managed key support
Azure NetApp Files application volume group for SAP HANA extension 1 and Oracle support volume deployments with customer-managed keys, offering increased security and compliance.
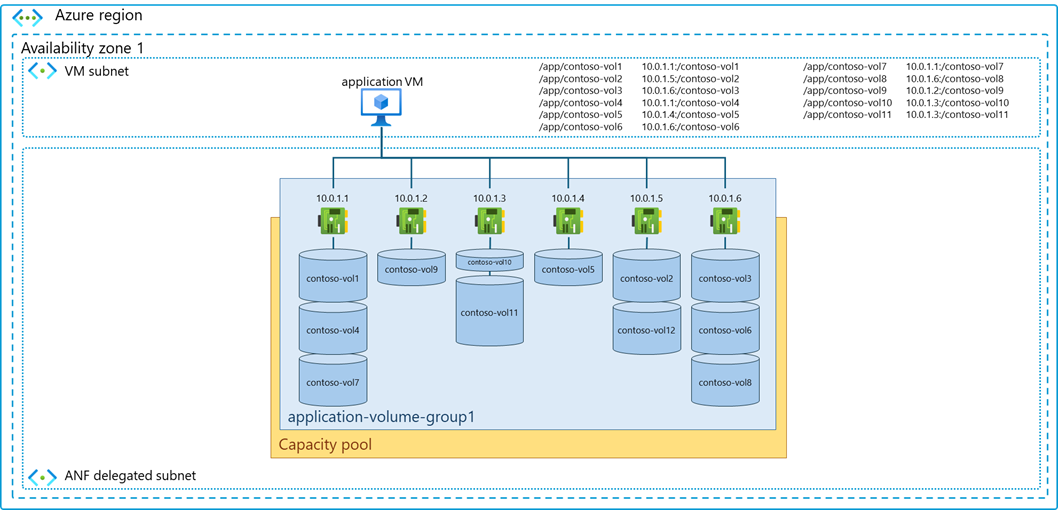
Constrained zone resource availability
Upon execution of volume deployment, application volume group detects available resources and applies logic to place volumes in the most optimal locations. In resource-constrained zones, volumes can share storage endpoints:
Summary
Application volume group in Azure NetApp Files empowers you to optimize deployment procedures, application performance, availability, cost, and compliance for application workloads. Strategically allocating storage resources and leveraging advanced placement strategies enables you to enhance the agility, resilience, and efficiency of your storage infrastructure to meet evolving business needs.
Best practices
Adhering to best practices improves the efficacy of your application volume group deployment.
Prepare for the deployment
Obtain application specific information before deploying the volumes by studying the performance capabilities of Azure NetApp Files volumes and by observing application volume sizes and performance data in the current (on-premises) implementation.
Monitor regularly and optimize
Implement a proactive monitoring strategy to assess the performance of volumes within an application volume group. Regularly optimize resource allocations and policies based on changing application requirements.
Document and communicate
Maintain comprehensive documentation outlining application volume group configurations, policies, and any changes made over time. Effective communication regarding application volume group structures is vital for collaborative management.
Benefits
Volumes deployed by application volume group are placed in the regional or zonal infrastructure to achieve optimized latency and throughput for the application VMs.
Resulting volumes provide the same flexibility for resizing capacity and throughput as individually created volumes. These volumes also support Azure NetApp Files data protection solutions including snapshots and cross-region/cross-zone replication.
Availability
Application volume group is currently available for SAP HANA and Oracle databases.
Conclusion
Application volume group is a pivotal concept in modern data management, providing a structured approach to handling volumes within application environments. By leveraging application volume group, you can enhance performance, streamline administration, and ensure the resilience of your applications in dynamic and evolving scenarios.