Supported KQL features in Azure Monitor transformations
Transformations in Azure Monitor allow you to run a KQL query against incoming Azure Monitor data to filter or modify incoming data before it's stored in a Log Analytics workspace. This article details KQL considerations and supported features in transformation queries in addition to special operators that are only available in transformations.
Since transformations are applied to each record individually, they can't use any KQL operators that act on multiple records. Only operators that take a single row as input and return no more than one row are supported. For example, summarize isn't supported since it summarizes multiple records.
Only the operators listed in this article are supported in transformations. Any other operators that may be used in other log queries are not supported in transformations.
Special considerations
Parse command
The parse command in a transformation is limited to 10 columns per statement for performance reasons. If your transformation requires parsing more than 10 columns, split it into multiple statements as described in Break up large parse commands.
Handling dynamic data
Consider the following input with dynamic data:
{
"TimeGenerated" : "2021-11-07T09:13:06.570354Z",
"Message": "Houston, we have a problem",
"AdditionalContext": {
"Level": 2,
"DeviceID": "apollo13"
}
}
To access the properties in AdditionalContext, define it as dynamic-type column in the input stream:
"columns": [
{
"name": "TimeGenerated",
"type": "datetime"
},
{
"name": "Message",
"type": "string"
},
{
"name": "AdditionalContext",
"type": "dynamic"
}
]
The content of the AdditionalContext column can now be parsed and used in the KQL transformation:
source
| extend parsedAdditionalContext = parse_json(AdditionalContext)
| extend Level = toint (parsedAdditionalContext.Level)
| extend DeviceId = tostring(parsedAdditionalContext.DeviceID)
Dynamic literals
Use the parse_json function to handle dynamic literals.
For example, the following queries provide the same functionality:
print d=dynamic({"a":123, "b":"hello", "c":[1,2,3], "d":{}})
print d=parse_json('{"a":123, "b":"hello", "c":[1,2,3], "d":{}}')
Special functions
The following functions are only available in transformations. They cannot be used in other log queries.
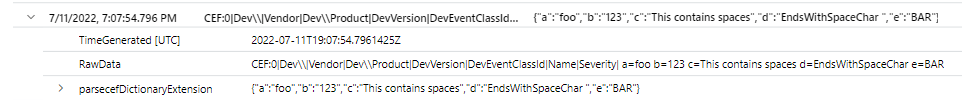
parse_cef_dictionary
Given a string containing a CEF message, parse_cef_dictionary parses the Extension property of the message into a dynamic key/value object. Semicolon is a reserved character that should be replaced prior to passing the raw message into the method, as shown in the example.
| extend cefMessage=iff(cefMessage contains_cs ";", replace(";", " ", cefMessage), cefMessage)
| extend parsedCefDictionaryMessage =parse_cef_dictionary(cefMessage)
| extend parsecefDictionaryExtension = parsedCefDictionaryMessage["Extension"]
| project TimeGenerated, cefMessage, parsecefDictionaryExtension
geo_location
Given a string containing IP address (IPv4 and IPv6 are supported), geo_location function returns approximate geographical location, including the following attributes:
- Country
- Region
- State
- City
- Latitude
- Longitude
| extend GeoLocation = geo_location("1.0.0.5")
Important
Due to nature of IP geolocation service utilized by this function, it may introduce data ingestion latency if used excessively. Exercise caution when using this function more than several times per transformation.
Supported statements
Let statement
The right-hand side of let can be a scalar expression, a tabular expression, or a user-defined function. Only user-defined functions with scalar arguments are supported.
Tabular expression statements
The only supported data sources for the KQL statement in a transformation are as follows:
source, which represents the source data. For example:
source | where ActivityId == "383112e4-a7a8-4b94-a701-4266dfc18e41" | project PreciseTimeStamp, Messageprintoperator, which always produces a single row. For example:print x = 2 + 2, y = 5 | extend z = exp2(x) + exp2(y)
Supported tabular operators
extendprojectprintwhereparseproject-awayproject-renamedatatablecolumnifexists(use columnifexists instead of column_ifexists)
Supported scalar operators
- All Numerical operators are supported.
- All Datetime and Timespan arithmetic operators are supported.
- The following String operators are supported.
- `=
!==~!~contains!containscontains_cs!contains_cshas!hashas_cs!has_csstartswith!startswithstartswith_cs!startswith_csendswith!endswithendswith_cs!endswith_csmatches regexin!in
- The following Bitwise operators are supported.
binary_and()binary_or()binary_xor()binary_not()binary_shift_left()binary_shift_right()
Scalar functions
- Bitwise functions
- Conversion functions
- DateTime and TimeSpan functions
- Dynamic and array functions
- Mathematical functions
- Conditional functions
- String functions
base64_encodestring(use base64_encodestring instead of base64_encode_tostring)base64_decodestring(use base64_decodestring instead of base64_decode_tostring)countofextractextract_allindexofisemptyisnotemptyparse_jsonsplitstrcatstrcat_delimstrlensubstringtolowertoupperhash_sha256
- Type functions
Identifier quoting
Use Identifier quoting as required.
Next steps
- Create a data collection rule and an association to it from a virtual machine using the Azure Monitor agent.