Natural language processing technology
Natural language processing has many applications, such as sentiment analysis, topic detection, language detection, key phrase extraction, and document categorization.
Specifically, you can use natural language processing to:
- Classify documents. For example, you can label them as sensitive or spam.
- Conduct subsequent processing or searches by using natural language processing outputs.
- Summarize text by identifying entities in the document.
- Tag documents with keywords by using identified entities.
- Conduct content-based search and retrieval by using tags.
- Summarize a document's key topics by using identified entities.
- Categorize documents for navigation by using detected topics.
- Enumerate related documents based on a selected topic.
- Assess text sentiment to understand its positive or negative tone.
As technology advances, you can use natural language processing to categorize and analyze text data. You can also use it to enhance interpretable AI functions across diverse domains. The integration of language models significantly enhances the capabilities of natural language processing. Language models like GPT and BERT can generate humanlike, contextually aware text. This capability makes them highly effective for complex language processing tasks. They complement existing natural language processing techniques by handling broader cognitive tasks, which improve conversation systems and customer engagement, especially with models like Databricks' Dolly 2.0.
Relationship and differences between language models and natural language processing
Natural language processing is a comprehensive field that encompasses various techniques for processing human language. In contrast, language models are a specific subset of natural language processing. They focus on deep learning to perform high-level language tasks. Language models enhance natural language processing by providing advanced text generation and understanding capabilities, but they aren't synonymous with natural language processing. Instead, they serve as powerful tools within the broader natural language processing domain by enabling more sophisticated language processing.
Note
This article focuses on natural language processing. The relationship between natural language processing and language models demonstrates that language models enhance natural language processing processes through superior language understanding and generation capabilities.
Potential use cases
Business scenarios that can benefit from custom natural language processing include:
Document intelligence for handwritten or machine-created documents in finance, healthcare, retail, government, and other sectors.
Industry-agnostic natural language processing tasks for text processing, such as named-entity recognition (NER), classification, summarization, and relation extraction.
These tasks help you automatically retrieve, identify, and analyze document information like text and unstructured data. Examples of these tasks include risk stratification models, ontology classification, and retail summarizations.
Information retrieval and knowledge graph creation for semantic search. This functionality makes it possible to create medical knowledge graphs that support drug discovery and clinical trials.
Text translation for conversational AI systems in customer-facing applications across retail, finance, travel, and other industries.
Sentiment and enhanced emotional intelligence in analytics, particularly for monitoring brand perception and customer feedback analytics.
Automated report generation. Synthesize and generate comprehensive textual reports from structured data inputs. These tasks help sectors such as finance and compliance where thorough documentation is necessary.
Voice-activated interfaces that integrate natural language processing for voice recognition and natural conversation capabilities. This integration enhances user interactions in Internet of Things applications and smart device applications.
Adaptive language models that can dynamically adjust language output to suit various audience comprehension levels. This capability is crucial for educational content and accessibility improvements.
Cybersecurity text analysis to analyze communication patterns and language usage in real time. This analysis helps you identify potential security threats in digital communication and improve the detection of phishing attempts or misinformation.
Apache Spark as a customized natural language processing framework
Apache Spark is a powerful parallel processing framework that enhances the performance of big-data analytic applications by using in-memory processing. Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure HDInsight, and Azure Databricks provide robust access to Spark's processing capabilities. This access helps you run large-scale data operations seamlessly.
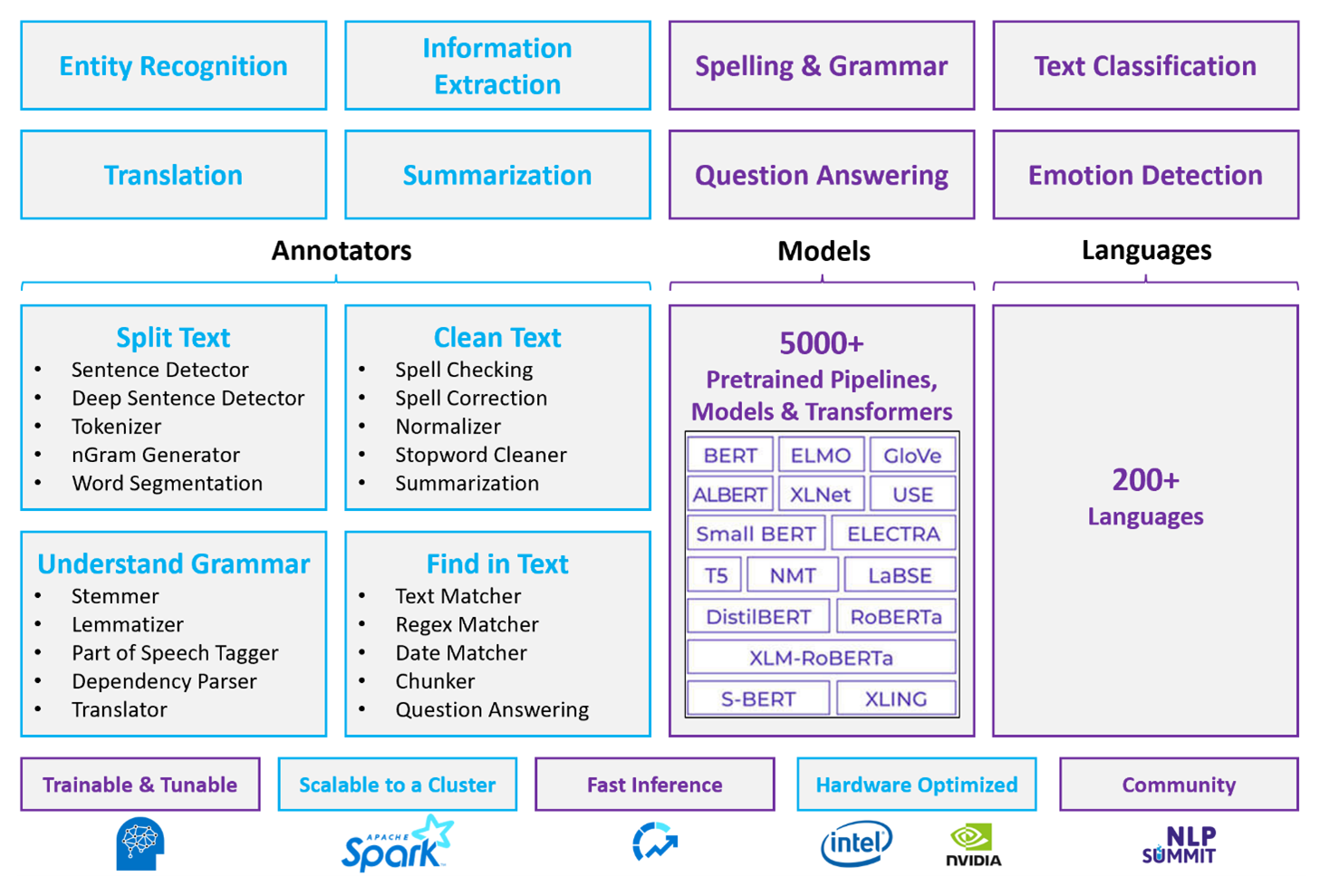
Spark NLP is an efficient framework that can process large volumes of text for customized natural language processing workloads. This open-source library provides extensive functionality by using Python, Java, and Scala libraries. These libraries deliver the sophistication that you can find in prominent natural language processing libraries like spaCy and Natural Language Toolkit. Spark NLP includes advanced features like spell check, sentiment analysis, and document classification. These features help you consistently ensure optimal accuracy and scalability.
Apache®, Apache Spark, and the flame logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation in the United States and/or other countries. No endorsement by The Apache Software Foundation is implied by the use of these marks.
Recent public benchmarks highlight Spark NLP's performance. These benchmarks show significant speed improvements over other libraries. Spark NLP also maintains comparable accuracy for training custom models. Notably, the integration of the Llama 2 models and OpenAI Whisper enhances conversational interfaces and multilingual speech recognition. These capabilities mark significant strides in optimized processing capabilities.
Spark NLP effectively utilizes a distributed Spark cluster that functions as a native extension of Spark ML and operates directly on data frames. This integration supports enhanced performance gains on clusters, which facilitates the creation of unified natural language processing and machine learning pipelines for tasks like document classification and risk prediction. MPNet embeddings and extensive ONNX support further enrich these capabilities and allow for precise and context-aware processing.
Spark NLP delivers highly accurate results across an expanding array of natural language processing tasks. The library comes with prebuilt deep learning models for named entity recognition, document classification, and sentiment detection. Its feature-rich design includes pretrained language models that support word, chunk, sentence, and document embeddings.
Spark NLP's infrastructure scales by using optimized builds for CPUs, GPUs, and the latest Intel Xeon chips, which enable training and inference processes to fully utilize Spark clusters. This capability helps ensure efficient handling of natural language processing tasks across diverse environments and applications.
Challenges
Resource processing: Processing a collection of free-form text documents requires a significant amount of computational resources. The processing is also time intensive. This kind of processing often involves GPU compute deployment. Recent advancements that support quantization, such as optimizations in Spark NLP architectures like Llama 2, help streamline these intensive tasks by allocating resources more efficiently.
Standardization: Without a standardized document format, it can be difficult to achieve consistently accurate results when you use free-form text processing to extract specific facts from a document. For example, extracting the invoice number and date from various invoices poses challenges. The integration of adaptable natural language processing models like M2M100 improves processing accuracy across multiple languages and formats. This improved accuracy leads to more consistent results.
Data variety and complexity: Addressing the variety of document structures and linguistic nuances remains complex. Innovations such as MPNet embeddings provide enhanced contextual understanding, which leads to more intuitive handling of diverse textual formats and more reliable data processing.
Key selection criteria
In Azure, Spark services like Azure Databricks, Microsoft Fabric, and HDInsight provide natural language processing functionality when you use them with Spark NLP. Azure AI services is another option for natural language processing functionality. To help you decide which service to use, consider the following aspects:
If you want to use prebuilt or pretrained models, consider using the APIs that AI services provides. Or you can download your model of choice through Spark NLP, which includes advanced models like Llama 2 and MPNet for enhanced capabilities.
If you need to train custom models against a large collection of text data, consider using Azure Databricks, Fabric, or HDInsight with Spark NLP. These platforms provide the computational power and flexibility that you need for extensive model training.
If you need low-level natural language processing capabilities like tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and term frequency/inverse document frequency (TF/IDF), consider using Azure Databricks, Fabric, or HDInsight with Spark NLP. Alternatively, use an open-source software library in your processing tool of choice.
If you need simple, high-level natural language processing capabilities like entity and intent identification, topic detection, spell check, or sentiment analysis, consider using the APIs that AI services provides. Or download your model of choice through Spark NLP to use prebuilt functions for these tasks.
Capability matrix
The following tables summarize the key differences in the capabilities of natural language processing services.
General capabilities
| Capability | Spark service (Azure Databricks, Fabric, HDInsight) with Spark NLP | AI services |
|---|---|---|
| Provides pretrained models as a service | Yes | Yes |
| REST API | Yes | Yes |
| Programmability | Python, Scala | See supported programming languages |
| Supports processing of large datasets and large documents | Yes | No |
Annotator capabilities
| Capability | Spark service (Azure Databricks, Fabric, HDInsight) with Spark NLP | AI services |
|---|---|---|
| Sentence detector | Yes | No |
| Deep sentence detector | Yes | Yes |
| Tokenizer | Yes | Yes |
| N-gram generator | Yes | No |
| Word segmentation | Yes | Yes |
| Stemmer | Yes | No |
| Lemmatizer | Yes | No |
| Part-of-speech tagging | Yes | No |
| Dependency parser | Yes | No |
| Translation | Yes | No |
| Stopword cleaner | Yes | No |
| Spell correction | Yes | No |
| Normalizer | Yes | Yes |
| Text matcher | Yes | No |
| TF/IDF | Yes | No |
| Regular expression matcher | Yes | Embedded in the conversational language understanding (CLU) feature |
| Date matcher | Yes | Possible in CLU through DateTime recognizers |
| Chunker | Yes | No |
Note
Language Understanding (LUIS) will be retired on October 1, 2025. You should migrate existing LUIS applications to the conversational language understanding (CLU) feature of Azure AI Language, which enhances language understanding capabilities and provides new features.
High-level natural language processing capabilities
| Capability | Spark service (Azure Databricks, Fabric, HDInsight) with Spark NLP | AI services |
|---|---|---|
| Spell check | Yes | No |
| Summarization | Yes | Yes |
| Question answering | Yes | Yes |
| Sentiment detection | Yes | Yes |
| Emotion detection | Yes | Supports opinion mining |
| Token classification | Yes | Yes, through custom models |
| Text classification | Yes | Yes, through custom models |
| Text representation | Yes | No |
| NER | Yes | Yes, text analytics provide a set of NER |
| Entity recognition | Yes | Yes, through custom models |
| Language detection | Yes | Yes |
| Supports languages besides English | Yes, supports over 200 languages | Yes, supports over 97 languages |
Set up Spark NLP in Azure
To install Spark NLP, use the following code, but replace <version> with the latest version number. For more information, see Spark NLP documentation.
# Install Spark NLP from PyPI.
pip install spark-natural language processing==<version>
# Install Spark NLP from Anaconda or Conda.
conda install -c johnsnowlabs spark-natural language processing
# Load Spark NLP with Spark Shell.
spark-shell --packages com.johnsnowlabs.natural language processing:spark-natural language processing_<version>
# Load Spark NLP with PySpark.
pyspark --packages com.johnsnowlabs.natural language processing:spark-natural language processing_<version>
# Load Spark NLP with Spark Submit.
spark-submit --packages com.johnsnowlabs.natural language processing:spark-natural language processing_<version>
# Load Spark NLP as an external JAR after compiling and building Spark NLP by using SBT assembly.
spark-shell --jars spark-natural language processing-assembly-3 <version>.jar
Develop natural language processing pipelines
Spark NLP follows the same development concept as traditional Spark ML machine learning models when it runs a natural language processing pipeline. It also applies specialized natural language processing techniques.
A Spark NLP pipeline includes the following core components:
DocumentAssembler is a transformer that prepares data by converting it into a format that Spark NLP can process. This stage is the entry point for every Spark NLP pipeline. DocumentAssembler reads either a
Stringcolumn or anArray[String]and can preprocess the text by usingsetCleanupMode, which is off by default.SentenceDetector is an annotator that identifies sentence boundaries by using predefined approaches. It can return each detected sentence in an
Arrayor in separate rows whenexplodeSentencesis set to true.Tokenizer is an annotator that divides raw text into discrete tokens, like words, numbers, and symbols, and outputs them as a
TokenizedSentence. Tokenizer is nonfitted and uses input configuration within theRuleFactoryto create tokenizing rules. You can add custom rules if the default ones are insufficient.Normalizer is an annotator tasked with refining tokens. Normalizer applies regular expressions and dictionary transformations to clean text and remove extraneous characters.
WordEmbeddings are lookup annotators that map tokens to vectors and facilitate semantic processing. You can specify a custom embedding dictionary by using
setStoragePath, where each line contains a token and its vector, separated by spaces. Unresolved tokens default to zero vectors.
Spark NLP uses Spark MLlib pipelines that have native support from MLflow, an open-source platform that manages the machine learning lifecycle. MLflow has the following key components:
MLflow Tracking records experimental runs and provides robust querying capabilities to analyze outcomes.
MLflow Projects lets you run data science code on diverse platforms. This capability enhances portability and reproducibility.
MLflow Models supports versatile model deployment across different environments through a consistent framework.
Model Registry provides comprehensive model management by storing versions centrally for streamlined access and deployment. This step facilitates production-readiness.
MLflow is integrated with platforms like Azure Databricks, but you can also install it in other Spark-based environments to manage and track your experiments. This integration allows you to use the MLflow Model Registry to make models available for production purposes. You can streamline the deployment process and maintain model governance.
By using MLflow alongside Spark NLP, you can ensure more efficient management and deployment of natural language processing pipelines. You can also address modern requirements for scalability and integration while supporting advanced techniques like word embeddings and language model adaptations.
Contributors
Microsoft maintains this article. The following contributors wrote this article.
Principal authors:
- Freddy Ayala | Cloud Solution Architect
- Moritz Steller | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
To see nonpublic LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
Spark NLP documentation:
Azure components:
Learn resources: