Predicates and PredicateValidations
Note
In Azure Active Directory B2C, custom policies are designed primarily to address complex scenarios. For most scenarios, we recommend that you use built-in user flows. If you've not done so, learn about custom policy starter pack in Get started with custom policies in Active Directory B2C.
The Predicates and PredicateValidations elements enable you to perform a validation process to ensure that only properly formed data is entered into your Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C) tenant.
The following diagram shows the relationship between the elements:
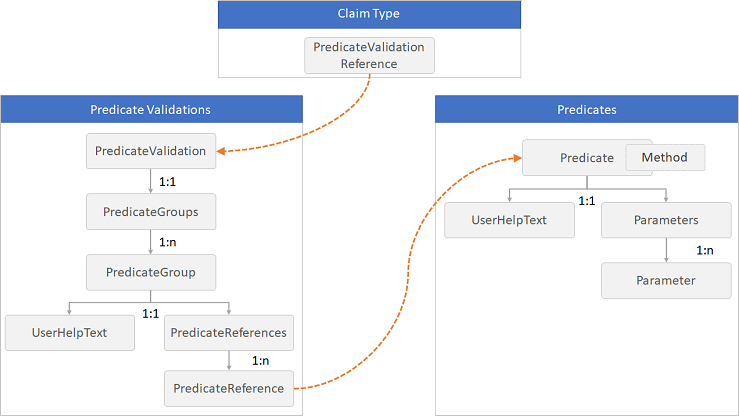
Predicates
The Predicate element defines a basic validation to check the value of a claim type and returns true or false. The validation is done by using a specified Method element and a set of Parameter elements relevant to the method. For example, a predicate can check whether the length of a string claim value is within the range of minimum and maximum parameters specified, or whether a string claim value contains a character set. The UserHelpText element provides an error message for users if the check fails. The value of UserHelpText element can be localized using language customization.
The Predicates element must appear directly following the ClaimsSchema element within the BuildingBlocks element.
The Predicates element contains the following element:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Predicate | 1:n | A list of predicates. |
The Predicate element contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Yes | An identifier that's used for the predicate. Other elements can use this identifier in the policy. |
| Method | Yes | The method type to use for validation. Possible values: IsLengthRange, MatchesRegex, IncludesCharacters, or IsDateRange. |
| HelpText | No | An error message for users if the check fails. This string can be localized using the language customization |
The Predicate element contains the following elements:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UserHelpText | 0:1 | (Deprecated) An error message for users if the check fails. |
| Parameters | 1:1 | The parameters for the method type of the string validation. |
The Parameters element contains the following elements:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | 1:n | The parameters for the method type of the string validation. |
The Parameter element contains the following attributes:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | 1:1 | The identifier of the parameter. |
Predicate methods
IsLengthRange
The IsLengthRange method checks whether the length of a string claim value is within the range of minimum and maximum parameters specified. Check out the Live demo of this predicate method. The predicate element supports the following parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Yes | The maximum number of characters that can be entered. |
| Minimum | Yes | The minimum number of characters that must be entered. |
The following example shows an IsLengthRange method with the parameters Minimum and Maximum that specify the length range of the string:
<Predicate Id="IsLengthBetween8And64" Method="IsLengthRange" HelpText="The password must be between 8 and 64 characters.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="Minimum">8</Parameter>
<Parameter Id="Maximum">64</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
MatchesRegex
The MatchesRegex method checks whether a string claim value matches a regular expression. Check out the Live demo of this predicate method. The predicate element supports the following parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RegularExpression | Yes | The regular expression pattern to match. |
The following example shows a MatchesRegex method with the parameter RegularExpression that specifies a regular expression:
<Predicate Id="PIN" Method="MatchesRegex" HelpText="The password must be numbers only.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="RegularExpression">^[0-9]+$</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
IncludesCharacters
The IncludesCharacters method checks whether a string claim value contains a character set. Check out the Live demo of this predicate method. The predicate element supports the following parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CharacterSet | Yes | The set of characters that can be entered. For example, lowercase characters a-z, uppercase characters A-Z, digits 0-9, or a list of symbols, such as @#$%^&*\-_+=[]{}|\\:',?/~"();!. |
The following example shows a IncludesCharacters method with the parameter CharacterSet that specifies the set of characters:
<Predicate Id="Lowercase" Method="IncludesCharacters" HelpText="a lowercase letter">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="CharacterSet">a-z</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
IsDateRange
The IsDateRange method checks whether a date claim value is between a range of minimum and maximum parameters specified. Check out the Live demo of this predicate method. The predicate element supports the following parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Yes | The largest possible date that can be entered. The format of the date follows yyyy-mm-dd convention, or Today. |
| Minimum | Yes | The smallest possible date that can be entered. The format of the date follows yyyy-mm-dd convention, or Today. |
The following example shows a IsDateRange method with the parameters Minimum and Maximum that specify the date range with a format of yyyy-mm-dd and Today.
<Predicate Id="DateRange" Method="IsDateRange" HelpText="The date must be between 1970-01-01 and today.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="Minimum">1970-01-01</Parameter>
<Parameter Id="Maximum">Today</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
PredicateValidations
While the predicates define the validation to check against a claim type, the PredicateValidations group a set of predicates to form a user input validation that can be applied to a claim type. Each PredicateValidation element contains a set of PredicateGroup elements that contain a set of PredicateReference elements that points to a Predicate. To pass the validation, the value of the claim should pass all of the tests of any predicate under all of the PredicateGroup with their set of PredicateReference elements.
The PredicateValidations element must appear directly following the Predicates element within the BuildingBlocks element.
<PredicateValidations>
<PredicateValidation Id="">
<PredicateGroups>
<PredicateGroup Id="">
<UserHelpText></UserHelpText>
<PredicateReferences MatchAtLeast="">
<PredicateReference Id="" />
...
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
...
</PredicateGroups>
</PredicateValidation>
...
</PredicateValidations>
The PredicateValidations element contains the following element:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PredicateValidation | 1:n | A list of predicate validation. |
The PredicateValidation element contains the following attribute:
| Attribute | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Yes | An identifier that's used for the predicate validation. The ClaimType element can use this identifier in the policy. |
The PredicateValidation element contains the following element:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PredicateGroups | 1:n | A list of predicate groups. |
The PredicateGroups element contains the following element:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PredicateGroup | 1:n | A list of predicates. |
The PredicateGroup element contains the following attribute:
| Attribute | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Yes | An identifier that's used for the predicate group. |
The PredicateGroup element contains the following elements:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UserHelpText | 0:1 | A description of the predicate that can be helpful for users to know what value they should type. |
| PredicateReferences | 1:n | A list of predicate references. |
The PredicateReferences element contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MatchAtLeast | No | Specifies that the value must match at least that many predicate definitions for the input to be accepted. If not specified, the value must match all predicate definitions. |
The PredicateReferences element contains the following elements:
| Element | Occurrences | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PredicateReference | 1:n | A reference to a predicate. |
The PredicateReference element contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Yes | An identifier that's used for the predicate validation. |
Configure password complexity
With Predicates and PredicateValidationsInput you can control the complexity requirements for passwords provided by a user when creating an account. By default, Azure AD B2C uses strong passwords. Azure AD B2C also supports configuration options to control the complexity of passwords that customers can use. You can define password complexity by using these predicate elements:
- IsLengthBetween8And64 using the
IsLengthRangemethod, validates that the password must be between 8 and 64 characters. - Lowercase using the
IncludesCharactersmethod, validates that the password contains a lowercase letter. - Uppercase using the
IncludesCharactersmethod, validates that the password contains an uppercase letter. - Number using the
IncludesCharactersmethod, validates that the password contains a digit. - Symbol using the
IncludesCharactersmethod, validates that the password contains one of several symbol characters. - PIN using the
MatchesRegexmethod, validates that the password contains numbers only. - AllowedAADCharacters using the
MatchesRegexmethod, validates that the password only invalid character was provided. - DisallowedWhitespace using the
MatchesRegexmethod, validates that the password doesn't begin or end with a whitespace character.
<Predicates>
<Predicate Id="IsLengthBetween8And64" Method="IsLengthRange" HelpText="The password must be between 8 and 64 characters.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="Minimum">8</Parameter>
<Parameter Id="Maximum">64</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="Lowercase" Method="IncludesCharacters" HelpText="a lowercase letter">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="CharacterSet">a-z</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="Uppercase" Method="IncludesCharacters" HelpText="an uppercase letter">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="CharacterSet">A-Z</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="Number" Method="IncludesCharacters" HelpText="a digit">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="CharacterSet">0-9</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="Symbol" Method="IncludesCharacters" HelpText="a symbol">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="CharacterSet">@#$%^&*\-_+=[]{}|\\:',.?/`~"();!</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="PIN" Method="MatchesRegex" HelpText="The password must be numbers only.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="RegularExpression">^[0-9]+$</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="AllowedAADCharacters" Method="MatchesRegex" HelpText="An invalid character was provided.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="RegularExpression">(^([0-9A-Za-z\d@#$%^&*\-_+=[\]{}|\\:',?/`~"();! ]|(\.(?!@)))+$)|(^$)</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
<Predicate Id="DisallowedWhitespace" Method="MatchesRegex" HelpText="The password must not begin or end with a whitespace character.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="RegularExpression">(^\S.*\S$)|(^\S+$)|(^$)</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
After you define the basic validations, you can combine them together and create a set of password policies that you can use in your policy:
- SimplePassword validates the DisallowedWhitespace, AllowedAADCharacters, and IsLengthBetween8And64
- StrongPassword validates the DisallowedWhitespace, AllowedAADCharacters, IsLengthBetween8And64. The last group
CharacterClassesruns an additional set of predicates withMatchAtLeastset to 3. The user password must be between 8 and 16 characters, and three of the following characters: Lowercase, Uppercase, Number, or Symbol. - CustomPassword validates only DisallowedWhitespace, AllowedAADCharacters. So, user can provide any password with any length, as long as the characters are valid.
<PredicateValidations>
<PredicateValidation Id="SimplePassword">
<PredicateGroups>
<PredicateGroup Id="DisallowedWhitespaceGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="DisallowedWhitespace" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
<PredicateGroup Id="AllowedAADCharactersGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="AllowedAADCharacters" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
<PredicateGroup Id="LengthGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="IsLengthBetween8And64" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
</PredicateGroups>
</PredicateValidation>
<PredicateValidation Id="StrongPassword">
<PredicateGroups>
<PredicateGroup Id="DisallowedWhitespaceGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="DisallowedWhitespace" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
<PredicateGroup Id="AllowedAADCharactersGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="AllowedAADCharacters" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
<PredicateGroup Id="LengthGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="IsLengthBetween8And64" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
<PredicateGroup Id="CharacterClasses">
<UserHelpText>The password must have at least 3 of the following:</UserHelpText>
<PredicateReferences MatchAtLeast="3">
<PredicateReference Id="Lowercase" />
<PredicateReference Id="Uppercase" />
<PredicateReference Id="Number" />
<PredicateReference Id="Symbol" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
</PredicateGroups>
</PredicateValidation>
<PredicateValidation Id="CustomPassword">
<PredicateGroups>
<PredicateGroup Id="DisallowedWhitespaceGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="DisallowedWhitespace" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
<PredicateGroup Id="AllowedAADCharactersGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="AllowedAADCharacters" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
</PredicateGroups>
</PredicateValidation>
</PredicateValidations>
In your claim type, add the PredicateValidationReference element and specify the identifier as one of the predicate validations, such as SimplePassword, StrongPassword, or CustomPassword.
<ClaimType Id="password">
<DisplayName>Password</DisplayName>
<DataType>string</DataType>
<AdminHelpText>Enter password</AdminHelpText>
<UserHelpText>Enter password</UserHelpText>
<UserInputType>Password</UserInputType>
<PredicateValidationReference Id="StrongPassword" />
</ClaimType>
The following shows how the elements are organized when Azure AD B2C displays the error message:
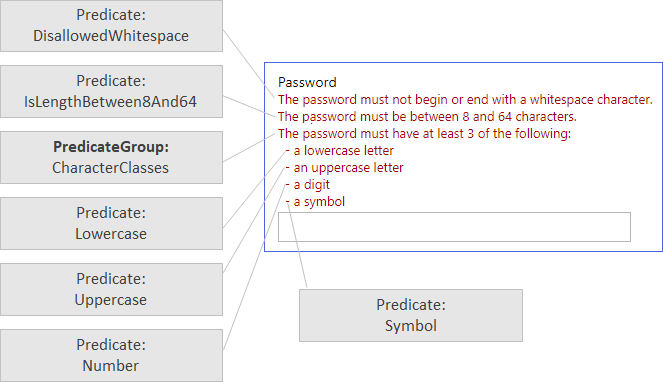
Configure a date range
With the Predicates and PredicateValidations elements you can control the minimum and maximum date values of the UserInputType by using a DateTimeDropdown. To do this, create a Predicate with the IsDateRange method and provide the minimum and maximum parameters.
<Predicates>
<Predicate Id="DateRange" Method="IsDateRange" HelpText="The date must be between 01-01-1980 and today.">
<Parameters>
<Parameter Id="Minimum">1980-01-01</Parameter>
<Parameter Id="Maximum">Today</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</Predicate>
</Predicates>
Add a PredicateValidation with a reference to the DateRange predicate.
<PredicateValidations>
<PredicateValidation Id="CustomDateRange">
<PredicateGroups>
<PredicateGroup Id="DateRangeGroup">
<PredicateReferences>
<PredicateReference Id="DateRange" />
</PredicateReferences>
</PredicateGroup>
</PredicateGroups>
</PredicateValidation>
</PredicateValidations>
In your claim type, add PredicateValidationReference element and specify the identifier as CustomDateRange.
<ClaimType Id="dateOfBirth">
<DisplayName>Date of Birth</DisplayName>
<DataType>date</DataType>
<AdminHelpText>The user's date of birth.</AdminHelpText>
<UserHelpText>Your date of birth.</UserHelpText>
<UserInputType>DateTimeDropdown</UserInputType>
<PredicateValidationReference Id="CustomDateRange" />
</ClaimType>
Next steps
- Learn how to Configure password complexity using custom policies in Azure Active Directory B2C using predicate validations.