Die Formatierungs-API in einer Power Apps-Komponente verwenden
Das Power Apps Component Framework zeigt eine Formatierungs-API an, die besonders nützlich sein kann, wenn Sie verschiedene Werte in Ihrer Anwendung formatieren müssen. Diese Lerneinheit zeigt, wie diese API verwendet wird. Dazu wird eine HTML-Tabelle erstellt, um zu veranschaulichen, wie verschiedene Methoden verwendet werden können.
Ihr Komponentenprojekt initialisieren
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor, um Ihr Komponentenprojekt zu initialisieren:
Starten Sie Visual Studio Code.
Wählen Sie Terminal und dann Neues Terminal aus.
Wechseln Sie das Verzeichnis zu Ihrem Quellordner.
cd sourceErstellen Sie aus Ihrem Quellverzeichnis ein Verzeichnis mit dem Namen Formatting-API.
md Formatting-APIFühren den folgenden Befehl aus, um zum neuen Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
cd Formatting-APIInitialisieren Sie das Projekt, indem Sie den folgenden Befehl ausführen.
pac pcf init --namespace SampleNamespace --name FormattingAPI --template fieldFühren Sie „npm install“ aus, um abhängige Bibliotheken in Ihr Projekt zu laden.
npm installÖffnen Sie das Projekt in Visual Studio Code, indem Sie den folgenden Befehl ausführen.
code -a .
Logik der Codekomponente implementieren
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor, um die Logik der Codekomponente zu implementieren:
Erweitern Sie den Ordner FormattingAPI, und öffnen Sie die Datei ControlManifest.Input.xml.
Ersetzen Sie das gesamte Manifest durch die folgende XML-Datei.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <manifest> <control namespace="SampleNamespace" constructor="FormattingAPI" version="1.1.0" display-name-key="TS_FormattingAPI_Display_Key" description-key="TS_FormattingAPI_Desc_Key" control-type="standard"> <property name="controlValue" display-name-key="controlValue_Display_Key" description-key="controlValue_Desc_Key" of-type="SingleLine.Text" usage="bound" required="true" /> <resources> <code path="index.ts" order="1" /> <css path="css/TS_FormattingAPI.css" order="2" /> </resources> </control> </manifest>Sie fügen die unterstützenden Dateien hinzu, die später in diesem Manifest enthalten sind.
Öffnen Sie die Datei Index.ts.
Fügen Sie über der Methode constructor die folgenden privaten Variablen ein.
// PCF framework delegate that will be assigned to this object that would be called whenever any update happens. private _notifyOutputChanged: () => void; // Reference to the div element that holds together all the HTML elements that you are creating as part of this control private divElement: HTMLDivElement; // Reference to HTMLTableElement rendered by control private _tableElement: HTMLTableElement; // Reference to the control container HTMLDivElement // This element contains all elements of your custom control example private _container: HTMLDivElement; // Reference to ComponentFramework Context object private _context: ComponentFramework.Context<IInputs>; // Flag if control view has been rendered private _controlViewRendered: Boolean;Fügen Sie in der Methode init die folgende Logik ein.
this._notifyOutputChanged = notifyOutputChanged; this._controlViewRendered = false; this._context = context; this._container = document.createElement("div"); this._container.classList.add("TSFormatting_Container"); container.appendChild(this._container);Fügen Sie der Methode updateView die folgende Methode hinzu:
if (!this._controlViewRendered) { // Render and add HTMLTable to the custom control container element let tableElement: HTMLTableElement = this.createHTMLTableElement(); this._container.appendChild(tableElement); this._controlViewRendered = true; }Fügen Sie die folgenden Hilfsmethoden hinzu, um Ihre HTML-Tabelle zu generieren, in der formatierte Werte nach der Methode destroy angezeigt werden.
/** * Helper method to create an HTML Table Row Element * @param key : string value to show in left column cell * @param value : string value to show in right column cell * @param isHeaderRow : true if method should generate a header row */ private createHTMLTableRowElement(key: string, value: string, isHeaderRow: boolean): HTMLTableRowElement { let keyCell: HTMLTableCellElement = this.createHTMLTableCellElement(key, "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell_Key", isHeaderRow); let valueCell: HTMLTableCellElement = this.createHTMLTableCellElement(value, "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell_Value", isHeaderRow); let rowElement: HTMLTableRowElement = document.createElement("tr"); rowElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlRow"); rowElement.appendChild(keyCell); rowElement.appendChild(valueCell); return rowElement; } /** * Helper method to create an HTML Table Cell Element * @param cellValue : string value to inject in the cell * @param className : class name for the cell * @param isHeaderRow : true if method should generate a header row cell */ private createHTMLTableCellElement(cellValue: string, className: string, isHeaderRow: boolean): HTMLTableCellElement { let cellElement: HTMLTableCellElement; if (isHeaderRow) { cellElement = document.createElement("th"); cellElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlHeaderCell " + className); let textElement: Text = document.createTextNode(cellValue); cellElement.appendChild(textElement); } else { cellElement = document.createElement("td"); cellElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell " + className); let textElement: Text = document.createTextNode(cellValue); cellElement.appendChild(textElement); } return cellElement; }Fügen Sie die folgende Methode hinzu, die beispielhafte Verwendungen der Formatierungs-API enthält, indem Sie sie als Tabellenzellen nach den Hilfsmethoden speichern.
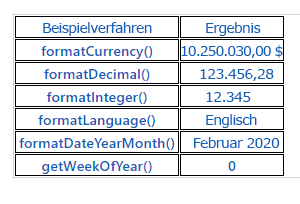
/** * Creates an HTML Table that showcases examples of basic methods available to the custom control * The left column of the table shows the method name or property that is being used * The right column of the table shows the result of that method name or property */ private createHTMLTableElement(): HTMLTableElement { // Create HTML Table Element let tableElement: HTMLTableElement = document.createElement("table"); tableElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlTable"); // Create header row for table let key: string = "Example Method"; let value: string = "Result"; tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, true)); // Example use of formatCurrency() method // Change the default currency and the precision or pass in the precision and currency as additional parameters. key = "formatCurrency()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatCurrency(10250030); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example use of formatDecimal() method // Change the settings from user settings to see the output change its format accordingly key = "formatDecimal()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatDecimal(123456.2782); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example use of formatInteger() method // change the settings from user settings to see the output change its format accordingly. key = "formatInteger()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatInteger(12345); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example use of formatLanguage() method // Install additional languages and pass in the corresponding language code to see its string value key = "formatLanguage()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatLanguage(1033); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example of formatDateYearMonth() method // Pass a JavaScript Data object set to the current time into formatDateYearMonth method to format the data // and get the return in Year, Month format key = "formatDateYearMonth()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatDateYearMonth(new Date()); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example of getWeekOfYear() method // Pass a JavaScript Data object set to the current time into getWeekOfYear method to get the value for week of the year key = "getWeekOfYear()"; value = this._context.formatting.getWeekOfYear(new Date()).toString(); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); return tableElement; }Wählen Sie Datei aus, und Alle speichern Sie alle Ihre Änderungen.
Nachdem Sie die Aktualisierungen vorgenommen haben, sollte Ihre abgeschlossene Klasse in etwa wie folgt aussehen.
import {IInputs, IOutputs} from "./generated/ManifestTypes"; export class FormattingAPI implements ComponentFramework.StandardControl<IInputs, IOutputs> { // PCF framework delegate that will be assigned to this object that would be called whenever any update happens. private _notifyOutputChanged: () => void; // Reference to the div element that holds together all the HTML elements that you are creating as part of this control private divElement: HTMLDivElement; // Reference to HTMLTableElement rendered by control private _tableElement: HTMLTableElement; // Reference to the control container HTMLDivElement // This element contains all elements of your custom control example private _container: HTMLDivElement; // Reference to ComponentFramework Context object private _context: ComponentFramework.Context<IInputs>; // Flag if control view has been rendered private _controlViewRendered: Boolean; /** * Used to initialize the control instance. Controls can kick off remote server calls and other initialization actions here. * Dataset values are not initialized here, use updateView. * @param context The entire property bag is available to control through the Context Object; It contains values as set up by the customizer and mapped to property names that are defined in the manifest and to utility functions. * @param notifyOutputChanged A callback method to alert the framework that the control has new outputs ready to be retrieved asynchronously. * @param state A piece of data that persists in one session for a single user. Can be set at any point in a control's life cycle by calling 'setControlState' in the Mode interface. * @param container If a control is marked control-type='starndard', it will receive an empty div element within which it can render its content. */ public init(context: ComponentFramework.Context<IInputs>, notifyOutputChanged: () => void, state: ComponentFramework.Dictionary, container:HTMLDivElement) { this._notifyOutputChanged = notifyOutputChanged; this._controlViewRendered = false; this._context = context; this._container = document.createElement("div"); this._container.classList.add("TSFormatting_Container"); container.appendChild(this._container); } /** * Called when any value in the property bag has changed. This includes field values, datasets, global values such as container height and width, offline status, control metadata values such as label, visible, and so on. * @param context The entire property bag that is available to control through the Context Object; It contains values as set up by the customizer that are mapped to names defined in the manifest and to utility functions */ public updateView(context: ComponentFramework.Context<IInputs>): void { if (!this._controlViewRendered) { // Render and add HTMLTable to the custom control container element let tableElement: HTMLTableElement = this.createHTMLTableElement(); this._container.appendChild(tableElement); this._controlViewRendered = true; } } /** * It is called by the framework prior to a control receiving new data. * @returns an object based on nomenclature that is defined in the manifest, expecting object[s] for property marked as "bound" or "output" */ public getOutputs(): IOutputs { return { }; } /** * Called when the control is to be removed from the DOM tree. Controls should use this call for cleanup, * such as canceling any pending remote calls, removing listeners, and so on. */ public destroy() { } /** * Helper method to create an HTML Table Row Element * @param key : string value to show in left column cell * @param value : string value to show in right column cell * @param isHeaderRow : true if method should generate a header row */ private createHTMLTableRowElement(key: string, value: string, isHeaderRow: boolean): HTMLTableRowElement { let keyCell: HTMLTableCellElement = this.createHTMLTableCellElement(key, "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell_Key", isHeaderRow); let valueCell: HTMLTableCellElement = this.createHTMLTableCellElement(value, "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell_Value", isHeaderRow); let rowElement: HTMLTableRowElement = document.createElement("tr"); rowElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlRow"); rowElement.appendChild(keyCell); rowElement.appendChild(valueCell); return rowElement; } /** * Helper method to create an HTML Table Cell Element * @param cellValue : string value to inject in the cell * @param className : class name for the cell * @param isHeaderRow : true if method should generate a header row cell */ private createHTMLTableCellElement(cellValue: string, className: string, isHeaderRow: boolean): HTMLTableCellElement { let cellElement: HTMLTableCellElement; if (isHeaderRow) { cellElement = document.createElement("th"); cellElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlHeaderCell " + className); let textElement: Text = document.createTextNode(cellValue); cellElement.appendChild(textElement); } else { cellElement = document.createElement("td"); cellElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell " + className); let textElement: Text = document.createTextNode(cellValue); cellElement.appendChild(textElement); } return cellElement; } /** * Creates an HTML Table that showcases examples of basic methods that are available to the custom control * The left column of the table shows the method name or property that is being used * The right column of the table shows the result of that method name or property */ private createHTMLTableElement(): HTMLTableElement { // Create HTML Table Element let tableElement: HTMLTableElement = document.createElement("table"); tableElement.setAttribute("class", "FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlTable"); // Create header row for table let key: string = "Example Method"; let value: string = "Result"; tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, true)); // Example use of formatCurrency() method // Change the default currency and the precision or pass in the precision and currency as additional parameters. key = "formatCurrency()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatCurrency(10250030); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example use of formatDecimal() method // Change the settings from user settings to see the output change its format accordingly key = "formatDecimal()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatDecimal(123456.2782); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example use of formatInteger() method // change the settings from user settings to see the output change its format accordingly. key = "formatInteger()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatInteger(12345); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example use of formatLanguage() method // Install additional languages and pass in the corresponding language code to see its string value key = "formatLanguage()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatLanguage(1033); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example of formatDateYearMonth() method // Pass a JavaScript Data object set to the current time into formatDateYearMonth method to format the data // and get the return in Year, Month format key = "formatDateYearMonth()"; value = this._context.formatting.formatDateYearMonth(new Date()); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); // Example of getWeekOfYear() method // Pass a JavaScript Data object set to the current time into getWeekOfYear method to get the value for week of the year key = "getWeekOfYear()"; value = this._context.formatting.getWeekOfYear(new Date()).toString(); tableElement.appendChild(this.createHTMLTableRowElement(key, value, false)); return tableElement; } }
Ihrer Codekomponente Stil hinzufügen
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor, um Ihrer Codekomponente einen Stil hinzuzufügen:
Erstellen Sie einen neuen css-Unterordner unter dem Ordner „FormattingAPI“.
Erstellen Sie im CSS-Unterordner eine neue TS_FormattingAPI.css-Datei.
Fügen Sie der Datei „TS_FormattingAPI.css“ den folgenden Stilinhalt hinzu.
.SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI { font-family: 'SegoeUI-Semibold', 'Segoe UI Semibold', 'Segoe UI Regular', 'Segoe UI'; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .TSFormatting_Container { overflow-x: auto; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlRow { background-color: #FFFFFF; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlHeaderCell { text-align: center; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell, .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlHeaderCell { border: 1px solid black; padding-left: 3px; padding-right: 3px; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlInputTextCell { border: 1px solid black; padding: 0px; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlHeaderCell { font-weight: bold; font-size: 16px; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell_Key { color: #1160B7; } .SampleNamespace\.FormattingAPI .FormattingControlSampleHtmlTable_HtmlCell_Value { color: #1160B7; text-align: center; }Wählen Sie Datei aus, und Alle speichern Sie alle Ihre Änderungen.
Ihre Komponente erstellen und ausführen
Gehen Sie wie folgt vor, um die Ihre Komponente zu erstellen und auszuführen:
Erstellen Sie Ihre Lösung, indem Sie folgenden Befehl ausführen.
npm run buildNach einer erfolgreichen Erstellung können Sie Ihre neue Formatierungs-API-Komponente testen, indem Sie „npm start“ ausführen.
npm startSchließen Sie das Testumgebungs-Browserfenster.
Wechseln Sie zurück zum Terminal, und stoppen Sie den Beobachter, indem Sie [CONTROL] + C gedrückt halten.
Geben Sie Y ein und dann [ENTER].
Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Formatierungs-API-Komponente implementieren.