Unit testing JavaScript and TypeScript in Visual Studio
Applies to: ![]() Visual Studio
Visual Studio ![]() Visual Studio for Mac
Visual Studio for Mac
Note
This article applies to Visual Studio 2017. If you're looking for the latest Visual Studio documentation, see Visual Studio documentation. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of Visual Studio. Download it here
You can write and run unit tests in Visual Studio using some of the more popular JavaScript frameworks without the need to switch to a command prompt. Both Node.js and ASP.NET Core projects are supported.
The supported frameworks are:
- Mocha (mochajs.org)
- Jasmine (Jasmine.github.io)
- Tape (github.com/substack/tape)
- Jest (jestjs.io)
- Export Runner (this framework is specific to Node.js Tools for Visual Studio)
For ASP.NET Core and JavaScript or TypeScript, see Write unit tests for ASP.NET Core .
If your favorite framework is not supported, see Add support for a unit test framework for information on adding support.
Write unit tests in a Node.js project (.njsproj)
For Node.js projects, before adding unit tests to your project, make sure the framework you plan to use is installed locally in your project. This is easy to do using the npm package installation window.
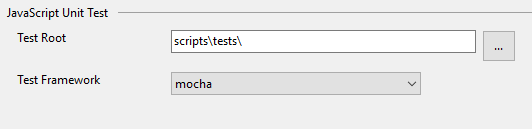
The preferred way to add unit tests to your project is by creating a tests folder in your project, and setting that as the test root in project properties. You also need to select the test framework you want to use.
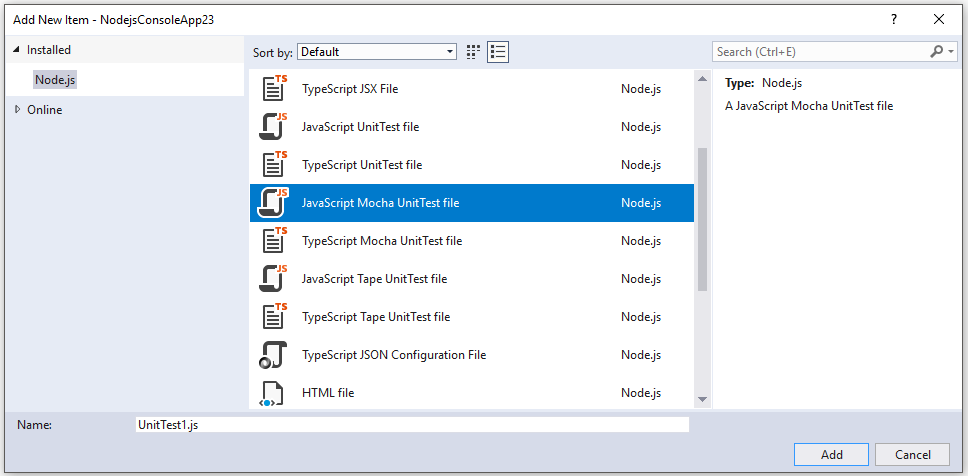
You can add simple blank tests to your project, using the Add New Item dialog box. Both JavaScript and TypeScript are supported in the same project.
For a Mocha unit test, use the following code:
var assert = require('assert');
describe('Test Suite 1', function() {
it('Test 1', function() {
assert.ok(true, "This shouldn't fail");
})
it('Test 2', function() {
assert.ok(1 === 1, "This shouldn't fail");
assert.ok(false, "This should fail");
})
})
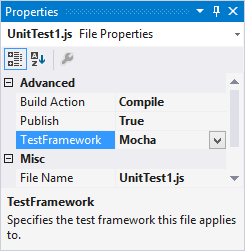
If you haven't set the unit test options in the project properties, you must ensure the Test Framework property in the Properties window is set to the correct test framework for your unit test files. This is done automatically by the unit test file templates.
Note
The unit test options will take preference over the settings for individual files.
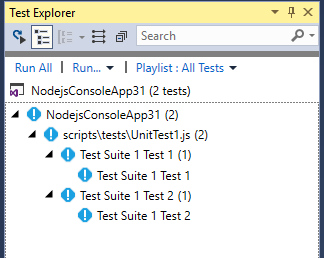
After opening Test Explorer (choose Test > Windows > Test Explorer), Visual Studio discovers and displays tests. If tests are not showing initially, then rebuild the project to refresh the list.
Note
For TypeScript, do not use the outdir or outfile option in tsconfig.json, because Test Explorer won't be able to find your unit tests.
Run tests (Node.js)
You can run tests in Visual Studio or from the command line.
Run tests in Visual Studio
You can run the tests by clicking the Run All link in Test Explorer. Or, you can run tests by selecting one or more tests or groups, right-clicking, and selecting Run Selected Tests from the shortcut menu. Tests run in the background, and Test Explorer automatically updates and shows the results. Furthermore, you can also debug selected tests by selecting Debug Selected Tests.
For TypeScript, unit tests are run against the generated JavaScript code.
Note
In most TypeScript scenarios, you can debug a unit test by setting a breakpoint in TypeScript code, right-clicking a test in Test Explorer, and choosing Debug. In more complex scenarios, such as some scenarios that use source maps, you may have difficulty hitting breakpoints in TypeScript code. As a workaround, try using the debugger keyword.
Note
We don't currently support profiling tests, or code coverage.
Run tests from the command line
You can run the tests from Developer Command Prompt for Visual Studio using the following command:
vstest.console.exe <path to project file>\NodejsConsoleApp23.njsproj /TestAdapterPath:<VisualStudioFolder>\Common7\IDE\Extensions\Microsoft\NodeJsTools\TestAdapter
This command shows output similar to the following:
Microsoft (R) Test Execution Command Line Tool Version 15.5.0
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Starting test execution, please wait...
Processing: NodejsConsoleApp23\NodejsConsoleApp23\UnitTest1.js
Creating TestCase:NodejsConsoleApp23\NodejsConsoleApp23\UnitTest1.js::Test Suite 1 Test 1::mocha
Creating TestCase:NodejsConsoleApp23\NodejsConsoleApp23\UnitTest1.js::Test Suite 1 Test 2::mocha
Processing finished for framework of Mocha
Passed Test Suite 1 Test 1
Standard Output Messages:
Using default Mocha settings
1..2
ok 1 Test Suite 1 Test 1
Failed Test Suite 1 Test 2
Standard Output Messages:
not ok 1 Test Suite 1 Test 2
AssertionError [ERR_ASSERTION]: This should fail
at Context.<anonymous> (NodejsConsoleApp23\NodejsConsoleApp23\UnitTest1.js:10:16)
Total tests: 2. Passed: 1. Failed: 1. Skipped: 0.
Test Run Failed.
Test execution time: 1.5731 Seconds
Note
If you get an error indicating that vstest.console.exe cannot be found, make sure you've opened the Developer Command Prompt and not a regular command prompt.
Write unit tests for ASP.NET Core
Create an ASP.NET Core project and add TypeScript support.
For an example project, see Create an ASP.NET Core app with TypeScript. For unit testing support, we recommend you start with a standard ASP.NET Core project template.
Use the NuGet package to add TypeScript support instead of the npm TypeScript package.
Install the NuGet package Microsoft.JavaScript.UnitTest
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project node and choose Unload Project.
The .csproj file should open in Visual Studio.
Add the following elements to the .csproj file in the
PropertyGroupelement.This example specifies Mocha as the test framework. You could specify Jest, Tape, or Jasmine instead.
<PropertyGroup> ... <JavaScriptTestRoot>tests\</JavaScriptTestRoot> <JavaScriptTestFramework>Mocha</JavaScriptTestFramework> <GenerateProgramFile>false</GenerateProgramFile> </PropertyGroup>The
JavaScriptTestRootelement specifies that your unit tests will be in the tests folder of the project root.In Solution Explorer, right-click the project node and choose Reload Project.
Add npm support as described in the npm package management article under ASP.NET Core projects.
This requires installing the Node.js runtime for npm support and adding package.json in the project root.
In package.json, add the npm package you want under dependencies.
For example, for mocha, you might use the following:
"dependencies": { "mocha": "8.3.0",Some unit testing frameworks, such as Jest, require additional npm packages. For Jest, use the following JSON:
"dependencies": { "jest": "26.6.3", "jest-editor-support": "28.1.0"Note
In some scenarios, Solution Explorer may not show the npm node due to a known issue described here. If you need to see the npm node, you can unload the project (right-click the project and choose Unload Project) and then reload the project to make the npm node re-appear.
Add code to test.
If you are using the example described in Create an ASP.NET Core app with TypeScript, add the following code at the end of the library.ts file, which is in the scripts folder.
function getData(value) { if (value > 1) { return true; } } module.exports = getData;For TypeScript, unit tests are run against the generated JavaScript code.
Add your unit tests to the tests folder in the project root.
For example, you might use the following code by selecting the correct documentation tab that matches your test framework, in this example either Mocha or Jest. This code tests a function called
getData.Open Test Explorer (choose Test > Windows > Test Explorer) and Visual Studio discovers and displays tests. If tests are not showing initially, then rebuild the project to refresh the list.
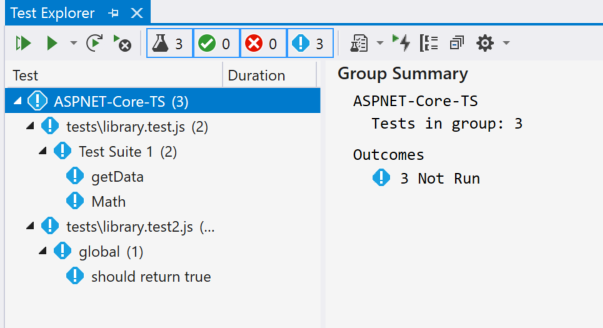
Note
For TypeScript, do not use the
outfileoption in tsconfig.json, because Test Explorer won't be able to find your unit tests. You can use theoutdiroption, but make sure that configuration files such aspackage.jsonandtsconfig.jsonare in the project root.
Run tests (ASP.NET Core)
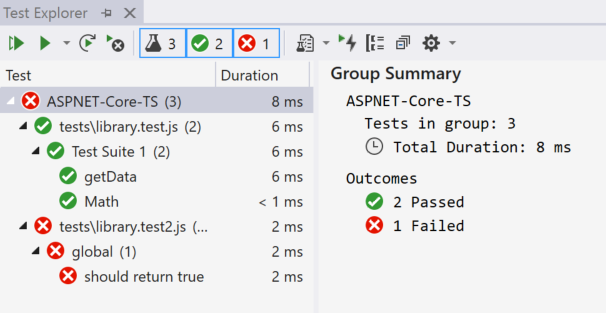
You can run the tests by clicking the Run All link in Test Explorer. Or, you can run tests by selecting one or more tests or groups, right-clicking, and selecting Run Selected Tests from the shortcut menu. Tests run in the background, and Test Explorer automatically updates and shows the results. Furthermore, you can also debug selected tests by selecting Debug Selected Tests.
For TypeScript, unit tests are run against the generated JavaScript code.
Note
In most TypeScript scenarios, you can debug a unit test by setting a breakpoint in TypeScript code, right-clicking a test in Test Explorer, and choosing Debug. In more complex scenarios, such as some scenarios that use source maps, you may have difficulty hitting breakpoints in TypeScript code. As a workaround, try using the debugger keyword.
Note
We don't currently support profiling tests, or code coverage.
Add support for a unit test framework
You can add support for additional test frameworks by implementing the discovery and execution logic using JavaScript.
Note
For ASP.NET Core, add the NuGet package Microsoft.JavaScript.UnitTest to your project to add support.
You do this by adding a folder with the name of the test framework under:
<VisualStudioFolder>\Common7\IDE\Extensions\Microsoft\NodeJsTools\TestAdapter\TestFrameworks
If you don't see the NodeJsTools folder in an ASP.NET Core project, add the Node.js development workload using the Visual Studio Installer. This workload includes support for unit testing JavaScript and TypeScript.
This folder has to contain a JavaScript file with the same name which exports the following two functions:
find_testsrun_tests
For a good example of the find_tests and the run_tests implementations, see the implementation for the Mocha
unit testing framework in:
<VisualStudioFolder>\Common7\IDE\Extensions\Microsoft\NodeJsTools\TestAdapter\TestFrameworks\mocha\mocha.js
Discovery of available test frameworks occurs at Visual Studio start. If a framework is added while Visual Studio is running, restart Visual Studio to detect the framework. However you don't need to restart when making changes to the implementation.
Unit tests in .NET Framework
You are not limited to writing unit tests in just your Node.js and ASP.NET Core projects. When you add the TestFramework and TestRoot properties to any C# or Visual Basic project, those tests will be enumerated and you can run them using the Test Explorer window.
To enable this, right-click the project node in the Solution Explorer, choose Unload Project, and then choose Edit Project. Then in the project file, add the following two elements to a property group.
Important
Make sure that the property group you're adding the elements to doesn't have a condition specified. This can cause unexpected behavior.
<PropertyGroup>
<JavaScriptTestRoot>tests\</JavaScriptTestRoot>
<JavaScriptTestFramework>Tape</JavaScriptTestFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
Next, add your tests to the test root folder you specified, and they will be available to run in the Test Explorer window. If they don't initially appear, you may need to rebuild the project.
Unit test .NET Core and .NET Standard
In addition to the preceding properties, you also need to install the NuGet package Microsoft.JavaScript.UnitTest and set the property:
<PropertyGroup>
<GenerateProgramFile>false</GenerateProgramFile>
</PropertyGroup>
Some test frameworks may require additional npm packages for test detection. For example, jest requires the jest-editor-support npm package. If necessary, check the documentation for the specific framework.