Price structure overview (preview)
[This article is prerelease documentation and is subject to change.]
When a sales order is placed, you can review the detailed price breakdown, including the price component. The breakdown corresponds to the price structure that you configured. The price details provide an audit record that shows how the price was determined. They can serve as a starting point for future price investigation.
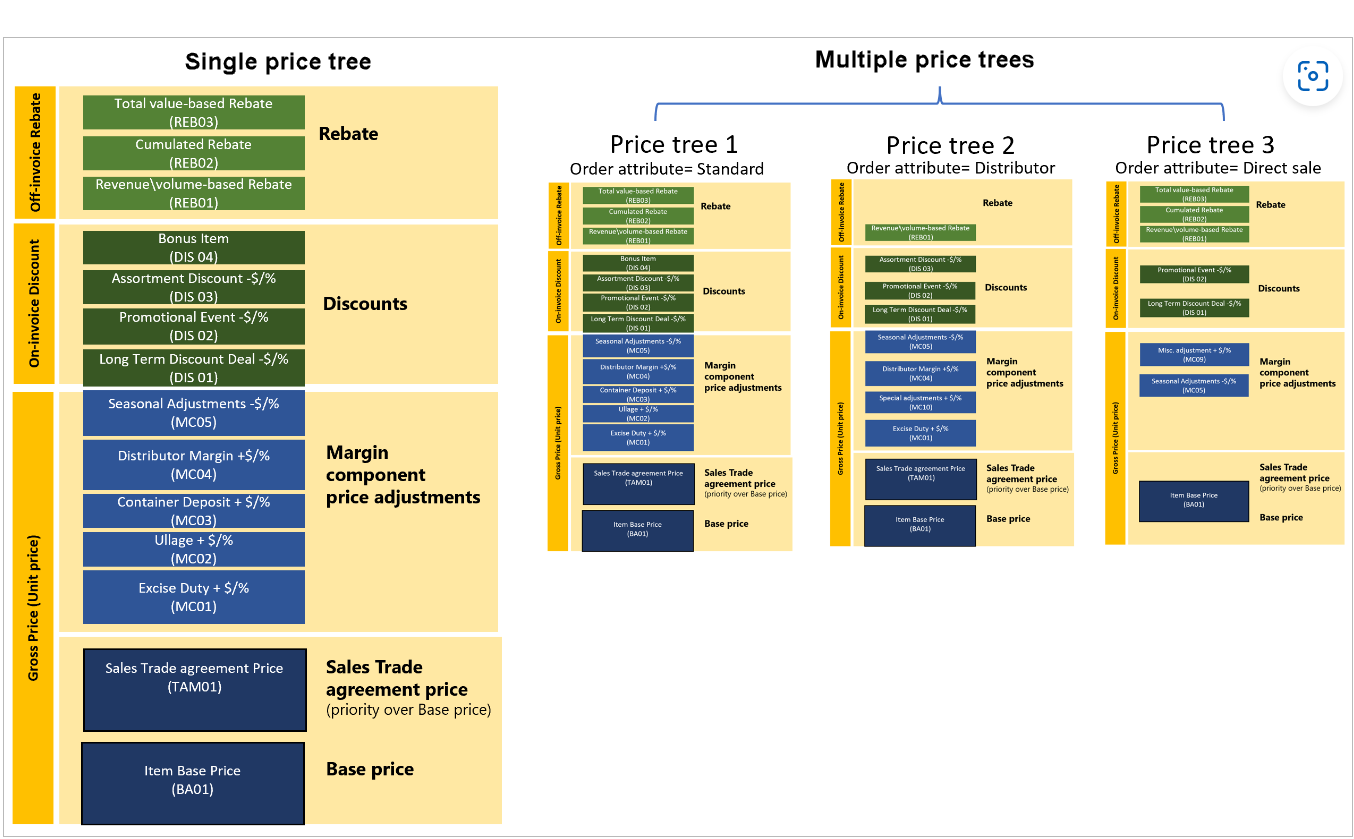
You can set up your system to use either a single price structure or multiple price structures.
Price component types
The following table summarizes the main types of components that can be included in a price structure.
| Price component | Price position | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Base price | Unit Price | The base price represents the common price for general use. It's at the level of the stock keeping unit (SKU). You can have only one price component code of this type in each price structure. That price component code can be of any of the following base price types:
The base price comes from the Item base price page. it can be either calculated or manually entered. If you set up the base price by using a price structure (price trees), and no matching record exists on the Item base price page, the system determines whether the item is a standard cost item. If it's a standard cost item, the system uses the active item standard cost as the source for the base price. |
| Sales trade agreement price | Unit Price | If the sales trade agreement price is available, it takes precedence over the base price, because it represents a special price arrangement with a specific group of consumers for a specific set of products. You can have only one price component code of this type. However, any number of sales trade agreement prices can apply to that code in different situations. |
| Margin component price adjustment | Unit Price | Margin component price adjustments move item prices up or down from the base price. Margin component price adjustments can be associated with many types of agreements, promotions, and events. They let you easily adjust prices without changing the base price. You can have multiple price component codes of this type, and you can associate any number of pricing rules with each one. Price adjustments are compounded across price component codes and add up to the total price adjustment. |
| Discounts | On-invoice discounts | Discounts let you adjust prices based on a wide range of calculation methods that are designed to encourage the purchase of specific products, volumes, packages, and so on. You can have multiple price component codes of this type, and you can associate any number of pricing rules with each one. |
| Rebate management | Off-invoice discounts | You can have multiple price component codes of this type. |
Concurrency rules
If your price structure has multiple price rules that apply to the same price component code and/or to multiple price component codes of the same type, the system applies concurrency rules to resolve them.
- If more than one pricing rule applies to the same price component code in a price structure, within-price-component-code concurrency rules are applied to determine which rules apply and how they are combined. Learn more in Resolve concurrency within price component codes.
- If your price structure includes more than one price component code of the same type, across-price-component-code concurrency rules are applied to determine how they are combined. Learn more in Resolve concurrency across price component codes.