Exemplarische Vorgehensweise: Erstellen einer UWP-App mithilfe von WRL und Media Foundation
Hinweis
Für neue UWP-Apps und -Komponenten empfehlen wir die Verwendung von C++/WinRT, einer neuen C++17-Sprachprojektion für Windows-Runtime-APIs. C++/WinRT ist in Windows SDK ab Version 1803 (10.0.17134.0) erhältlich. C++/WinRT wird vollständig in Headerdateien implementiert und wurde entwickelt, um Ihnen erstklassigen Zugriff auf die moderne Windows-API zu ermöglichen.
In diesem Lernprogramm erfahren Sie, wie Sie mit der Windows-Runtime C++-Vorlagenbibliothek (WRL) eine Universelle Windows-Plattform (UWP)-App erstellen, die Microsoft Media Foundation verwendet.
In diesem Beispiel wird eine benutzerdefinierte Media Foundation-Transformation erstellt. Es wendet einen Graustufeneffekt auf Bilder an, die von einer Webcam erfasst werden. Die App verwendet C++ zum Definieren der benutzerdefinierten Transformation und C# zum Verwenden der Komponente für das Transformieren der erfassten Bilder.
Hinweis
Anstelle von C# können Sie auch JavaScript, Visual Basic oder C++ verwenden, um die benutzerdefinierte Transformierenkomponente zu verwenden.
In der Regel können Sie C++/CX verwenden, um Windows-Runtime Komponenten zu erstellen. Manchmal müssen Sie jedoch die WRL verwenden. Wenn Sie beispielsweise eine Medienerweiterung für Microsoft Media Foundation erstellen, müssen Sie eine Komponente erstellen, die sowohl COM- als auch Windows-Runtime-Schnittstellen implementiert. Da C++/CX nur Windows-Runtime Objekte erstellen kann, müssen Sie die WRL verwenden, um eine Medienerweiterung zu erstellen. Das liegt daran, dass die Implementierung von COM- und Windows-Runtime-Schnittstellen ermöglicht wird.
Hinweis
Auch wenn dieses Codebeispiel lang ist, stellt es das erforderliche Minimum dar, um eine nützliche Media Foundation-Transformation zu erstellen. Sie können es als Ausgangspunkt für Ihre eigene benutzerdefinierte Transformation verwenden. Dieses Beispiel wird aus dem Beispiel für Medienerweiterungen angepasst, das Medienerweiterungen verwendet, um Effekte auf Video anzuwenden, Video zu decodieren und Schemahandler zu erstellen, die Medienstreams erzeugen.
Voraussetzungen
In Visual Studio 2017 und höher ist die UWP-Unterstützung eine optionale Komponente. Um sie zu installieren, öffnen Sie die Visual Studio-Installer aus dem Windows Menü , und suchen Sie Ihre Version von Visual Studio. Wählen Sie "Ändern" aus, und stellen Sie dann sicher, dass die Kachel "Universelle Windows-Plattform Entwicklung" aktiviert ist. Überprüfen Sie unter "Optionale Komponenten" C++-Tools für UWP (v141) für Visual Studio 2017 oder C++-Tools für UWP (v142) für Visual Studio 2019. Überprüfen Sie dann die Version des Windows SDK, das Sie verwenden möchten.
Erleben Sie die Windows-Runtime.
Erfahrungen mit COM.
Eine Webcam.
Wesentliche Punkte
Verwenden Sie zum Erstellen einer benutzerdefinierten Media Foundation-Komponente eine MIDL-Definitionsdatei (Microsoft Interface Definition Language) zum Definieren einer Schnittstelle, Implementieren dieser Schnittstelle und zum Einstellen derselben, dass sie aus anderen Komponenten aktiviert werden kann.
Die
namespaceAttribute undruntimeclassderNTDDI_WIN8Versionsattributwert sind wichtige Teile der MIDL-Definition für eine Media Foundation-Komponente, die WRL verwendet.Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClassist die Basisklasse für die benutzerdefinierte Media Foundation-Komponente. Der [Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClassType::WinRtClassicComMix](runtimeclasstype-enumeration.md)-Enumerationswert, der als Vorlagenargument bereitgestellt wird, kennzeichnet die Klasse für die Verwendung sowohl als Windows-Runtime-Klasse als auch als klassische COM-Laufzeitklasse.Das
InspectableClassMakro implementiert grundlegende COM-Funktionen, z. B. Verweiszählung undQueryInterfaceMethode, und legt den Namen und die Vertrauensstufe der Laufzeitklasse fest.Verwenden Sie die
Microsoft::WRL::ModuleKlasse, um DLL-Einstiegspunktfunktionen wieDllGetActivationFactory, undDllCanUnloadNowDllGetClassObject.Verknüpfen Sie die Komponenten-DLL mit
runtimeobject.lib. Geben Sie/WINMDaußerdem in der Linkerzeile an, um Windows-Metadaten zu generieren.Verwenden Sie Projektverweise, um WRL-Komponenten für UWP-Apps zugänglich zu machen.
So erstellen Sie die Graustufentransformationskomponente von Media Foundation mit der WRL
Erstellen Sie in Visual Studio ein leeres Projektmappenprojekt . Nennen Sie das Projekt, z. B. MediaCapture.
Fügen Sie der Projektmappe ein DLL-Projekt (Universelle Windows-Datei) hinzu. Nennen Sie das Projekt, z. B. GrayscaleTransform.
Fügen Sie dem Projekt eine MIDL-Dateidatei (IDL) -Datei hinzu. Nennen Sie die Datei, z. B
GrayscaleTransform.idl. .Fügen Sie diesen Code zu GrayscaleTransform.idl hinzu:
import "Windows.Media.idl"; #include <sdkddkver.h> namespace GrayscaleTransform { [version(NTDDI_WIN8), activatable(NTDDI_WIN8)] runtimeclass GrayscaleEffect { [default] interface Windows.Media.IMediaExtension; } }Verwenden Sie den folgenden Code, um den Inhalt von
pch.h:#pragma once #include "targetver.h" #include <new> #include <mfapi.h> #include <mftransform.h> #include <mfidl.h> #include <mferror.h> #include <strsafe.h> #include <assert.h> // Note: The Direct2D helper library is included for its 2D matrix operations. #include <D2d1helper.h> #include <wrl\implements.h> #include <wrl\module.h> #include <windows.media.h>Fügen Sie dem Projekt eine neue Headerdatei hinzu, nennen Sie sie
BufferLock.h, und ersetzen Sie dann den Inhalt durch diesen Code:#pragma once // Locks a video buffer that might or might not support IMF2DBuffer. class VideoBufferLock { public: VideoBufferLock(IMFMediaBuffer *pBuffer) : m_p2DBuffer(nullptr) { m_pBuffer = pBuffer; m_pBuffer->AddRef(); // Query for the 2-D buffer interface. OK if this fails. m_pBuffer->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_p2DBuffer)); } ~VideoBufferLock() { UnlockBuffer(); m_pBuffer->Release(); if (m_p2DBuffer) { m_p2DBuffer->Release(); } } // LockBuffer: // Locks the buffer. Returns a pointer to scan line 0 and returns the stride. // The caller must provide the default stride as an input parameter, in case // the buffer does not expose IMF2DBuffer. You can calculate the default stride // from the media type. HRESULT LockBuffer( LONG lDefaultStride, // Minimum stride (with no padding). DWORD dwHeightInPixels, // Height of the image, in pixels. BYTE **ppbScanLine0, // Receives a pointer to the start of scan line 0. LONG *plStride // Receives the actual stride. ) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // Use the 2-D version if available. if (m_p2DBuffer) { hr = m_p2DBuffer->Lock2D(ppbScanLine0, plStride); } else { // Use non-2D version. BYTE *pData = nullptr; hr = m_pBuffer->Lock(&pData, nullptr, nullptr); if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { *plStride = lDefaultStride; if (lDefaultStride < 0) { // Bottom-up orientation. Return a pointer to the start of the // last row *in memory* which is the top row of the image. *ppbScanLine0 = pData + abs(lDefaultStride) * (dwHeightInPixels - 1); } else { // Top-down orientation. Return a pointer to the start of the // buffer. *ppbScanLine0 = pData; } } } return hr; } HRESULT UnlockBuffer() { if (m_p2DBuffer) { return m_p2DBuffer->Unlock2D(); } else { return m_pBuffer->Unlock(); } } private: IMFMediaBuffer *m_pBuffer; IMF2DBuffer *m_p2DBuffer; };GrayscaleTransform.hwird in diesem Beispiel nicht verwendet. Sie können ihn bei Bedarf aus dem Projekt entfernen.Verwenden Sie den folgenden Code, um den Inhalt von
GrayscaleTransform.cpp:#include "pch.h" #include "GrayscaleTransform_h.h" #include "BufferLock.h" using namespace Microsoft::WRL; // // * IMPORTANT: If you implement your own MFT, create a new GUID for the CLSID. * // // Configuration attributes // {7BBBB051-133B-41F5-B6AA-5AFF9B33A2CB} GUID const MFT_GRAYSCALE_DESTINATION_RECT = {0x7bbbb051, 0x133b, 0x41f5, 0xb6, 0xaa, 0x5a, 0xff, 0x9b, 0x33, 0xa2, 0xcb}; // {14782342-93E8-4565-872C-D9A2973D5CBF} GUID const MFT_GRAYSCALE_SATURATION = {0x14782342, 0x93e8, 0x4565, 0x87, 0x2c, 0xd9, 0xa2, 0x97, 0x3d, 0x5c, 0xbf}; // {E0BADE5D-E4B9-4689-9DBA-E2F00D9CED0E} GUID const MFT_GRAYSCALE_CHROMA_ROTATION = {0xe0bade5d, 0xe4b9, 0x4689, 0x9d, 0xba, 0xe2, 0xf0, 0xd, 0x9c, 0xed, 0xe}; template <class T> void SafeRelease(T **ppT) { if (*ppT) { (*ppT)->Release(); *ppT = nullptr; } } // Function pointer for the function that transforms the image. typedef void (*IMAGE_TRANSFORM_FN)( const D2D1::Matrix3x2F& mat, // Chroma transform matrix. const D2D_RECT_U& rcDest, // Destination rectangle for the transformation. BYTE* pDest, // Destination buffer. LONG lDestStride, // Destination stride. const BYTE* pSrc, // Source buffer. LONG lSrcStride, // Source stride. DWORD dwWidthInPixels, // Image width in pixels. DWORD dwHeightInPixels // Image height in pixels. ); // Implements a grayscale video effect. class CGrayscale : public RuntimeClass< RuntimeClassFlags<RuntimeClassType::WinRtClassicComMix>, ABI::Windows::Media::IMediaExtension, IMFTransform> { InspectableClass(RuntimeClass_GrayscaleTransform_GrayscaleEffect, BaseTrust) public: CGrayscale(); STDMETHOD(RuntimeClassInitialize)(); // IMediaExtension STDMETHODIMP SetProperties(ABI::Windows::Foundation::Collections::IPropertySet *pConfiguration); // IMFTransform STDMETHODIMP GetStreamLimits( DWORD *pdwInputMinimum, DWORD *pdwInputMaximum, DWORD *pdwOutputMinimum, DWORD *pdwOutputMaximum ); STDMETHODIMP GetStreamCount( DWORD *pcInputStreams, DWORD *pcOutputStreams ); STDMETHODIMP GetStreamIDs( DWORD dwInputIDArraySize, DWORD *pdwInputIDs, DWORD dwOutputIDArraySize, DWORD *pdwOutputIDs ); STDMETHODIMP GetInputStreamInfo( DWORD dwInputStreamID, MFT_INPUT_STREAM_INFO * pStreamInfo ); STDMETHODIMP GetOutputStreamInfo( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, MFT_OUTPUT_STREAM_INFO * pStreamInfo ); STDMETHODIMP GetAttributes(IMFAttributes** pAttributes); STDMETHODIMP GetInputStreamAttributes( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFAttributes **ppAttributes ); STDMETHODIMP GetOutputStreamAttributes( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, IMFAttributes **ppAttributes ); STDMETHODIMP DeleteInputStream(DWORD dwStreamID); STDMETHODIMP AddInputStreams( DWORD cStreams, DWORD *adwStreamIDs ); STDMETHODIMP GetInputAvailableType( DWORD dwInputStreamID, DWORD dwTypeIndex, // 0-based IMFMediaType **ppType ); STDMETHODIMP GetOutputAvailableType( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, DWORD dwTypeIndex, // 0-based IMFMediaType **ppType ); STDMETHODIMP SetInputType( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFMediaType *pType, DWORD dwFlags ); STDMETHODIMP SetOutputType( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, IMFMediaType *pType, DWORD dwFlags ); STDMETHODIMP GetInputCurrentType( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFMediaType **ppType ); STDMETHODIMP GetOutputCurrentType( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, IMFMediaType **ppType ); STDMETHODIMP GetInputStatus( DWORD dwInputStreamID, DWORD *pdwFlags ); STDMETHODIMP GetOutputStatus(DWORD *pdwFlags); STDMETHODIMP SetOutputBounds( LONGLONG hnsLowerBound, LONGLONG hnsUpperBound ); STDMETHODIMP ProcessEvent( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFMediaEvent *pEvent ); STDMETHODIMP ProcessMessage( MFT_MESSAGE_TYPE eMessage, ULONG_PTR ulParam ); STDMETHODIMP ProcessInput( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFSample *pSample, DWORD dwFlags ); STDMETHODIMP ProcessOutput( DWORD dwFlags, DWORD cOutputBufferCount, MFT_OUTPUT_DATA_BUFFER *pOutputSamples, // one per stream DWORD *pdwStatus ); private: ~CGrayscale(); // HasPendingOutput: Returns TRUE if the MFT is holding an input sample. BOOL HasPendingOutput() const { return m_pSample != nullptr; } // IsValidInputStream: Returns TRUE if dwInputStreamID is a valid input stream identifier. BOOL IsValidInputStream(DWORD dwInputStreamID) const { return dwInputStreamID == 0; } // IsValidOutputStream: Returns TRUE if dwOutputStreamID is a valid output stream identifier. BOOL IsValidOutputStream(DWORD dwOutputStreamID) const { return dwOutputStreamID == 0; } HRESULT OnGetPartialType(DWORD dwTypeIndex, IMFMediaType **ppmt); HRESULT OnCheckInputType(IMFMediaType *pmt); HRESULT OnCheckOutputType(IMFMediaType *pmt); HRESULT OnCheckMediaType(IMFMediaType *pmt); void OnSetInputType(IMFMediaType *pmt); void OnSetOutputType(IMFMediaType *pmt); HRESULT BeginStreaming(); HRESULT EndStreaming(); HRESULT OnProcessOutput(IMFMediaBuffer *pIn, IMFMediaBuffer *pOut); HRESULT OnFlush(); HRESULT UpdateFormatInfo(); CRITICAL_SECTION m_critSec; // Transformation parameters D2D1::Matrix3x2F m_transform; // Chroma transform matrix. D2D_RECT_U m_rcDest; // Destination rectangle for the effect. // Streaming bool m_bStreamingInitialized; IMFSample *m_pSample; // Input sample. IMFMediaType *m_pInputType; // Input media type. IMFMediaType *m_pOutputType; // Output media type. // Fomat information UINT32 m_imageWidthInPixels; UINT32 m_imageHeightInPixels; DWORD m_cbImageSize; // Image size, in bytes. IMFAttributes *m_pAttributes; // Image transform function. (Changes based on the media type.) IMAGE_TRANSFORM_FN m_pTransformFn; }; ActivatableClass(CGrayscale); #pragma comment(lib, "d2d1") /* This sample implements a video effect as a Media Foundation transform (MFT). The video effect manipulates chroma values in a YUV image. In the default setting, the entire image is converted to grayscale. Optionally, the application may set any of the following attributes: MFT_GRAYSCALE_DESTINATION_RECT (type = blob, UINT32[4] array) Sets the destination rectangle for the effect. Pixels outside the destination rectangle are not altered. MFT_GRAYSCALE_SATURATION (type = double) Sets the saturation level. The nominal range is [0...1]. Values beyond 1.0f result in supersaturated colors. Values below 0.0f create inverted colors. MFT_GRAYSCALE_CHROMA_ROTATION (type = double) Rotates the chroma values of each pixel. The attribue value is the angle of rotation in degrees. The result is a shift in hue. The effect is implemented by treating the chroma value of each pixel as a vector [u,v], and applying a transformation matrix to the vector. The saturation parameter is applied as a scaling transform. NOTES ON THE MFT IMPLEMENTATION 1. The MFT has fixed streams: One input stream and one output stream. 2. The MFT supports the following formats: UYVY, YUY2, NV12. 3. If the MFT is holding an input sample, SetInputType and SetOutputType both fail. 4. The input and output types must be identical. 5. If both types are set, no type can be set until the current type is cleared. 6. Preferred input types: (a) If the output type is set, that's the preferred type. (b) Otherwise, the preferred types are partial types, constructed from the list of supported subtypes. 7. Preferred output types: As above. 8. Streaming: The private BeingStreaming() method is called in response to the MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_BEGIN_STREAMING message. If the client does not send MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_BEGIN_STREAMING, the MFT calls BeginStreaming inside the first call to ProcessInput or ProcessOutput. This is a good approach for allocating resources that your MFT requires for streaming. 9. The configuration attributes are applied in the BeginStreaming method. If the client changes the attributes during streaming, the change is ignored until streaming is stopped (either by changing the media types or by sending the MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_END_STREAMING message) and then restarted. */ // Video FOURCC codes. const DWORD FOURCC_YUY2 = '2YUY'; const DWORD FOURCC_UYVY = 'YVYU'; const DWORD FOURCC_NV12 = '21VN'; // Static array of media types (preferred and accepted). const GUID g_MediaSubtypes[] = { MFVideoFormat_NV12, MFVideoFormat_YUY2, MFVideoFormat_UYVY }; HRESULT GetImageSize(DWORD fcc, UINT32 width, UINT32 height, DWORD* pcbImage); HRESULT GetDefaultStride(IMFMediaType *pType, LONG *plStride); bool ValidateRect(const RECT& rc); template <typename T> inline T clamp(const T& val, const T& minVal, const T& maxVal) { return (val < minVal ? minVal : (val > maxVal ? maxVal : val)); } // TransformChroma: // Apply the transforms to calculate the output chroma values. void TransformChroma(const D2D1::Matrix3x2F& mat, BYTE *pu, BYTE *pv) { // Normalize the chroma values to [-112, 112] range D2D1_POINT_2F pt = { static_cast<float>(*pu) - 128, static_cast<float>(*pv) - 128 }; pt = mat.TransformPoint(pt); // Clamp to valid range. clamp(pt.x, -112.0f, 112.0f); clamp(pt.y, -112.0f, 112.0f); // Map back to [16...240] range. *pu = static_cast<BYTE>(pt.x + 128.0f); *pv = static_cast<BYTE>(pt.y + 128.0f); } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // Functions to convert a YUV images to grayscale. // // In all cases, the same transformation is applied to the 8-bit // chroma values, but the pixel layout in memory differs. // // The image conversion functions take the following parameters: // // mat Transfomation matrix for chroma values. // rcDest Destination rectangle. // pDest Pointer to the destination buffer. // lDestStride Stride of the destination buffer, in bytes. // pSrc Pointer to the source buffer. // lSrcStride Stride of the source buffer, in bytes. // dwWidthInPixels Frame width in pixels. // dwHeightInPixels Frame height, in pixels. //------------------------------------------------------------------- // Convert UYVY image. void TransformImage_UYVY( const D2D1::Matrix3x2F& mat, const D2D_RECT_U& rcDest, _Inout_updates_(_Inexpressible_(lDestStride * dwHeightInPixels)) BYTE *pDest, _In_ LONG lDestStride, _In_reads_(_Inexpressible_(lSrcStride * dwHeightInPixels)) const BYTE* pSrc, _In_ LONG lSrcStride, _In_ DWORD dwWidthInPixels, _In_ DWORD dwHeightInPixels) { DWORD y = 0; const DWORD y0 = min(rcDest.bottom, dwHeightInPixels); // Lines above the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < rcDest.top; y++) { memcpy(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels * 2); pSrc += lSrcStride; pDest += lDestStride; } // Lines within the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < y0; y++) { WORD *pSrc_Pixel = (WORD*)pSrc; WORD *pDest_Pixel = (WORD*)pDest; for (DWORD x = 0; (x + 1) < dwWidthInPixels; x += 2) { // Byte order is U0 Y0 V0 Y1 // Each WORD is a byte pair (U/V, Y) // Windows is little-endian so the order appears reversed. if (x >= rcDest.left && x < rcDest.right) { BYTE u = pSrc_Pixel[x] & 0x00FF; BYTE v = pSrc_Pixel[x+1] & 0x00FF; TransformChroma(mat, &u, &v); pDest_Pixel[x] = (pSrc_Pixel[x] & 0xFF00) | u; pDest_Pixel[x+1] = (pSrc_Pixel[x+1] & 0xFF00) | v; } else { #pragma warning(push) #pragma warning(disable: 6385) #pragma warning(disable: 6386) pDest_Pixel[x] = pSrc_Pixel[x]; pDest_Pixel[x+1] = pSrc_Pixel[x+1]; #pragma warning(pop) } } pDest += lDestStride; pSrc += lSrcStride; } // Lines below the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < dwHeightInPixels; y++) { memcpy(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels * 2); pSrc += lSrcStride; pDest += lDestStride; } } // Convert YUY2 image. void TransformImage_YUY2( const D2D1::Matrix3x2F& mat, const D2D_RECT_U& rcDest, _Inout_updates_(_Inexpressible_(lDestStride * dwHeightInPixels)) BYTE *pDest, _In_ LONG lDestStride, _In_reads_(_Inexpressible_(lSrcStride * dwHeightInPixels)) const BYTE* pSrc, _In_ LONG lSrcStride, _In_ DWORD dwWidthInPixels, _In_ DWORD dwHeightInPixels) { DWORD y = 0; const DWORD y0 = min(rcDest.bottom, dwHeightInPixels); // Lines above the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < rcDest.top; y++) { memcpy(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels * 2); pSrc += lSrcStride; pDest += lDestStride; } // Lines within the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < y0; y++) { WORD *pSrc_Pixel = (WORD*)pSrc; WORD *pDest_Pixel = (WORD*)pDest; for (DWORD x = 0; (x + 1) < dwWidthInPixels; x += 2) { // Byte order is Y0 U0 Y1 V0 // Each WORD is a byte pair (Y, U/V) // Windows is little-endian so the order appears reversed. if (x >= rcDest.left && x < rcDest.right) { BYTE u = pSrc_Pixel[x] >> 8; BYTE v = pSrc_Pixel[x+1] >> 8; TransformChroma(mat, &u, &v); pDest_Pixel[x] = (pSrc_Pixel[x] & 0x00FF) | (u<<8); pDest_Pixel[x+1] = (pSrc_Pixel[x+1] & 0x00FF) | (v<<8); } else { #pragma warning(push) #pragma warning(disable: 6385) #pragma warning(disable: 6386) pDest_Pixel[x] = pSrc_Pixel[x]; pDest_Pixel[x+1] = pSrc_Pixel[x+1]; #pragma warning(pop) } } pDest += lDestStride; pSrc += lSrcStride; } // Lines below the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < dwHeightInPixels; y++) { memcpy(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels * 2); pSrc += lSrcStride; pDest += lDestStride; } } // Convert NV12 image void TransformImage_NV12( const D2D1::Matrix3x2F& mat, const D2D_RECT_U& rcDest, _Inout_updates_(_Inexpressible_(2 * lDestStride * dwHeightInPixels)) BYTE *pDest, _In_ LONG lDestStride, _In_reads_(_Inexpressible_(2 * lSrcStride * dwHeightInPixels)) const BYTE* pSrc, _In_ LONG lSrcStride, _In_ DWORD dwWidthInPixels, _In_ DWORD dwHeightInPixels) { // NV12 is planar: Y plane, followed by packed U-V plane. // Y plane for (DWORD y = 0; y < dwHeightInPixels; y++) { CopyMemory(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels); pDest += lDestStride; pSrc += lSrcStride; } // U-V plane // NOTE: The U-V plane has 1/2 the number of lines as the Y plane. // Lines above the destination rectangle. DWORD y = 0; const DWORD y0 = min(rcDest.bottom, dwHeightInPixels); for ( ; y < rcDest.top/2; y++) { memcpy(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels); pSrc += lSrcStride; pDest += lDestStride; } // Lines within the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < y0/2; y++) { for (DWORD x = 0; (x + 1) < dwWidthInPixels; x += 2) { if (x >= rcDest.left && x < rcDest.right) { BYTE u = pSrc[x]; BYTE v = pSrc[x+1]; TransformChroma(mat, &u, &v); pDest[x] = u; pDest[x+1] = v; } else { pDest[x] = pSrc[x]; pDest[x+1] = pSrc[x+1]; } } pDest += lDestStride; pSrc += lSrcStride; } // Lines below the destination rectangle. for ( ; y < dwHeightInPixels/2; y++) { memcpy(pDest, pSrc, dwWidthInPixels); pSrc += lSrcStride; pDest += lDestStride; } } CGrayscale::CGrayscale() : m_pSample(nullptr), m_pInputType(nullptr), m_pOutputType(nullptr), m_pTransformFn(nullptr), m_imageWidthInPixels(0), m_imageHeightInPixels(0), m_cbImageSize(0), m_transform(D2D1::Matrix3x2F::Identity()), m_rcDest(D2D1::RectU()), m_bStreamingInitialized(false), m_pAttributes(nullptr) { InitializeCriticalSectionEx(&m_critSec, 3000, 0); } CGrayscale::~CGrayscale() { SafeRelease(&m_pInputType); SafeRelease(&m_pOutputType); SafeRelease(&m_pSample); SafeRelease(&m_pAttributes); DeleteCriticalSection(&m_critSec); } // Initialize the instance. STDMETHODIMP CGrayscale::RuntimeClassInitialize() { // Create the attribute store. return MFCreateAttributes(&m_pAttributes, 3); } // IMediaExtension methods //------------------------------------------------------------------- // SetProperties // Sets the configuration of the effect //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::SetProperties(ABI::Windows::Foundation::Collections::IPropertySet *pConfiguration) { return S_OK; } // IMFTransform methods. Refer to the Media Foundation SDK documentation for details. //------------------------------------------------------------------- // GetStreamLimits // Returns the minimum and maximum number of streams. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::GetStreamLimits( DWORD *pdwInputMinimum, DWORD *pdwInputMaximum, DWORD *pdwOutputMinimum, DWORD *pdwOutputMaximum ) { // This MFT has a fixed number of streams. *pdwInputMinimum = 1; *pdwInputMaximum = 1; *pdwOutputMinimum = 1; *pdwOutputMaximum = 1; return S_OK; } // Returns the actual number of streams. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetStreamCount( DWORD *pcInputStreams, DWORD *pcOutputStreams ) { // This MFT has a fixed number of streams. *pcInputStreams = 1; *pcOutputStreams = 1; return S_OK; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // GetStreamIDs // Returns stream IDs for the input and output streams. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::GetStreamIDs( DWORD dwInputIDArraySize, DWORD *pdwInputIDs, DWORD dwOutputIDArraySize, DWORD *pdwOutputIDs ) { // It is not required to implement this method if the MFT has a fixed number of // streams AND the stream IDs are numbered sequentially from zero (that is, the // stream IDs match the stream indexes). // In that case, it is OK to return E_NOTIMPL. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // GetInputStreamInfo // Returns information about an input stream. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::GetInputStreamInfo( DWORD dwInputStreamID, MFT_INPUT_STREAM_INFO * pStreamInfo ) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidInputStream(dwInputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } // NOTE: This method should succeed even when there is no media type on the // stream. If there is no media type, we only need to fill in the dwFlags // member of MFT_INPUT_STREAM_INFO. The other members depend on having a // a valid media type. pStreamInfo->hnsMaxLatency = 0; pStreamInfo->dwFlags = MFT_INPUT_STREAM_WHOLE_SAMPLES | MFT_INPUT_STREAM_SINGLE_SAMPLE_PER_BUFFER; if (m_pInputType == nullptr) { pStreamInfo->cbSize = 0; } else { pStreamInfo->cbSize = m_cbImageSize; } pStreamInfo->cbMaxLookahead = 0; pStreamInfo->cbAlignment = 0; LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return S_OK; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // GetOutputStreamInfo // Returns information about an output stream. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::GetOutputStreamInfo( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, MFT_OUTPUT_STREAM_INFO * pStreamInfo ) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidOutputStream(dwOutputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } // NOTE: This method should succeed even when there is no media type on the // stream. If there is no media type, we only need to fill in the dwFlags // member of MFT_OUTPUT_STREAM_INFO. The other members depend on having a // a valid media type. pStreamInfo->dwFlags = MFT_OUTPUT_STREAM_WHOLE_SAMPLES | MFT_OUTPUT_STREAM_SINGLE_SAMPLE_PER_BUFFER | MFT_OUTPUT_STREAM_FIXED_SAMPLE_SIZE ; if (m_pOutputType == nullptr) { pStreamInfo->cbSize = 0; } else { pStreamInfo->cbSize = m_cbImageSize; } pStreamInfo->cbAlignment = 0; LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return S_OK; } // Returns the attributes for the MFT. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetAttributes(IMFAttributes** ppAttributes) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); *ppAttributes = m_pAttributes; (*ppAttributes)->AddRef(); LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return S_OK; } // Returns stream-level attributes for an input stream. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetInputStreamAttributes( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFAttributes **ppAttributes ) { // This MFT does not support any stream-level attributes, so the method is not implemented. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // GetOutputStreamAttributes // Returns stream-level attributes for an output stream. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::GetOutputStreamAttributes( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, IMFAttributes **ppAttributes ) { // This MFT does not support any stream-level attributes, so the method is not implemented. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // DeleteInputStream //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::DeleteInputStream(DWORD dwStreamID) { // This MFT has a fixed number of input streams, so the method is not supported. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // AddInputStreams //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::AddInputStreams( DWORD cStreams, DWORD *adwStreamIDs ) { // This MFT has a fixed number of output streams, so the method is not supported. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // GetInputAvailableType // Returns a preferred input type. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::GetInputAvailableType( DWORD dwInputStreamID, DWORD dwTypeIndex, // 0-based IMFMediaType **ppType ) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidInputStream(dwInputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } HRESULT hr = S_OK; // If the output type is set, return that type as our preferred input type. if (m_pOutputType == nullptr) { // The output type is not set. Create a partial media type. hr = OnGetPartialType(dwTypeIndex, ppType); } else if (dwTypeIndex > 0) { hr = MF_E_NO_MORE_TYPES; } else { *ppType = m_pOutputType; (*ppType)->AddRef(); } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } // Returns a preferred output type. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetOutputAvailableType( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, DWORD dwTypeIndex, // 0-based IMFMediaType **ppType ) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidOutputStream(dwOutputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } HRESULT hr = S_OK; if (m_pInputType == nullptr) { // The input type is not set. Create a partial media type. hr = OnGetPartialType(dwTypeIndex, ppType); } else if (dwTypeIndex > 0) { hr = MF_E_NO_MORE_TYPES; } else { *ppType = m_pInputType; (*ppType)->AddRef(); } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } HRESULT CGrayscale::SetInputType( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFMediaType *pType, // Can be nullptr to clear the input type. DWORD dwFlags ) { // Validate flags. if (dwFlags & ~MFT_SET_TYPE_TEST_ONLY) { return E_INVALIDARG; } EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidInputStream(dwInputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } HRESULT hr = S_OK; // Does the caller want us to set the type, or just test it? BOOL bReallySet = ((dwFlags & MFT_SET_TYPE_TEST_ONLY) == 0); // If we have an input sample, the client cannot change the type now. if (HasPendingOutput()) { hr = MF_E_TRANSFORM_CANNOT_CHANGE_MEDIATYPE_WHILE_PROCESSING; goto done; } // Validate the type, if non-nullptr. if (pType) { hr = OnCheckInputType(pType); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } } // The type is OK. Set the type, unless the caller was just testing. if (bReallySet) { OnSetInputType(pType); // When the type changes, end streaming. hr = EndStreaming(); } done: LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } HRESULT CGrayscale::SetOutputType( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, IMFMediaType *pType, // Can be nullptr to clear the output type. DWORD dwFlags ) { // Validate flags. if (dwFlags & ~MFT_SET_TYPE_TEST_ONLY) { return E_INVALIDARG; } EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidOutputStream(dwOutputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } HRESULT hr = S_OK; // Does the caller want us to set the type, or just test it? BOOL bReallySet = ((dwFlags & MFT_SET_TYPE_TEST_ONLY) == 0); // If we have an input sample, the client cannot change the type now. if (HasPendingOutput()) { hr = MF_E_TRANSFORM_CANNOT_CHANGE_MEDIATYPE_WHILE_PROCESSING; goto done; } // Validate the type, if non-nullptr. if (pType) { hr = OnCheckOutputType(pType); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } } // The type is OK. Set the type, unless the caller was just testing. if (bReallySet) { OnSetOutputType(pType); // When the type changes, end streaming. hr = EndStreaming(); } done: LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } // Returns the current input type. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetInputCurrentType( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFMediaType **ppType ) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidInputStream(dwInputStreamID)) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } else if (!m_pInputType) { hr = MF_E_TRANSFORM_TYPE_NOT_SET; } else { *ppType = m_pInputType; (*ppType)->AddRef(); } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } // Returns the current output type. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetOutputCurrentType( DWORD dwOutputStreamID, IMFMediaType **ppType ) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidOutputStream(dwOutputStreamID)) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } else if (!m_pOutputType) { hr = MF_E_TRANSFORM_TYPE_NOT_SET; } else { *ppType = m_pOutputType; (*ppType)->AddRef(); } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } // Query if the MFT is accepting more input. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetInputStatus( DWORD dwInputStreamID, DWORD *pdwFlags ) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); if (!IsValidInputStream(dwInputStreamID)) { LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; } // If an input sample is already queued, do not accept another sample until the // client calls ProcessOutput or Flush. // NOTE: It is possible for an MFT to accept more than one input sample. For // example, this might be required in a video decoder if the frames do not // arrive in temporal order. In the case, the decoder must hold a queue of // samples. For the video effect, each sample is transformed independently, so // there is no reason to queue multiple input samples. if (m_pSample == nullptr) { *pdwFlags = MFT_INPUT_STATUS_ACCEPT_DATA; } else { *pdwFlags = 0; } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return S_OK; } // Query if the MFT can produce output. HRESULT CGrayscale::GetOutputStatus(DWORD *pdwFlags) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); // The MFT can produce an output sample if (and only if) there an input sample. if (m_pSample != nullptr) { *pdwFlags = MFT_OUTPUT_STATUS_SAMPLE_READY; } else { *pdwFlags = 0; } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return S_OK; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // SetOutputBounds // Sets the range of time stamps that the MFT will output. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::SetOutputBounds( LONGLONG hnsLowerBound, LONGLONG hnsUpperBound ) { // Implementation of this method is optional. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // ProcessEvent // Sends an event to an input stream. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::ProcessEvent( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFMediaEvent *pEvent ) { // This MFT does not handle any stream events, so the method can // return E_NOTIMPL. This tells the pipeline that it can stop // sending any more events to this MFT. return E_NOTIMPL; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // ProcessMessage //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::ProcessMessage( MFT_MESSAGE_TYPE eMessage, ULONG_PTR ulParam ) { EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); HRESULT hr = S_OK; switch (eMessage) { case MFT_MESSAGE_COMMAND_FLUSH: // Flush the MFT. hr = OnFlush(); break; case MFT_MESSAGE_COMMAND_DRAIN: // Drain: Tells the MFT to reject further input until all pending samples are // processed. That is our default behavior already, so there is nothing to do. // // For a decoder that accepts a queue of samples, the MFT might need to drain // the queue in response to this command. break; case MFT_MESSAGE_SET_D3D_MANAGER: // Sets a pointer to the IDirect3DDeviceManager9 interface. // The pipeline should never send this message unless the MFT sets the MF_SA_D3D_AWARE // attribute set to TRUE. Because this MFT does not set MF_SA_D3D_AWARE, it is an error // to send the MFT_MESSAGE_SET_D3D_MANAGER message to the MFT. Return an error code in // this case. // NOTE: If this MFT were D3D-enabled, it would cache the IDirect3DDeviceManager9 // pointer for use during streaming. hr = E_NOTIMPL; break; case MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_BEGIN_STREAMING: hr = BeginStreaming(); break; case MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_END_STREAMING: hr = EndStreaming(); break; // The next two messages do not require any action from this MFT. case MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_END_OF_STREAM: break; case MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_START_OF_STREAM: break; } LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } // Process an input sample. HRESULT CGrayscale::ProcessInput( DWORD dwInputStreamID, IMFSample *pSample, DWORD dwFlags ) { if (dwFlags != 0) { return E_INVALIDARG; // dwFlags is reserved and must be zero. } HRESULT hr = S_OK; EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); // Validate the input stream number. if (!IsValidInputStream(dwInputStreamID)) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDSTREAMNUMBER; goto done; } // Check for valid media types. // The client must set input and output types before calling ProcessInput. if (!m_pInputType || !m_pOutputType) { hr = MF_E_NOTACCEPTING; goto done; } // Check if an input sample is already queued. if (m_pSample != nullptr) { hr = MF_E_NOTACCEPTING; // We already have an input sample. goto done; } // Initialize streaming. hr = BeginStreaming(); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Cache the sample. We do the actual work in ProcessOutput. m_pSample = pSample; pSample->AddRef(); // Hold a reference count on the sample. done: LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } //------------------------------------------------------------------- // ProcessOutput // Process an output sample. //------------------------------------------------------------------- HRESULT CGrayscale::ProcessOutput( DWORD dwFlags, DWORD cOutputBufferCount, MFT_OUTPUT_DATA_BUFFER *pOutputSamples, // one per stream DWORD *pdwStatus ) { // Check input parameters... // This MFT does not accept any flags for the dwFlags parameter. // The only defined flag is MFT_PROCESS_OUTPUT_DISCARD_WHEN_NO_BUFFER. This flag // applies only when the MFT marks an output stream as lazy or optional. But this // MFT has no lazy or optional streams, so the flag is not valid. if (dwFlags != 0) { return E_INVALIDARG; } // There must be exactly one output buffer. if (cOutputBufferCount != 1) { return E_INVALIDARG; } // It must contain a sample. if (pOutputSamples[0].pSample == nullptr) { return E_INVALIDARG; } HRESULT hr = S_OK; IMFMediaBuffer *pInput = nullptr; IMFMediaBuffer *pOutput = nullptr; EnterCriticalSection(&m_critSec); // There must be an input sample available for processing. if (m_pSample == nullptr) { hr = MF_E_TRANSFORM_NEED_MORE_INPUT; goto done; } // Initialize streaming. hr = BeginStreaming(); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Get the input buffer. hr = m_pSample->ConvertToContiguousBuffer(&pInput); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Get the output buffer. hr = pOutputSamples[0].pSample->ConvertToContiguousBuffer(&pOutput); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } hr = OnProcessOutput(pInput, pOutput); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Set status flags. pOutputSamples[0].dwStatus = 0; *pdwStatus = 0; // Copy the duration and time stamp from the input sample, if present. LONGLONG hnsDuration = 0; LONGLONG hnsTime = 0; if (SUCCEEDED(m_pSample->GetSampleDuration(&hnsDuration))) { hr = pOutputSamples[0].pSample->SetSampleDuration(hnsDuration); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } } if (SUCCEEDED(m_pSample->GetSampleTime(&hnsTime))) { hr = pOutputSamples[0].pSample->SetSampleTime(hnsTime); } done: SafeRelease(&m_pSample); // Release our input sample. SafeRelease(&pInput); SafeRelease(&pOutput); LeaveCriticalSection(&m_critSec); return hr; } // PRIVATE METHODS // All methods that follow are private to this MFT and are not part of the IMFTransform interface. // Create a partial media type from our list. // // dwTypeIndex: Index into the list of peferred media types. // ppmt: Receives a pointer to the media type. HRESULT CGrayscale::OnGetPartialType(DWORD dwTypeIndex, IMFMediaType **ppmt) { if (dwTypeIndex >= ARRAYSIZE(g_MediaSubtypes)) { return MF_E_NO_MORE_TYPES; } IMFMediaType *pmt = nullptr; HRESULT hr = MFCreateMediaType(&pmt); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } hr = pmt->SetGUID(MF_MT_MAJOR_TYPE, MFMediaType_Video); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } hr = pmt->SetGUID(MF_MT_SUBTYPE, g_MediaSubtypes[dwTypeIndex]); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } *ppmt = pmt; (*ppmt)->AddRef(); done: SafeRelease(&pmt); return hr; } // Validate an input media type. HRESULT CGrayscale::OnCheckInputType(IMFMediaType *pmt) { assert(pmt != nullptr); HRESULT hr = S_OK; // If the output type is set, see if they match. if (m_pOutputType != nullptr) { DWORD flags = 0; hr = pmt->IsEqual(m_pOutputType, &flags); // IsEqual can return S_FALSE. Treat this as failure. if (hr != S_OK) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDMEDIATYPE; } } else { // Output type is not set. Just check this type. hr = OnCheckMediaType(pmt); } return hr; } // Validate an output media type. HRESULT CGrayscale::OnCheckOutputType(IMFMediaType *pmt) { assert(pmt != nullptr); HRESULT hr = S_OK; // If the input type is set, see if they match. if (m_pInputType != nullptr) { DWORD flags = 0; hr = pmt->IsEqual(m_pInputType, &flags); // IsEqual can return S_FALSE. Treat this as failure. if (hr != S_OK) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDMEDIATYPE; } } else { // Input type is not set. Just check this type. hr = OnCheckMediaType(pmt); } return hr; } // Validate a media type (input or output) HRESULT CGrayscale::OnCheckMediaType(IMFMediaType *pmt) { BOOL bFoundMatchingSubtype = FALSE; // Major type must be video. GUID major_type; HRESULT hr = pmt->GetGUID(MF_MT_MAJOR_TYPE, &major_type); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } if (major_type != MFMediaType_Video) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDMEDIATYPE; goto done; } // Subtype must be one of the subtypes in our global list. // Get the subtype GUID. GUID subtype; hr = pmt->GetGUID(MF_MT_SUBTYPE, &subtype); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Look for the subtype in our list of accepted types. for (DWORD i = 0; i < ARRAYSIZE(g_MediaSubtypes); i++) { if (subtype == g_MediaSubtypes[i]) { bFoundMatchingSubtype = TRUE; break; } } if (!bFoundMatchingSubtype) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDMEDIATYPE; // The MFT does not support this subtype. goto done; } // Reject single-field media types. UINT32 interlace = MFGetAttributeUINT32(pmt, MF_MT_INTERLACE_MODE, MFVideoInterlace_Progressive); if (interlace == MFVideoInterlace_FieldSingleUpper || interlace == MFVideoInterlace_FieldSingleLower) { hr = MF_E_INVALIDMEDIATYPE; } done: return hr; } // Set or clear the input media type. // // Prerequisite: The input type was already validated. void CGrayscale::OnSetInputType(IMFMediaType *pmt) { // if pmt is nullptr, clear the type. // if pmt is non-nullptr, set the type. SafeRelease(&m_pInputType); m_pInputType = pmt; if (m_pInputType) { m_pInputType->AddRef(); } // Update the format information. UpdateFormatInfo(); } // Set or clears the output media type. // // Prerequisite: The output type was already validated. void CGrayscale::OnSetOutputType(IMFMediaType *pmt) { // If pmt is nullptr, clear the type. Otherwise, set the type. SafeRelease(&m_pOutputType); m_pOutputType = pmt; if (m_pOutputType) { m_pOutputType->AddRef(); } } // Initialize streaming parameters. // // This method is called if the client sends the MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_BEGIN_STREAMING // message, or when the client processes a sample, whichever happens first. HRESULT CGrayscale::BeginStreaming() { HRESULT hr = S_OK; if (!m_bStreamingInitialized) { // Get the configuration attributes. // Get the destination rectangle. RECT rcDest; hr = m_pAttributes->GetBlob(MFT_GRAYSCALE_DESTINATION_RECT, (UINT8*)&rcDest, sizeof(rcDest), nullptr); if (hr == MF_E_ATTRIBUTENOTFOUND || !ValidateRect(rcDest)) { // The client did not set this attribute, or the client provided an invalid rectangle. // Default to the entire image. m_rcDest = D2D1::RectU(0, 0, m_imageWidthInPixels, m_imageHeightInPixels); hr = S_OK; } else if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { m_rcDest = D2D1::RectU(rcDest.left, rcDest.top, rcDest.right, rcDest.bottom); } else { goto done; } // Get the chroma transformations. float scale = (float)MFGetAttributeDouble(m_pAttributes, MFT_GRAYSCALE_SATURATION, 0.0f); float angle = (float)MFGetAttributeDouble(m_pAttributes, MFT_GRAYSCALE_CHROMA_ROTATION, 0.0f); m_transform = D2D1::Matrix3x2F::Scale(scale, scale) * D2D1::Matrix3x2F::Rotation(angle); m_bStreamingInitialized = true; } done: return hr; } // End streaming. // This method is called if the client sends an MFT_MESSAGE_NOTIFY_END_STREAMING // message, or when the media type changes. In general, it should be called whenever // the streaming parameters need to be reset. HRESULT CGrayscale::EndStreaming() { m_bStreamingInitialized = false; return S_OK; } // Generate output data. HRESULT CGrayscale::OnProcessOutput(IMFMediaBuffer *pIn, IMFMediaBuffer *pOut) { BYTE *pDest = nullptr; // Destination buffer. LONG lDestStride = 0; // Destination stride. BYTE *pSrc = nullptr; // Source buffer. LONG lSrcStride = 0; // Source stride. // Helper objects to lock the buffers. VideoBufferLock inputLock(pIn); VideoBufferLock outputLock(pOut); // Stride if the buffer does not support IMF2DBuffer LONG lDefaultStride = 0; HRESULT hr = GetDefaultStride(m_pInputType, &lDefaultStride); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Lock the input buffer. hr = inputLock.LockBuffer(lDefaultStride, m_imageHeightInPixels, &pSrc, &lSrcStride); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Lock the output buffer. hr = outputLock.LockBuffer(lDefaultStride, m_imageHeightInPixels, &pDest, &lDestStride); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Invoke the image transform function. assert (m_pTransformFn != nullptr); if (m_pTransformFn) { (*m_pTransformFn)(m_transform, m_rcDest, pDest, lDestStride, pSrc, lSrcStride, m_imageWidthInPixels, m_imageHeightInPixels); } else { hr = E_UNEXPECTED; goto done; } // Set the data size on the output buffer. hr = pOut->SetCurrentLength(m_cbImageSize); // The VideoBufferLock class automatically unlocks the buffers. done: return hr; } // Flush the MFT. HRESULT CGrayscale::OnFlush() { // For this MFT, flushing just means releasing the input sample. SafeRelease(&m_pSample); return S_OK; } // Update the format information. This method is called whenever the // input type is set. HRESULT CGrayscale::UpdateFormatInfo() { HRESULT hr = S_OK; GUID subtype = GUID_NULL; m_imageWidthInPixels = 0; m_imageHeightInPixels = 0; m_cbImageSize = 0; m_pTransformFn = nullptr; if (m_pInputType != nullptr) { hr = m_pInputType->GetGUID(MF_MT_SUBTYPE, &subtype); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } if (subtype == MFVideoFormat_YUY2) { m_pTransformFn = TransformImage_YUY2; } else if (subtype == MFVideoFormat_UYVY) { m_pTransformFn = TransformImage_UYVY; } else if (subtype == MFVideoFormat_NV12) { m_pTransformFn = TransformImage_NV12; } else { hr = E_UNEXPECTED; goto done; } hr = MFGetAttributeSize(m_pInputType, MF_MT_FRAME_SIZE, &m_imageWidthInPixels, &m_imageHeightInPixels); if (FAILED(hr)) { goto done; } // Calculate the image size (not including padding) hr = GetImageSize(subtype.Data1, m_imageWidthInPixels, m_imageHeightInPixels, &m_cbImageSize); } done: return hr; } // Calculate the size of the buffer needed to store the image. // fcc: The FOURCC code of the video format. HRESULT GetImageSize(DWORD fcc, UINT32 width, UINT32 height, DWORD* pcbImage) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; switch (fcc) { case FOURCC_YUY2: case FOURCC_UYVY: // check overflow if ((width > MAXDWORD / 2) || (width * 2 > MAXDWORD / height)) { hr = E_INVALIDARG; } else { // 16 bpp *pcbImage = width * height * 2; } break; case FOURCC_NV12: // check overflow if ((height/2 > MAXDWORD - height) || ((height + height/2) > MAXDWORD / width)) { hr = E_INVALIDARG; } else { // 12 bpp *pcbImage = width * (height + (height/2)); } break; default: hr = E_FAIL; // Unsupported type. } return hr; } // Get the default stride for a video format. HRESULT GetDefaultStride(IMFMediaType *pType, LONG *plStride) { LONG lStride = 0; // Try to get the default stride from the media type. HRESULT hr = pType->GetUINT32(MF_MT_DEFAULT_STRIDE, (UINT32*)&lStride); if (FAILED(hr)) { // Attribute not set. Try to calculate the default stride. GUID subtype = GUID_NULL; UINT32 width = 0; UINT32 height = 0; // Get the subtype and the image size. hr = pType->GetGUID(MF_MT_SUBTYPE, &subtype); if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { hr = MFGetAttributeSize(pType, MF_MT_FRAME_SIZE, &width, &height); } if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { if (subtype == MFVideoFormat_NV12) { lStride = width; } else if (subtype == MFVideoFormat_YUY2 || subtype == MFVideoFormat_UYVY) { lStride = ((width * 2) + 3) & ~3; } else { hr = E_INVALIDARG; } } // Set the attribute for later reference. if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { (void)pType->SetUINT32(MF_MT_DEFAULT_STRIDE, UINT32(lStride)); } } if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { *plStride = lStride; } return hr; } // Validate that a rectangle meets the following criteria: // // - All coordinates are non-negative. // - The rectangle is not flipped (top > bottom, left > right) // // These are the requirements for the destination rectangle. bool ValidateRect(const RECT& rc) { if (rc.left < 0 || rc.top < 0) { return false; } if (rc.left > rc.right || rc.top > rc.bottom) { return false; } return true; }Fügen Sie dem Projekt eine neue Moduldefinitionsdatei hinzu, nennen Sie sie
GrayscaleTransform.def, und fügen Sie dann diesen Code hinzu:EXPORTS DllCanUnloadNow PRIVATE DllGetActivationFactory PRIVATE DllGetClassObject PRIVATEVerwenden Sie den folgenden Code, um den Inhalt von
dllmain.cpp:#include "pch.h" #include <initguid.h> #include <wrl\module.h> using namespace Microsoft::WRL; STDAPI_(BOOL) DllMain(_In_ HINSTANCE hInstance, _In_ DWORD reason, _In_opt_ void *reserved) { if (DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH == reason) { DisableThreadLibraryCalls(hInstance); } return TRUE; } STDAPI DllGetActivationFactory(_In_ HSTRING activatibleClassId, _COM_Outptr_ IActivationFactory **factory) { return Module<InProc>::GetModule().GetActivationFactory(activatibleClassId, factory); } STDAPI DllCanUnloadNow() { return Module<InProc>::GetModule().Terminate() ? S_OK : S_FALSE; } STDAPI DllGetClassObject(_In_ REFCLSID rclsid, _In_ REFIID riid, _COM_Outptr_ void **ppv) { return Module<InProc>::GetModule().GetClassObject(rclsid, riid, ppv); }Legen Sie im Dialogfeld Eigenschaftenseiten des Projekts die folgenden Linker-Eigenschaften fest.
Geben Sie unter "Eingabe" für die Moduldefinitionsdatei an
GrayScaleTransform.def.Außerdem fügen Sie unter "Eingabe", "Hinzufügen
runtimeobject.libmfuuid.lib" undmfplat.libzur Eigenschaft "Additional Dependencies" hinzu.Legen Sie unter Windows-Metadaten "Windows-Metadaten generieren" auf "Ja" (/WINMD) fest.
So verwenden Sie die WRL-Komponente der benutzerdefinierten Media Foundation-Komponente aus einer C#-App
Fügen Sie der
MediaCaptureProjektmappe ein neues C#-Projekt für leere App (Universelle Windows-App) hinzu. Nennen Sie das Projekt, z. B. MediaCapture.Fügen Sie im MediaCapture-Projekt einen Verweis auf das
GrayscaleTransformProjekt hinzu. Informationen dazu finden Sie unter How to: Add or remove references by using the reference manager.Package.appxmanifestWählen Sie auf der Registerkarte "Funktionen" die Option "Mikrofon" und "Webcam" aus. Beide Funktionen sind erforderlich, um Fotos von der Webcam zu erfassen.Fügen
MainPage.xamlSie in diesem Code dem StammelementGridhinzu:<StackPanel> <TextBlock x:Name="StatusBlock" Margin="10,10,0,0"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="1" Margin="0,10,0,0"> <Button x:Name="StartDevice" Click="StartDevice_Click" IsEnabled="true" Margin="10,0,10,0">StartDevice</Button> <Button x:Name="TakePhoto" Click="TakePhoto_Click" IsEnabled="false" Margin="0,0,10,0">TakePhoto</Button> </StackPanel> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="2" Margin="0,10,0,0"> <CheckBox x:Name="AddRemoveEffect" Margin="10,0,10,0" Content="Grayscale effect" IsEnabled="False" Checked="AddRemoveEffect_Checked" Unchecked="AddRemoveEffect_Unchecked"/> </StackPanel> <Image x:Name="CapturedImage" Width="320" Height="240" Margin="10,10,0,0" HorizontalAlignment="Left"/> </StackPanel>Verwenden Sie den folgenden Code, um den Inhalt von
MainPage.xaml.cs:using System; using Windows.Devices.Enumeration; using Windows.Media.Capture; using Windows.Media.Effects; using Windows.Media.MediaProperties; using Windows.Storage.Streams; using Windows.UI; using Windows.UI.Xaml; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Media; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Media.Imaging; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Navigation; namespace MediaCapture { public sealed partial class MainPage : Page { // Captures photos from the webcam. private Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCapture mediaCapture; // Used to display status messages. private Brush statusBrush = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Green); // Used to display error messages. private Brush exceptionBrush = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Red); public MainPage() { this.InitializeComponent(); } // Shows a status message. private void ShowStatusMessage(string text) { StatusBlock.Foreground = statusBrush; StatusBlock.Text = text; } // Shows an error message. private void ShowExceptionMessage(Exception ex) { StatusBlock.Foreground = exceptionBrush; StatusBlock.Text = ex.Message; } // Click event handler for the "Start Device" button. private async void StartDevice_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { try { StartDevice.IsEnabled = false; // Enumerate webcams. ShowStatusMessage("Enumerating webcams..."); var devInfoCollection = await DeviceInformation.FindAllAsync(DeviceClass.VideoCapture); if (devInfoCollection.Count == 0) { ShowStatusMessage("No webcams found"); return; } // Initialize the MediaCapture object, choosing the first found webcam. mediaCapture = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCapture(); var settings = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCaptureInitializationSettings(); settings.VideoDeviceId = devInfoCollection[0].Id; await mediaCapture.InitializeAsync(settings); // We can now take photos and enable the grayscale effect. TakePhoto.IsEnabled = true; AddRemoveEffect.IsEnabled = true; ShowStatusMessage("Device initialized successfully"); } catch (Exception ex) { ShowExceptionMessage(ex); } } // Takes a photo from the webcam and displays it. private async void TakePhoto_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { try { ShowStatusMessage("Taking photo..."); TakePhoto.IsEnabled = false; // Capture the photo to an in-memory stream. var photoStream = new InMemoryRandomAccessStream(); await mediaCapture.CapturePhotoToStreamAsync(ImageEncodingProperties.CreateJpeg(), photoStream); ShowStatusMessage("Create photo file successful"); // Display the photo. var bmpimg = new BitmapImage(); photoStream.Seek(0); await bmpimg.SetSourceAsync(photoStream); CapturedImage.Source = bmpimg; TakePhoto.IsEnabled = true; ShowStatusMessage("Photo taken"); } catch (Exception ex) { ShowExceptionMessage(ex); TakePhoto.IsEnabled = true; } } // Enables the grayscale effect. private async void AddRemoveEffect_Checked(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { try { AddRemoveEffect.IsEnabled = false; VideoEffectDefinition def = new VideoEffectDefinition("GrayscaleTransform.GrayscaleEffect"); await mediaCapture.AddVideoEffectAsync(def, MediaStreamType.Photo); ShowStatusMessage("Add effect to video preview successful"); AddRemoveEffect.IsEnabled = true; } catch (Exception ex) { ShowExceptionMessage(ex); } } // Removes the grayscale effect. private async void AddRemoveEffect_Unchecked(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { try { AddRemoveEffect.IsEnabled = false; await mediaCapture.ClearEffectsAsync(Windows.Media.Capture.MediaStreamType.Photo); ShowStatusMessage("Remove effect from preview successful"); AddRemoveEffect.IsEnabled = true; } catch (Exception ex) { ShowExceptionMessage(ex); } } } }
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt die MediaCapture app.
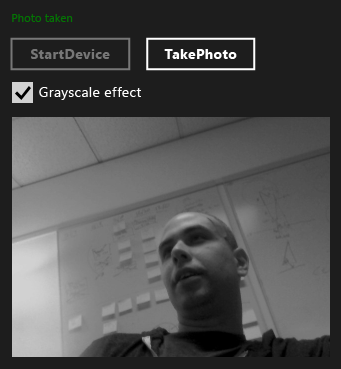
Nächste Schritte
Im Beispiel wird gezeigt, wie Fotos von der standardmäßigen Webcam nacheinander erfasst werden. Das Beispiel für Medienerweiterungen bietet mehr Möglichkeiten. Es veranschaulicht, wie Sie Webcamgeräte aufzählen und mit lokalen Schemahandlern arbeiten. Das Beispiel zeigt auch andere Medieneffekte, die sowohl auf einzelnen Fotos als auch auf Videostreams funktionieren.
Siehe auch
C++-Vorlagenbibliothek für Windows-Runtime (WRL)
Microsoft Media Foundation