[UPDATED] Kerberos - SharePoint 2013, SQL 2012 / 2014 (Always on) for Business Intelligence
This article has now been updated to include SQL 2014 Always On availability groups requirements
Link to the SPC14 presentation on this topic I presented with John Cole in Las Vegas in 2014.
https://channel9.msdn.com/events/SharePoint-Conference/2014/SPC422?term=kerberos
FOCUS AND CONTEXT
This article is focused on SharePoint 2013 but the same rules can be applied to SharePoint 2010 with some restrictions.
This is not a why or what is Kerberos article as that is well documented already in https://download.microsoft.com/download/B/B/F/BBF0C6F3-6E36-4979-8C43-DE165AD7AE34/SP2010%20Kerberos%20Guide.docx
The focus of this article is that you would like to configure Kerberos for all the BI functionality in SharePoint. It is a step by step checklist to ensure your Kerberos configuration is correct.
It also focuses on configuring as few items as possible so that you do not have to set 100's of Service principle names as that leads to lower security, duplication and misconfiguration.
I have highlighted in orange where I show examples of my account names and URL's which must be replaced by your account names and URL's
The highlights in blue are important points to note.
IF YOU WOULD LIKE A STEP BY STEP PRESENTATION THIS IS AVAILABLE ON CHANNEL9.MSDN.COM (https://channel9.msdn.com/Events/SharePoint-Conference/2014/SPC422)
SQL 2012 / 2014 IMPACT
There are some fundamental changes in SQL 2012 / 2014 that affect SharePoint and as such the Kerberos configuration requirements are simpler.
Reporting services has always been the caveat as it has never actually been managed by SharePoint.
With SQL 2012 / 2014, Reporting services is now a Service Application in SharePoint and is therefore managed by SharePoint.
This means that it is load balanced by SharePoint, requires constrained delegation and as such does not have a separate Reporting Services Config file to update.
The new reporting Services mode is called SQL Reporting Services SharePoint Mode (previously known as Integrated Mode).
I will therefore detail the configuration using Constrained Delegation for all components as I do not see the point of using mixed delegation i.e. Constrained and Basic together as most BI components in SharePoint 2013 require Constrained.
NOTES
The details below make a few assumptions:
- Recommended Practices have been followed,
- All services have been configured with an AD Service Account
Whilst services can run with Local system it is not a recommended practice and does complicate the Kerberos configuration - All configuration requirements for Kerberos are configured on all SharePoint servers in the farm regardless of role.
- This configuration details configuring Kerberos for 1 web application in the Farm. If you need more then you will need to setup a URL for each.
- SharePoint services must not be updated in the services console – USE THE SHAREPOINT UI ONLY.
REQUIRED STEPS
Identify all data sources i.e. where will you be getting your data from? (SQL, SQL Analysis Services, etc.)
While this seems obvious, every customer I have ever been to fails to declare all sources
You will need Server Name + Instance, Port (SQL only) and Service Account used that is physically running the service (If it is Local System then it is not configured correctly and must be changed to an AD Service Account)
e.g. SQL01\SP_Instance port 40000 Service Account svc_SQLServiceCreate a friendly URL and register it in DNS e.g. BI.BLUE.COM (replace with your URL on your Domain).
This should be registered in DNS as a Host A record (Not a CNAME) and the IP should be the Web Front End or if using a Load Balancer then your load Balancer IP.Configure Claims to Windows Token Service Account.
Create an AD account to be used by the Claims to Windows Token Service Account e.g. SP_C2WTS
Open a SharePoint PowerShell prompt as Administrator and run the following command:
$w = Get-SPWebApplication -Identity https://bi.blue.com (Put the URL of your web application)
$w.GrantAccessToProcessIdentity("blue\sp_c2wts") (Put your service account name)- Change the account in the SharePoint UI running the Claims to Windows token Service
- Navigate to Security in Central Admin,
- Click on managed Accounts and add the new C2WTS account as a Managed Account,
- Click Security again and Click on Service Accounts,
- Click the Drop Down and Select Claims to Windows Token Service,
- Select the new Managed Account SP_C2WTS and click OK. (Wait a few minutes for it to complete)
- Set the following permissions on all SharePoint servers in the farm (All must be done) – this is completed under Local Security Policy on each server
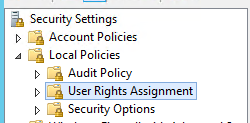
- Grant Log on as a service (this should have happened automatically)
- Impersonate a User (this should have happened automatically)
- Act as part of the operating system (If its greyed out then your domain admin will need to update the group policy to allow it)
- Local admin on all SharePoint servers
- STOP and START the Claims to Windows Token Service (From SharePoint UI) on all servers in the Farm. Simply navigate to Services in Farm and select each server from the link in the top right corner and Stop and Start each one individually waiting for them to finish
- Change the account in the SharePoint UI running the Claims to Windows token Service
Grant permission for the account running the application pool for the Service Application
e.g. Excel Services Service Application, Reporting Services Service Application, etc.
- For Analysis services this User must be Granted SQL Analysis Services Administrator access (Unfortunately this is required as Read permission is insufficient for the delegation of credentials)
- Check which account is being used by navigating to Central Admin Security and then select Service Accounts and from the drop down list validate each service or application pool.
- In my example I have an account SP_Services and that account is granted Admin permissions on Analysis Services and granted “SP_DataAccess” on SQL to the SharePoint web application content database(s).
- Validate that the account has the following permissions on each SharePoint server
(This should be completed automatically but should be validated under the Local Security Policy)- Grant Log on as a service
- Impersonate a User
- Grant process identity access to the Service account
$w = Get-SPWebApplication -Identity https://bi.blue.com (Put the URL of your web application)
$w.GrantAccessToProcessIdentity("blue\sp_Services") (Put your service account name)
If using PowerPivot – Setup the PowerPivot account
Change the account running the PowerPivot browser service to use an AD Account
(This is completed through the SQL Server Configuration manager) and restart the service (This will take a few minutes and it will not be accessible during this time).Check for existing Service Principal Name
(check each account prior to configuring as some may already exist and duplicates / misconfiguration break Kerberos)
This also impacts SQL connectivity as misconfiguration of Kerberos will throw invalid SSPI context errors in SQL as SQL will automatically use Kerberos if SPN’s are registered. It also self-registers the SPN’s if Local System is used.
SPN’s have to be set for the NetBIOS (Short name) and FQDN (Fully qualified name)
e.g. SETSPN –S HTTP/bi.blue.com blue\sp_webapp, SETSPN –S HTTP/bi blue\sp_webappConfigure SPN's
CONFIGURE SPN'S (SHAREPOINT SQL SERVER)
[REQUIRED FOR SQL SERVER FOR SHAREPOINT DATABASES - NOT REQUIRED FOR SQL ALWAYS ON AVAILABILITY GROUPS]
Details required: SQL Instance name, Static Port and SQL Service account
e.g. My SQL instance is SQL01\SQL2012 and my service account is SP_SQL and my port is 40000 (Replace the red with your server and account details).
The 1st one is on my instance name
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQL01:SQL2012 SP_SQL
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQL01.blue.com:SQL2012 SP_SQLand the 2nd one is on port
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQL01:40000 SP_SQL
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQL01.blue.com:40000 SP_SQL[REQUIRED FOR SQL 2014 ALWAYS ON AVAILABILITY GROUPS ONLY - this is required as a Listener registers in DNS exactly the same as a server name] This section Details required: Listener name only
e.g. My Listener is SQLSYNCLISTEN and my service account is SP_SQL and my port is 1433 (This must be 1433 or you will need to use a SQL Alias as a SQL Listener does not use SQL Browser).The 1st one is the SQL Listener without a port
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLSYNCLISTEN SP_SQL
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLSYNCLISTEN.blue.com SP_SQLand the 2nd one is with the port [If you use a SQL Alias then any port can be used but then replace 1433 below with the new port number]
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLSYNCLISTEN:1433 SP_SQL
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLSYNCLISTEN.blue.com:1433 SP_SQLCONFIGURE SPN'S (SQL Analysis Services Multidimensional) (Server name and Instance required)
e.g. SQLAS01\Multi
setspn -s MSOLAPSvc.3/SQLAS01:MULTI SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPSvc.3/SQLAS01.blue.com:MULTI SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPDisco.3/SQLAS01 SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPDisco.3/SQLAS01.blue.com SQL_ASCONFIGURE SPN'S (SQL Analysis Services Tabular)
(Server name and Instance required)
e.g. SQLAS01\Tabular
setspn -s MSOLAPSvc.3/SQLAS01:Tabular SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPSvc.3/SQLAS01.blue.com:Tabular SQL_ASCONFIGURE SPN'S (SQL Analysis Services PowerPivot)
(Server name and Instance required - POWERPIVOT)
e.g. APP01\POWERPIVOT
setspn -s MSOLAPSvc.3/APP01:POWERPIVOT SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPSvc.3/APP01.blue.com:POWERPIVOT SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPDisco.3/APP01 SQL_AS
setspn -s MSOLAPDisco.3/APP01.blue.com SQL_ASCONFIGURE SPN'S (SQL Server - DataWarehouse)
(Server name, Instance and Port is required)
e.g. SQLAS01\SQL_SQLDW and my port is 41000
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLAS01:SQLDW SQL_SQLDW
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLAS01.blue.com:SQLDW SQL_SQLDW
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLAS01:41000 SQL_SQLDW
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLAS01.blue.com:41000 SQL_SQLDWHOST HEADER / AAM
This is the same DNS entry you already configured)
e.g. https://bi.blue.com and my account is sp_webapp (This is the account that is running the application pool in IIS that requires Kerberos)
setspn -s HTTP/bi.blue.com sp_webapp
setspn -s HTTP/bi sp_webappFAKE SPN
(These are the accounts configured to run the Service Application app pools and the Claims to Windows Token Service)
FAKE SPN’s are used just to enable the delegation tab in Active Directory. (It doesn't matter what you use for the service name here - only the accounts matter)
e.g. sp_services and sp_c2wts
setspn -s SP/EXCEL sp_services
setspn -s SP/C2WTS sp_c2wts
Set Constrained Delegation
(Constrained delegation must be set for any account running the Service Application pools for the services that require Kerberos as well as the Claims to Windows Token Service account and the Account running PowerPivot SQL Service)
In my case this is SP_Services and SP_C2WTS and SQL_AS (only for PowerPivot Data Sources - this is a change with Excel 2013 as the connection refreshes with the worksheet)
The Domain Admin is required here and must log in to a Domain Controller.- Find the SP_Services(Replace with your account name) account and click on the Delegation tab
- Click on “Trust this user for delegation to specified services only”

- Use any authentication protocol
- This is where it can get confusing and you need to make sure you have all your service accounts ready that you setup previously.
(These are the ones you ran SETSPN for)
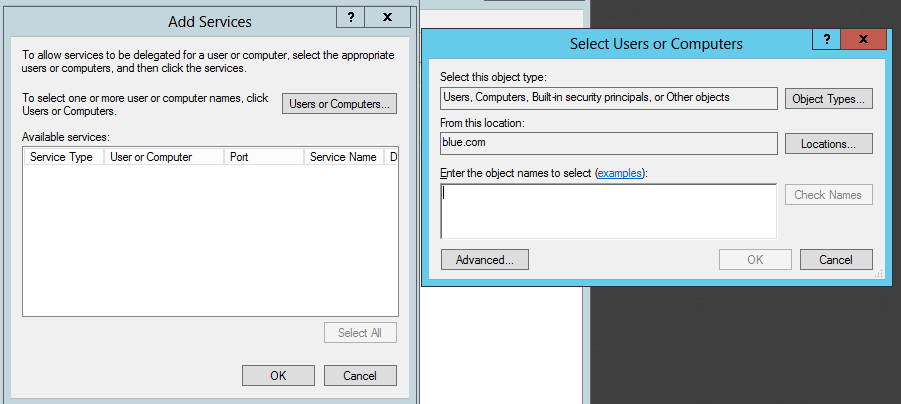
- Start with your first Data Source and type in your service account name (NOT SERVER NAMES) e.g. SP_SQL , SQL_AS, SQLDW_SQL and click OK.

- You will then be prompted with all the SPN’s and you need to select only the ones you need here i.e. the ones that are noted above.
- The worst case scenario here is if the account you use is utilized for many services and you will see many SPN's.
- Select the required SPN’s (The ones you added above) and click ok.
- Click “Apply” button after each add i.e. when you want to select another account otherwise you will get an error.

- Repeat this process selecting each account that you need to delegate to i.e. all the data sources and the web application. It’s all about where you want to allow it to delegate to.
- Now select the Claims to Windows Token Service Account e.g. SP_C2WTS (Replace with your account) and repeat the exact steps you did for the SP_Services account. (Technically for the SP_C2WTS you can exclude the Web Application but for simplicity sake I made the process the same)
- For my PowerPivot Service account SQL_AS I was connecting to a SQL Data Warehouse and my Analysis Services so you only set constrained for the destination data source so in my case I looked up SQL_SQLDW and "selected all", clicked ok and applied constrained delegation.
- Click on “Trust this user for delegation to specified services only”
- Find the SP_Services(Replace with your account name) account and click on the Delegation tab
Change Web Application to Kerberos (NB: Not required for SP2013 - applicable to SP2010 only)
- Navigate to Central Admin,
- Select web applications,
- Highlight the Web application (Do not click on the link – click next to it to highlight it and select it),
- Select Authentication providers and click Windows,
- Scroll down and change NTLM and select Kerberos
- Open a Command Prompt as Administrator and run IISRESET (USERS WILL LOSE CONNECTIVITY AND THEIR CURRENT SESSIONS SO DO THIS DURING SCHEDULED DOWNTIME)
DUPLICATE SPN CHECK SIDE NOTEI have attached a duplicate SPN check script that also assists in listing what you have set against each account.
It will list the Constrained delegation, delegation and duplicate SPN's (If duplicates are detected this means that the service in question will fail to generate a Kerberos context).
- Unzip the attached dhcheck.zip file to dhcheck.vbs (Please note that although this does a READONLY call I cannot take responsibility for it's execution)
- Provide the file to your AD Admin
- They must open an Administrative Command Prompt and execute the command as follows "CScript dhcheck.vbs accountname" (Replace with your Account you want to check)
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
Hi Eugene, In SP2010 the following Service applications / services support basic delegation:
Business Data Connectivity service and Microsoft Business Connectivity Services
InfoPath Forms Services
Access Services
Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) (pre SQL 2012)
Microsoft Project Server 2010
These do not utilize C2WTS which is why they can make use of basic / unconstrained delegation.
In SP2013 any service running as a Service Application and making use of the Claims to Windows Token Service (C2WTS) require Constrained delegation regardless of Classic or Claims.
You will however need to configure the Web App to Kerberos if configured as Classic mode whereas in Claims mode this is not required. - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
Great post! Quick question: Is basic Kerberos (not constrained) delegation supported for SharePoint 2010 or 2013 running in classic (not claims) mode?
Thanks! - Anonymous
May 07, 2015
Finally a description with all aspects needed.
Thank You. - Anonymous
June 02, 2015
You do NOT need to change the web app to Kerberos for the scenarios in this article - this is only required for basic delegation scenarios. - Anonymous
June 02, 2015
Thanks Spence. Should you wish to use PowerShell or if you are looking for a more detailed explanation then it's available on Spencers blog.http://www.harbar.net/archive/2015/06/02/Configuring-Kerberos-Constrained-Delegation-with-Protocol-Transition-and-the-Claims.aspx - Anonymous
June 04, 2015
Thank you for your post. Very clear and very useful.
I have a question: In section 7.a where SPN's are configured for SharePoint Server with Availability Groups, I don;t understand the syntax...
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLSYNCLISTEN SP:1433 SP_SQL
setspn -s MSSQLSvc/SQLSYNCLISTEN SP.blue.com:1433 SP_SQL
What are SP and sp.blue.com? - Anonymous
June 04, 2015
Leonardo, well spotted. The SP was a typo. I have corrected it. Thank you for the feedback. - Anonymous
June 15, 2015
I seem to be confused on the topic of delegation for computer objects. Is it required for delegation to be configured on the SharePoint and SQL server computer objects? I have always thought it was required, but as I have been revisiting our setup documentation I am not seeing a reference in most articles that this is required.
Thanks - Anonymous
June 22, 2015
Hi Jonathan, the only time that is required for the SQL Server is if the SQL service is not running under a standard AD account as per recommended practices. This article assumes that you have followed recommended configuration practices for SQL and therefore the delegation is configured on that Service Account. - Anonymous
July 17, 2015
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
July 17, 2015
Hi Greg, it is always recommended that SQL be configured on static ports. For Kerberos you really do need to do this as delegation settings i.e. SPN's are required for each port. The default port would work but should the port change then the delegation would fail. You may get away with it by creating an SPN for the browser service i.e. MSOLAPSvc.3. You should however follow recommended settings and set static ports in SQL and then configure SPN's for those ports. It is a far cleaner solution. In your case you should really be using 2 SQL accounts anyway, 1 for dev and 1 for Test. You would therefore need 2 SPN's anyway and would be able to troubleshoot a lot easier should something go wrong. - Anonymous
August 08, 2015
Great article, but one important correction:
> 8I. Repeat this process selecting each account that you need to delegate to i.e. all the data sources and the web application. It’s all about where you want to allow it to delegate to.
In delegation, the user is delegating authority to use their credentials to the server. So user delegates to SharePoint Web Server authority to present their credentials to data sources. Essentially "I am allowing you to say you are me to these services"
Another way to think of it - credentials are a police badge. The user shows the badge to the server to be allowed in. Delegation is the user handing the badge to the server to show to other servers.
So step 8l should read
"Repeat this process, selecting each SPN that you need the service account (now holding the user's delegated credentials) to present those credentials to"
Hope that helps. - Anonymous
June 09, 2016
Scott - concerning this comment:Set Constrained Delegation(Constrained delegation must be set for any account running the Service Application pools for the services that require Kerberos as well as the Claims to Windows Token Service account and the Account running PowerPivot SQL Service)In my case this is SP_Services and SP_C2WTS and SQL_AS (only for PowerPivot Data Sources – this is a change with Excel 2013 as the connection refreshes with the worksheet)If using Excel 2013 - is there something different that needs to be done, or is this saying this needs to be done using Excel 2013?- Anonymous
June 09, 2016
Hi Paul.In Excel 2010 the Power Pivot data connection cannot be refreshed from the browser directly i.e. it could only be refreshed via the scheduled data refresh timer job so no Kerberos would be required.Remember that the PowerPivot data is actually embedded within the Excel file so a normal refresh simply loads whatever data is in the PowerPivot data model i.e. it refreshes from the data that it already has.In Excel 2013 however the Power Pivot data connection can be refreshed from the browser and it is on by default.If a user clicks refresh then it will refresh the Power Pivot data model data and then refresh the Excel data from that.For this reason if you want to use this functionality then you would need to setup the account that the PowerPivot - SQL AS (SharePoint mode i.e. PowerPivot) is using.It is not recommended to refresh data in the browser for large datasets as they will crash the browser which is why I really don't like this Excel 2013 change.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
October 14, 2017
Great article)