Microsoft Connected Cache for Enterprise and Education Overview
Important
Microsoft Connected Cache is currently a preview feature. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Microsoft Connected Cache for Enterprise and Education (preview) is a software-only caching solution that delivers Microsoft content within enterprise and education networks. Connected Cache can be managed from the Azure portal or through Azure CLI. It can be deployed to as many Windows devices, Linux devices, or VMs as needed. Managed Windows devices can be configured to download cloud content from a Connected Cache server by applying the client policy using management tools such as Microsoft Intune.
For information about Microsoft Connected Cache in Configuration Manager, see Microsoft Connected Cache in Configuration Manager.
Microsoft Connected Cache deployed directly to Windows relies on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL and either a Group Managed Service Account, local user account, or domain user account are required to run WSL. WSL needs to run in a user context and any user, even if the currently logged-in user, could be used to run WSL and Microsoft Connected Cache.
Supported scenarios and configurations
Microsoft Connected Cache for Enterprise and Education (preview) is intended to support all Windows cloud downloads that use Delivery Optimization including, but not limited to, the following content delivery scenarios:
- Windows Autopilot deployment scenarios
- Co-managed clients that get monthly updates and Win32 apps from Microsoft Intune
- Cloud-only managed devices, such as Intune-enrolled devices without the Configuration Manager client, that get monthly updates and Win32 apps from Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Connected Cache is built for flexible deployments to support several different enterprise configurations:
Branch office
Customers may have globally dispersed offices that meet some or all of the following parameters:
- Have 10 to 50 Windows devices on-site
- Don't have dedicated server hardware
- Have internet bandwidth that is limited (satellite internet)
- Have intermittent internet connectivity
To support the branch office scenario, customers can deploy a Connected Cache node to a Windows 11 client device.
Large Enterprise
Customers may have office spaces, data centers, or Azure deployments that meet some or all of the following parameters:
- Have 100s or 1,000s of Windows devices (desktop or server)
- Have some existing server hardware (Decommissioned Distribution Point, file server, cloud print server)
- Have Azure VMs and/or Azure Virtual Desktop deployed
- Have limited internet bandwidth (T1 or T3 lines)
To support the large enterprise scenario, customers can deploy a Connected Cache node to a server running Windows Server 2022 or Ubuntu 22.04.
See Connected Cache node host machine requirements for recommended host machine specifications in each configuration.
| Enterprise configuration | Download speed range | Download speeds and approximate content volume delivered in 8 Hours |
|---|---|---|
| Branch office | < 1 Gbps Peak | 500 Mbps => 1,800 GB 250 Mbps => 900 GB 100 Mbps => 360 GB 50 Mbps => 180 GB |
| Small to medium enterprises/Autopilot provisioning center (50 - 500 devices in a single location) | 1 - 5 Gbps | 5 Gbps => 18,000 GB 3 Gbps => 10,800 GB 1 Gbps => 3,600 GB |
| Medium to large enterprises/Autopilot provisioning center (500 - 5,000 devices in a single location) | 5 - 10 Gbps Peak | 9 Gbps => 32,400 GB 5 Gbps => 18,000 GB 3 Gbps => 10,800 GB |
Supported content types
When clients download cloud-managed content, they use Delivery Optimization from the cache server installed on a Windows server or VM. Cloud-managed content includes the following types:
- Windows updates: Windows feature and quality updates
- Office Click-to-Run apps: Microsoft 365 Apps and updates
- Client apps: Intune, store apps, and updates
- Endpoint protection: Windows Defender definition updates
For the full list of content endpoints that Microsoft Connected Cache for Enterprise and Education supports, see Microsoft Connected Cache content and services endpoints.
How it works
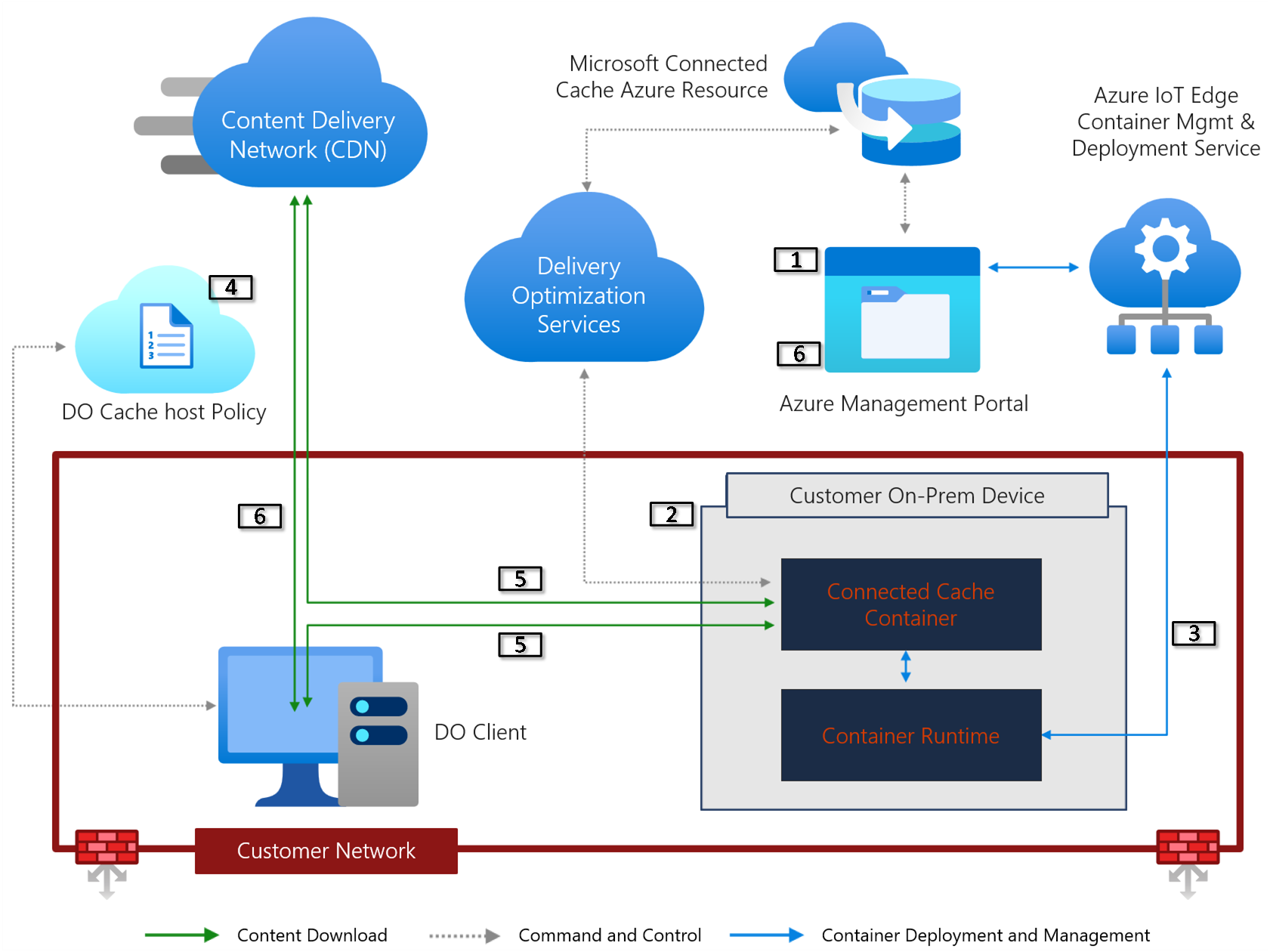
The following diagram displays an overview of how Connected Cache functions:
- The Azure management portal for Microsoft Connected Cache or CLI are used to create cache nodes, configure deployments, including unauthenticated proxy settings.
- Prepare Windows or Linux devices. If deploying to Windows devices, prepare accounts - gMSA, local user account, domain account. Deploy to Windows or Linux devices using scripts.
- The Microsoft Connected Cache container is deployed to the device using Azure IoT Edge container management services and the cache server begins reporting status and metrics to Delivery Optimization services.
- The DOCacheHost setting is configured using Intune or other MDM, DHCP custom option, or registry key.
- Devices request content from the cache server, the cache server forwards the requests to the CDN and fills the cache, the cache server delivers the content requested to the devices, and uses Peer to Peer (depending on DO Download mode settings) for all DO content.
- Devices can fall back to CDN if the cache server is unavailable for any reason or use Delivery Optimization delay fallback to http (CDN) settings to prefer the local cache server. You can view data about Microsoft Connected Cache downloads on management portal and Windows Update for Business reports.