InteractionTracker.PositionInertiaDecayRate Property
Definition
Important
Some information relates to prerelease product that may be substantially modified before it’s released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
Inertia decay rate for position. Range is from 0 to 1.
The PositionInertiaDecayRate property defines the rate at which InteractionTracker will slow to a stop when it has entered Inertia and position is changing. The closer to 1, the faster InteractionTracker will slow to a stop and vice versa. Defined as a Vector3, each component represents the inertia decay rate for x, y, z accordingly.
public:
property IReference<float3> ^ PositionInertiaDecayRate { IReference<float3> ^ get(); void set(IReference<float3> ^ value); };IReference<float3> PositionInertiaDecayRate();
void PositionInertiaDecayRate(IReference<float3> value);public System.Nullable<Vector3> PositionInertiaDecayRate { get; set; }var iReference = interactionTracker.positionInertiaDecayRate;
interactionTracker.positionInertiaDecayRate = iReference;Public Property PositionInertiaDecayRate As Nullable(Of Vector3)Property Value
Inertia decay rate for position. Range is from 0 to 1.
Examples
void SetupInteractionTracker()
{
// Setup InteractionTracker
_tracker = InteractionTracker.Create(_compositor);
// Set the PositionInertiaDecayRate value
_tracker.PositionInertiaDecayRate = new Vector3(0.95f);
}
Remarks
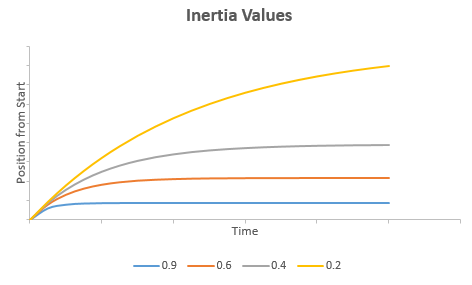
Below is a graph of the equation that models the PositionInertiaDecayRate property against the position from the starting position of InteractionTracker after entering inertia. Note that as the value of the property approaches 1, the impact of inertia increases more significantly.
In the graph, time is on the X axis, and position from the start of the interaction is on the Y. Notice that with a much larger value (closer to 1), the position from start is much smaller and plateaus earlier.