Speech recognition using Azure Speech Service
Azure Speech Service is a cloud-based API that offers the following functionality:
- Speech-to-text transcribes audio files or streams to text.
- Text-to-speech converts input text into human-like synthesized speech.
- Speech translation enables real-time, multi-language translation for both speech-to-text and speech-to-speech.
- Voice assistants can create human-like conversation interfaces for applications.
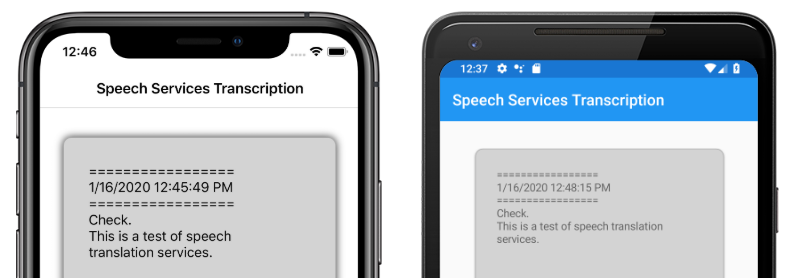
This article explains how speech-to-text is implemented in the sample Xamarin.Forms application using the Azure Speech Service. The following screenshots show the sample application on iOS and Android:
Create an Azure Speech Service resource
Azure Speech Service is part of Azure Cognitive Services, which provides cloud-based APIs for tasks such as image recognition, speech recognition and translation, and Bing search. For more information, see What are Azure Cognitive Services?.
The sample project requires an Azure Cognitive Services resource to be created in your Azure portal. A Cognitive Services resource can be created for a single service, such as Speech Service, or as a multi-service resource. The steps to create a Speech Service resource are as follows:
- Log into your Azure portal.
- Create a multi-service or single-service resource.
- Obtain the API key and region information for your resource.
- Update the sample Constants.cs file.
For a step-by-step guide to creating a resource, see Create a Cognitive Services resource.
Note
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin. Once you have an account, a single-service resource can be created at the free tier to try out the service.
Configure your app with the Speech Service
After creating a Cognitive Services resource, the Constants.cs file can be updated with the region and API key from your Azure resource:
public static class Constants
{
public static string CognitiveServicesApiKey = "YOUR_KEY_GOES_HERE";
public static string CognitiveServicesRegion = "westus";
}
Install NuGet Speech Service package
The sample application uses the Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech NuGet package to connect to the Azure Speech Service. Install this NuGet package in the shared project and each platform project.
Create an IMicrophoneService interface
Each platform requires permission to access to the microphone. The sample project provides an IMicrophoneService interface in the shared project, and uses the Xamarin.Forms DependencyService to obtain platform implementations of the interface.
public interface IMicrophoneService
{
Task<bool> GetPermissionAsync();
void OnRequestPermissionResult(bool isGranted);
}
Create the page layout
The sample project defines a basic page layout in the MainPage.xaml file. The key layout elements are a Button that starts the transcription process, a Label to contain the transcribed text, and an ActivityIndicator to show when transcription is in progress:
<ContentPage ...>
<StackLayout>
<Frame ...>
<ScrollView x:Name="scroll"
...>
<Label x:Name="transcribedText"
... />
</ScrollView>
</Frame>
<ActivityIndicator x:Name="transcribingIndicator"
IsRunning="False" />
<Button x:Name="transcribeButton"
...
Clicked="TranscribeClicked"/>
</StackLayout>
</ContentPage>
Implement the Speech Service
The MainPage.xaml.cs code-behind file contains all of the logic to send audio and receive transcribed text from the Azure Speech Service.
The MainPage constructor gets an instance of the IMicrophoneService interface from the DependencyService:
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
SpeechRecognizer recognizer;
IMicrophoneService micService;
bool isTranscribing = false;
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
micService = DependencyService.Resolve<IMicrophoneService>();
}
// ...
}
The TranscribeClicked method is called when the transcribeButton instance is tapped:
async void TranscribeClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool isMicEnabled = await micService.GetPermissionAsync();
// EARLY OUT: make sure mic is accessible
if (!isMicEnabled)
{
UpdateTranscription("Please grant access to the microphone!");
return;
}
// initialize speech recognizer
if (recognizer == null)
{
var config = SpeechConfig.FromSubscription(Constants.CognitiveServicesApiKey, Constants.CognitiveServicesRegion);
recognizer = new SpeechRecognizer(config);
recognizer.Recognized += (obj, args) =>
{
UpdateTranscription(args.Result.Text);
};
}
// if already transcribing, stop speech recognizer
if (isTranscribing)
{
try
{
await recognizer.StopContinuousRecognitionAsync();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
UpdateTranscription(ex.Message);
}
isTranscribing = false;
}
// if not transcribing, start speech recognizer
else
{
Device.BeginInvokeOnMainThread(() =>
{
InsertDateTimeRecord();
});
try
{
await recognizer.StartContinuousRecognitionAsync();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
UpdateTranscription(ex.Message);
}
isTranscribing = true;
}
UpdateDisplayState();
}
The TranscribeClicked method does the following:
- Checks if the application has access to the microphone and exits early if it does not.
- Creates an instance of
SpeechRecognizerclass if it doesn't already exist. - Stops continuous transcription if it is in progress.
- Inserts a timestamp and starts continuous transcription if it is not in progress.
- Notifies the application to update its appearance based on the new application state.
The remainder of the MainPage class methods are helpers for displaying the application state:
void UpdateTranscription(string newText)
{
Device.BeginInvokeOnMainThread(() =>
{
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(newText))
{
transcribedText.Text += $"{newText}\n";
}
});
}
void InsertDateTimeRecord()
{
var msg = $"=================\n{DateTime.Now.ToString()}\n=================";
UpdateTranscription(msg);
}
void UpdateDisplayState()
{
Device.BeginInvokeOnMainThread(() =>
{
if (isTranscribing)
{
transcribeButton.Text = "Stop";
transcribeButton.BackgroundColor = Color.Red;
transcribingIndicator.IsRunning = true;
}
else
{
transcribeButton.Text = "Transcribe";
transcribeButton.BackgroundColor = Color.Green;
transcribingIndicator.IsRunning = false;
}
});
}
The UpdateTranscription method writes the provided newText string to the Label element named transcribedText. It forces this update to happen on the UI thread so it can be called from any context without causing exceptions. The InsertDateTimeRecord writes the current date and time to the transcribedText instance to mark the start of a new transcription. Finally, the UpdateDisplayState method updates the Button and ActivityIndicator elements to reflect whether or not transcription is in progress.
Create platform microphone services
The application must have microphone access to collect speech data. The IMicrophoneService interface must be implemented and registered with the DependencyService on each platform for the application to function.
Android
The sample project defines an IMicrophoneService implementation for Android called AndroidMicrophoneService:
[assembly: Dependency(typeof(AndroidMicrophoneService))]
namespace CognitiveSpeechService.Droid.Services
{
public class AndroidMicrophoneService : IMicrophoneService
{
public const int RecordAudioPermissionCode = 1;
private TaskCompletionSource<bool> tcsPermissions;
string[] permissions = new string[] { Manifest.Permission.RecordAudio };
public Task<bool> GetPermissionAsync()
{
tcsPermissions = new TaskCompletionSource<bool>();
if ((int)Build.VERSION.SdkInt < 23)
{
tcsPermissions.TrySetResult(true);
}
else
{
var currentActivity = MainActivity.Instance;
if (ActivityCompat.CheckSelfPermission(currentActivity, Manifest.Permission.RecordAudio) != (int)Permission.Granted)
{
RequestMicPermissions();
}
else
{
tcsPermissions.TrySetResult(true);
}
}
return tcsPermissions.Task;
}
public void OnRequestPermissionResult(bool isGranted)
{
tcsPermissions.TrySetResult(isGranted);
}
void RequestMicPermissions()
{
if (ActivityCompat.ShouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(MainActivity.Instance, Manifest.Permission.RecordAudio))
{
Snackbar.Make(MainActivity.Instance.FindViewById(Android.Resource.Id.Content),
"Microphone permissions are required for speech transcription!",
Snackbar.LengthIndefinite)
.SetAction("Ok", v =>
{
((Activity)MainActivity.Instance).RequestPermissions(permissions, RecordAudioPermissionCode);
})
.Show();
}
else
{
ActivityCompat.RequestPermissions((Activity)MainActivity.Instance, permissions, RecordAudioPermissionCode);
}
}
}
}
The AndroidMicrophoneService has the following features:
- The
Dependencyattribute registers the class with theDependencyService. - The
GetPermissionAsyncmethod checks if permissions are required based on the Android SDK version, and callsRequestMicPermissionsif permission has not already been granted. - The
RequestMicPermissionsmethod uses theSnackbarclass to request permissions from the user if a rationale is required, otherwise it directly requests audio recording permissions. - The
OnRequestPermissionResultmethod is called with aboolresult once the user has responded to the permissions request.
The MainActivity class is customized to update the AndroidMicrophoneService instance when permissions requests are complete:
public class MainActivity : global::Xamarin.Forms.Platform.Android.FormsAppCompatActivity
{
IMicrophoneService micService;
internal static MainActivity Instance { get; private set; }
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
Instance = this;
// ...
micService = DependencyService.Resolve<IMicrophoneService>();
}
public override void OnRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, string[] permissions, [GeneratedEnum] Android.Content.PM.Permission[] grantResults)
{
// ...
switch(requestCode)
{
case AndroidMicrophoneService.RecordAudioPermissionCode:
if (grantResults[0] == Permission.Granted)
{
micService.OnRequestPermissionResult(true);
}
else
{
micService.OnRequestPermissionResult(false);
}
break;
}
}
}
The MainActivity class defines a static reference called Instance, which is required by the AndroidMicrophoneService object when requesting permissions. It overrides the OnRequestPermissionsResult method to update the AndroidMicrophoneService object when the permissions request is approved or denied by the user.
Finally, the Android application must include the permission to record audio in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<manifest ...>
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
</manifest>
iOS
The sample project defines an IMicrophoneService implementation for iOS called iOSMicrophoneService:
[assembly: Dependency(typeof(iOSMicrophoneService))]
namespace CognitiveSpeechService.iOS.Services
{
public class iOSMicrophoneService : IMicrophoneService
{
TaskCompletionSource<bool> tcsPermissions;
public Task<bool> GetPermissionAsync()
{
tcsPermissions = new TaskCompletionSource<bool>();
RequestMicPermission();
return tcsPermissions.Task;
}
public void OnRequestPermissionResult(bool isGranted)
{
tcsPermissions.TrySetResult(isGranted);
}
void RequestMicPermission()
{
var session = AVAudioSession.SharedInstance();
session.RequestRecordPermission((granted) =>
{
tcsPermissions.TrySetResult(granted);
});
}
}
}
The iOSMicrophoneService has the following features:
- The
Dependencyattribute registers the class with theDependencyService. - The
GetPermissionAsyncmethod callsRequestMicPermissionsto request permissions from the device user. - The
RequestMicPermissionsmethod uses the sharedAVAudioSessioninstance to request recording permissions. - The
OnRequestPermissionResultmethod updates theTaskCompletionSourceinstance with the providedboolvalue.
Finally, the iOS app Info.plist must include a message that tells the user why the app is requesting access to the microphone. Edit the Info.plist file to include the following tags within the <dict> element:
<plist>
<dict>
...
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Voice transcription requires microphone access</string>
</dict>
</plist>
UWP
The sample project defines an IMicrophoneService implementation for UWP called UWPMicrophoneService:
[assembly: Dependency(typeof(UWPMicrophoneService))]
namespace CognitiveSpeechService.UWP.Services
{
public class UWPMicrophoneService : IMicrophoneService
{
public async Task<bool> GetPermissionAsync()
{
bool isMicAvailable = true;
try
{
var mediaCapture = new MediaCapture();
var settings = new MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
settings.StreamingCaptureMode = StreamingCaptureMode.Audio;
await mediaCapture.InitializeAsync(settings);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
isMicAvailable = false;
}
if(!isMicAvailable)
{
await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-microphone"));
}
return isMicAvailable;
}
public void OnRequestPermissionResult(bool isGranted)
{
// intentionally does nothing
}
}
}
The UWPMicrophoneService has the following features:
- The
Dependencyattribute registers the class with theDependencyService. - The
GetPermissionAsyncmethod attempts to initialize aMediaCaptureinstance. If that fails, it launches a user request to enable the microphone. - The
OnRequestPermissionResultmethod exists to satisfy the interface but is not required for the UWP implementation.
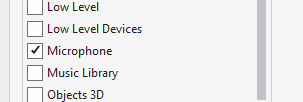
Finally, the UWP Package.appxmanifest must specify that the application uses the microphone. Double-click the Package.appxmanifest file and select the Microphone option on the Capabilities tab in Visual Studio 2019:
Test the application
Run the app and click the Transcribe button. The app should request microphone access and begin the transcription process. The ActivityIndicator will animate, showing that transcription is active. As you speak, the app will stream audio data to the Azure Speech Services resource, which will respond with transcribed text. The transcribed text will appear in the Label element as it is received.
Note
Android emulators fail to load and initialize the Speech Service libraries. Testing on a physical device is recommended for the Android platform.