Saving a Standard Document
Applies to: ![]() Visual Studio
Visual Studio ![]() Visual Studio for Mac
Visual Studio for Mac
Note
This article applies to Visual Studio 2017. If you're looking for the latest Visual Studio documentation, see Visual Studio documentation. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of Visual Studio. Download it here
The environment handles the Save, Save As, and Save All commands. When a user selects Save, Save As, or Save All from the File menu or closes the solution, resulting in a Save All, the following process occurs.
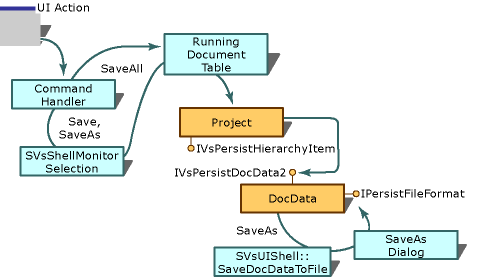 Save, Save As, and Save All command handling for a standard editor
Save, Save As, and Save All command handling for a standard editor
This process is detailed in the following steps:
When the Save and Save As commands are selected, the environment uses the SVsShellMonitorSelection service to determine the active document window and thus what items should be saved. Once the active document window is known, the environment finds the hierarchy pointer and item identifier (itemID) for the document in the running document table. For more information, see Running Document Table.
When the Save All command is selected, the environment uses the information in the running document table to compile the list of all items to save.
When the solution receives an QueryStatus call, it iterates through the set of selected items (that is, the multiple selections exposed by the SVsShellMonitorSelection service).
On each item in the selection, the solution uses the hierarchy pointer to call the IsItemDirty method to determine whether the Save menu command should be enabled. If one or more items are dirty, then the Save command is enabled. If the hierarchy uses a standard editor, then the hierarchy delegates querying for dirty status to the editor by calling the IsDocDataDirty method.
On each selected item that is dirty, the solution uses the hierarchy pointer to call the SaveItem method on the appropriate hierarchies.
It is common for the hierarchy to use a standard editor to edit the document. In this case, the document data object for that editor should support the IVsPersistDocData2 interface. Upon receiving the SaveItem method call, the project should inform the editor that the document is being saved by calling the SaveDocData method on the document data object. The editor can allow the environment to handle the Save As dialog box, by calling
Query Servicefor the SVsUIShell interface. This returns a pointer to the IVsUIShell interface. The editor must then call the SaveDocDataToFile method, passing a pointer to the editor's IPersistFileFormat implementation by means of thepPersistFileparameter. The environment then performs the Save operation and provides the Save As dialog box for the editor. The environment then calls back to the editor with IPersistFileFormat.If the user is attempting to save an untitled document (that is, a previously unsaved document), then a Save As command is actually performed.
For the Save As command, the environment displays the Save As dialog box, prompting the user for a file name.
If the name of the file has changed, then the hierarchy is responsible for updating the document frame's cached information by calling SetProperty(VSFPROPID_MkDocument).
If the Save As command moves the location of the document, and the hierarchy is sensitive to the document location, then the hierarchy is responsible for handing off the ownership of the open document window to another hierarchy. For example, this occurs if the project tracks whether the file is an internal or external file (Miscellaneous File) in relation to the project. Use the following procedure to change ownership of a file to the Miscellaneous Files project.
Changing File Ownership
To change file ownership to the Miscellaneous Files project
Query Service for the SVsExternalFilesManager interface.
A pointer to IVsExternalFilesManager2 is returned.
Call the TransferDocument (
pszMkDocumentNew,punkWindowFrame) method to transfer the document to the new hierarchy. The hierarchy performing the Save As command calls this method.