Execute Python Script
Important
Support for Machine Learning Studio (classic) will end on 31 August 2024. We recommend you transition to Azure Machine Learning by that date.
Beginning 1 December 2021, you will not be able to create new Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources. Through 31 August 2024, you can continue to use the existing Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources.
- See information on moving machine learning projects from ML Studio (classic) to Azure Machine Learning.
- Learn more about Azure Machine Learning.
ML Studio (classic) documentation is being retired and may not be updated in the future.
Executes a Python script from an Machine Learning experiment
Category: Python Language Modules
Note
Applies to: Machine Learning Studio (classic) only
Similar drag-and-drop modules are available in Azure Machine Learning designer.
Module overview
This article describes how to use the Execute Python Script module in Machine Learning Studio (classic) to run Python code. For more information about the architecture and design principles of Python in Studio (classic), see the following article.
With Python, you can perform tasks that aren't currently supported by existing Studio (classic) modules such as:
- Visualizing data using
matplotlib - Using Python libraries to enumerate datasets and models in your workspace
- Reading, loading, and manipulating data from sources not supported by the Import Data module
Machine Learning Studio (classic) uses the Anaconda distribution of Python, which includes many common utilities for data processing.
How to use Execute Python Script
The Execute Python Script module contains sample Python code that you can use as a starting point. To configure the Execute Python Script module, you provide a set of inputs and Python code to execute in the Python script text box.
Add the Execute Python Script module to your experiment.
Scroll to the bottom of the Properties pane, and for Python Version, select the version of the Python libraries and runtime to use in the script.
- Anaconda 2.0 distribution for Python 2.7.7
- Anaconda 4.0 distribution for Python 2.7.11
- Anaconda 4.0 distribution for Python 3.5 (default)
We recommend that you set the version before typing any new code. If you change the version later, a prompt asks you to acknowledge the change.
Important
If you use multiple instances of the Execute Python Script module in your experiment, you must choose a single version of Python for all modules in the experiment.
Add and connect on Dataset1 any datasets from Studio (classic) that you want to use for input. Reference this dataset in your Python script as DataFrame1.
Use of a dataset is optional, if you want to generate data using Python, or use Python code to import the data directly into the module.
This module supports addition of a second Studio (classic) dataset on Dataset2. Reference the second dataset in your Python script as DataFrame2.
Datasets stored in Studio (classic) are automatically converted to pandas data.frames when loaded with this module.
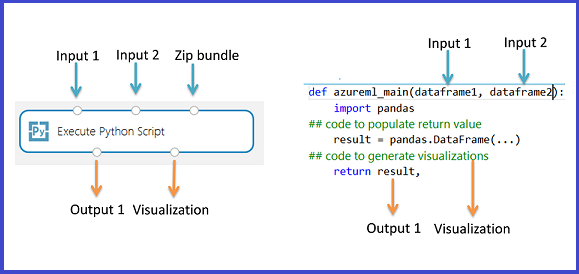
To include new Python packages or code, add the zipped file containing these custom resources on Script bundle. The input to Script bundle must be a zipped file already uploaded to your workspace. For more information about how to prepare and upload these resources, see Unpack Zipped Data.
Any file contained in the uploaded zipped archive can be used during experiment execution. If the archive includes a directory structure, the structure is preserved, but you must prepend a directory called src to the path.
In the Python script text box, type or paste valid Python script.
The Python script text box is pre-populated with some instructions in comments, and sample code for data access and output. You must edit or replace this code. Be sure to follow Python conventions about indentation and casing.
- The script must contain a function named
azureml_mainas the entry point for this module. - The entry point function can contain up to two input arguments:
Param<dataframe1>andParam<dataframe2> - Zipped files connected to the third input port are unzipped and stored in the directory,
.\Script Bundle, which is also added to the Pythonsys.path.
Therefore, if your zip file contains
mymodule.py, import it usingimport mymodule.- A single dataset can be returned to Studio (classic), which must be a sequence of type
pandas.DataFrame. You can create other outputs in your Python code and write them directly to Azure storage, or create visualizations using the Python device.
- The script must contain a function named
Run the experiment, or select the module and click Run selected to run just the Python script.
All of the data and code is loaded into a virtual machine, and run using the specified Python environment.
Results
The module returns these outputs:
Results Dataset. The results of any computations performed by the embedded Python code must be provided as a pandas data.frame, which is automatically converted to the Machine Learning dataset format, so that you can use the results with other modules in the experiment. The module is limited to a single dataset as output. For more information, see Data Table.
Python Device. This output supports both console output and display of PNG graphics using the Python interpreter.
How to attach script resources
The Execute Python Script module supports arbitrary Python script files as inputs, provided they are prepared in advance and uploaded to your workspace as part of a .ZIP file.
Upload a ZIP file containing Python code to your workspace
In the experiment area of Machine Learning Studio (classic), click Datasets, and then click New.
Select the option, From local file.
In the Upload a new dataset dialog box, click the dropdown list for Select a type for the new dataset, and select the Zip file (.zip) option.
Click Browse to locate the zipped file.
Type a new name for use in the workspace. The name you assign to the dataset becomes the name of the folder in your workspace where the contained files are extracted.
After you have uploaded the zipped package to Studio (classic), verify that the zipped file is available in the Saved Datasets list, and then connect the dataset to the Script Bundle input port.
All files that are contained in the ZIP file are available for use during run time: for example, sample data, scripts, or new Python packages.
If your zipped file contains any libraries that are not already installed in Machine Learning Studio (classic), you must install the Python library package as part of your custom script.
If there was a directory structure present, it is preserved. However, you must alter your code to prepend the directory src to the path.
Debugging Python code
The Execute Python Script module works best when the code has been factored as a function with clearly defined inputs and outputs, rather than a sequence of loosely related executable statements.
This Python module does not support features such as Intellisense and debugging. If the module fails at runtime, you can view some error details in the output log for the module. However, the full Python stack trace is not available. Thus we recommend that users develop and debug their Python scripts in a different environment and then import the code into the module.
Some common problems that you can look for:
Check the data types in the data frame you are returning back from
azureml_main. Errors are likely if columns contain data types other than numeric types and strings.Remove NA values from your dataset, using
dataframe.dropna()on export from Python script. When preparing your data, use the Clean Missing Data module.Check your embedded code for indentation and whitespace errors. If you get the error, "IndentationError: expected an indented block", see these resources for guidance:
Known limitations
The Python runtime is sandboxed and does not allow access to the network or to the local file system in a persistent manner.
All files saved locally are isolated and deleted once the module finishes. The Python code cannot access most directories on the machine it runs on, the exception being the current directory and its subdirectories.
When you provide a zipped file as resource, the files are copied from your workspace to the experiment execution space, unpacked, and then used. Copying and unpacking resources can consume memory.
The module can output a single data frame. It's not possible to return arbitrary Python objects such as trained models directly back to the Studio (classic) runtime. However, you can write objects to storage or to the workspace. Another option is to use
pickleto serialize multiple objects into a byte array and then return the array inside a data frame.
Examples
For examples of integrating Python script with Studio (classic) experiments, see these resources in the Azure AI Gallery:
- Execute Python Script: Use text tokenization, stemming, and other natural language processing using the Execute Python Script module.
- Custom R and Python scripts in Azure ML: Walks you through the process of adding custom code a(either R or Python), processing data, and visualizing the results.
- Analyzing PyPI Data to Determine Python 3 Support: Estimate the point when demand for Python 3 outstrips that for Python 2.7 using python.