CA1837: Use Environment.ProcessId instead of Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Rule ID | CA1837 |
| Title | Use Environment.ProcessId instead of Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id |
| Category | Performance |
| Fix is breaking or non-breaking | Non-breaking |
| Enabled by default in .NET 9 | As suggestion |
Cause
This rule locates calls to System.Diagnostics.Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id and suggests using System.Environment.ProcessId instead, because it is more efficient.
Rule description
System.Diagnostics.Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id is expensive:
- It allocates a Process instance, usually just to get the
Id. - The Process instance needs to be disposed, which has a performance impact.
- It's easy to forget to call Dispose() on the Process instance.
- If nothing else besides
Iduses theProcessinstance, then the linked size grows unnecessarily by increasing the graph of types referenced. - It is somewhat difficult to discover or find this API.
System.Environment.ProcessId avoids all the above.
Note
Rule CA1837 is available starting on .NET 5.0.
How to fix violations
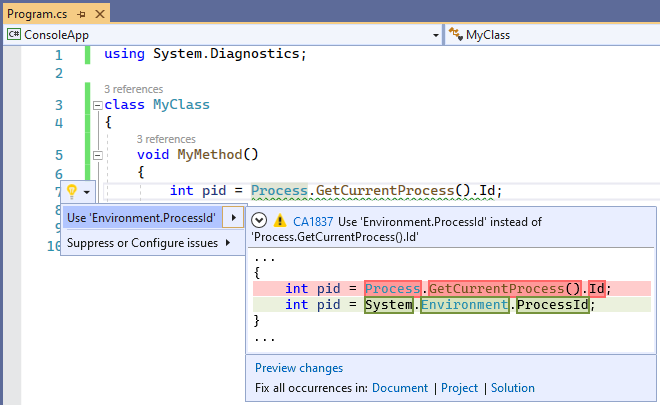
The violation can either be fixed manually, or, in some cases, using Quick Actions to fix code in Visual Studio.
The following two code snippets show a violation of the rule and how to fix it:
using System.Diagnostics;
class MyClass
{
void MyMethod()
{
int pid = Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id;
}
}
Imports System.Diagnostics
Class MyClass
Private Sub MyMethod()
Dim pid As Integer = Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id
End Function
End Class
using System.Diagnostics;
class MyClass
{
void MyMethod()
{
int pid = System.Environment.ProcessId;
}
}
Imports System.Diagnostics
Class MyClass
Private Sub MyMethod()
Dim pid As Integer = System.Environment.ProcessId
End Function
End Class
Tip
A code fix is available for this rule in Visual Studio. To use it, position the cursor on the violation and press Ctrl+. (period). Choose Use 'Environment.ProcessId' instead of 'Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id' from the list of options that's presented.
When to suppress warnings
It's safe to suppress a violation of this rule if you're not concerned about the performance impact from unnecessary allocation and eventual disposal of a Process instance.
Suppress a warning
If you just want to suppress a single violation, add preprocessor directives to your source file to disable and then re-enable the rule.
#pragma warning disable CA1837
// The code that's violating the rule is on this line.
#pragma warning restore CA1837
To disable the rule for a file, folder, or project, set its severity to none in the configuration file.
[*.{cs,vb}]
dotnet_diagnostic.CA1837.severity = none
For more information, see How to suppress code analysis warnings.
