Set up an appliance for servers on Hyper-V
Follow this article to set up the Azure Migrate appliance for discovery and assessment of servers on Hyper-V with the Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment tool.
The Azure Migrate appliance is a lightweight appliance used by Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment/ Migration to discover on-premises servers on Hyper-V, and send server metadata/performance data to Azure.
You can deploy the appliance using a couple of methods:
- Set up on a server on Hyper-V using a downloaded VHD. This method described in the current article.
- Set up on a server on Hyper-V or physical server with a PowerShell installer script. This method should be used if you can't set up a server using a VHD, or if you're in Azure Government.
After creating the appliance, you check that it can connect to Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment, configure it for the first time, and register it with the project.
Note
If you have already created a project, you can use the same project to register additional appliances to discover and assess more no of servers. Learn more.
Appliance deployment (VHD)
To set up the appliance using a VHD template:
- Provide an appliance name and generate a project key in the portal.
- Download a compressed Hyper-V VHD from the Azure portal.
- Create the appliance, and check that it can connect to Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment.
- Configure the appliance for the first time, and register it with the project using the project key.
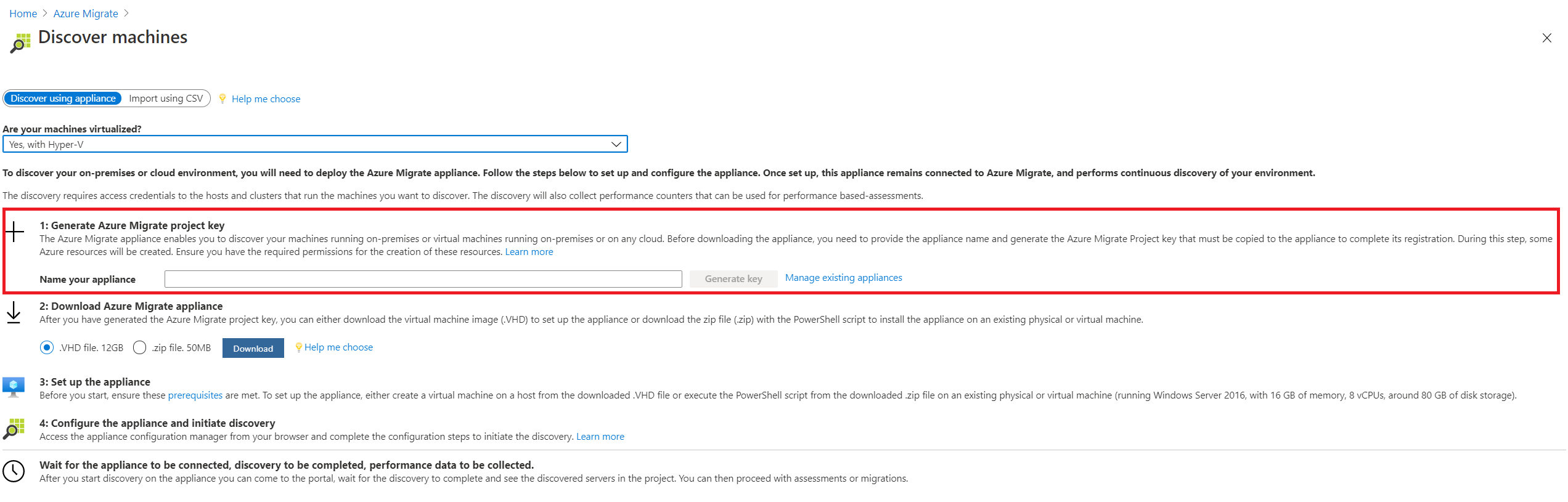
Generate the project key
- In Servers, databases and web apps > Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment, select Discover.
- In Discover servers > Are your servers virtualized?, select Yes, with Hyper-V.
- In 1:Generate project key, provide a name for the Azure Migrate appliance that you will set up for discovery of servers on Hyper-V. The name should be alphanumeric with 14 characters or fewer.
- Select Generate key to start the creation of the required Azure resources. Do not close the Discover servers page during the creation of resources.
- After the successful creation of the Azure resources, a project key is generated.
- Copy the key as you will need it to complete the registration of the appliance during its configuration.
Download the VHD
In 2: Download Azure Migrate appliance, select the .VHD file and select Download.
Verify security
Check that the zipped file is secure, before you deploy it.
- On the server to which you downloaded the file, open an administrator command window.
- Run the following command to generate the hash for the VHD
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile <file_location> [Hashing Algorithm]- Example usage:
C:\>Get-FileHash -Path ./AzureMigrateAppliance_v3.20.09.25.zip -Algorithm SHA256
Verify the latest hash value by comparing the outcome of above command to the value documented here
Create the appliance
Import the downloaded file, and create an appliance.
Extract the zipped VHD file to a folder on the Hyper-V host that will host the appliance. Three folders are extracted.
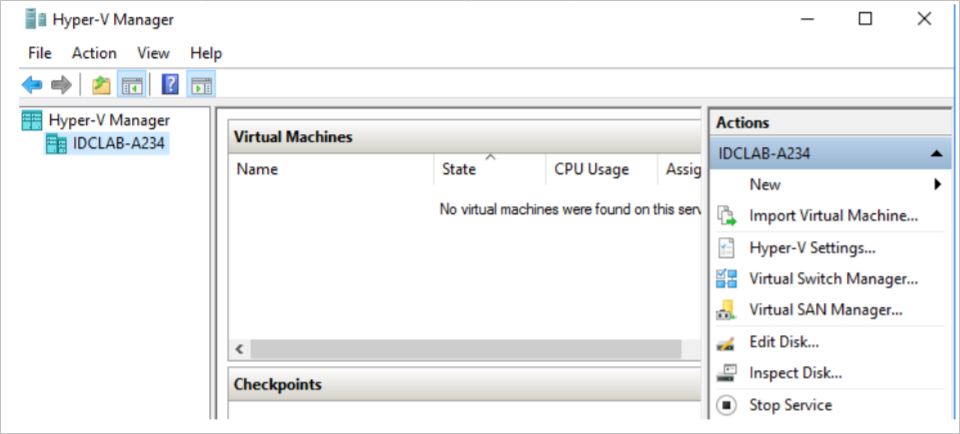
Open Hyper-V Manager. In Actions, select Import Virtual Machine.
In the Import Virtual Machine Wizard > Before you begin, select Next.
In Locate Folder, specify the folder containing the extracted VHD. Select Next.
In Select Virtual Machine, select Next.
In Choose Import Type, select Copy the virtual machine (create a new unique ID). Select Next.
In Choose Destination, leave the default setting. Select Next.
In Storage Folders, leave the default setting. Select Next.
In Choose Network, specify the virtual switch that the server will use. The switch needs internet connectivity to send data to Azure.
In Summary, review the settings. Select Finish.
In Hyper-V Manager > Virtual Machines, start the VM.
Verify appliance access to Azure
Make sure that the appliance can connect to Azure URLs for public and government clouds.
Configure the appliance
Set up the appliance for the first time.
Note
If you set up the appliance using a PowerShell script instead of the downloaded VHD, the first two steps in this procedure aren't relevant.
In Hyper-V Manager > Virtual Machines, right-click the server > Connect.
Provide the language, time zone, and password for the appliance.
Open a browser on any system that can connect to the appliance, and open the URL of the appliance web app: https://appliance name or IP address: 44368.
Alternately, you can open the app from the appliance desktop by selecting the app shortcut.
Accept the license terms, and read the third-party information.
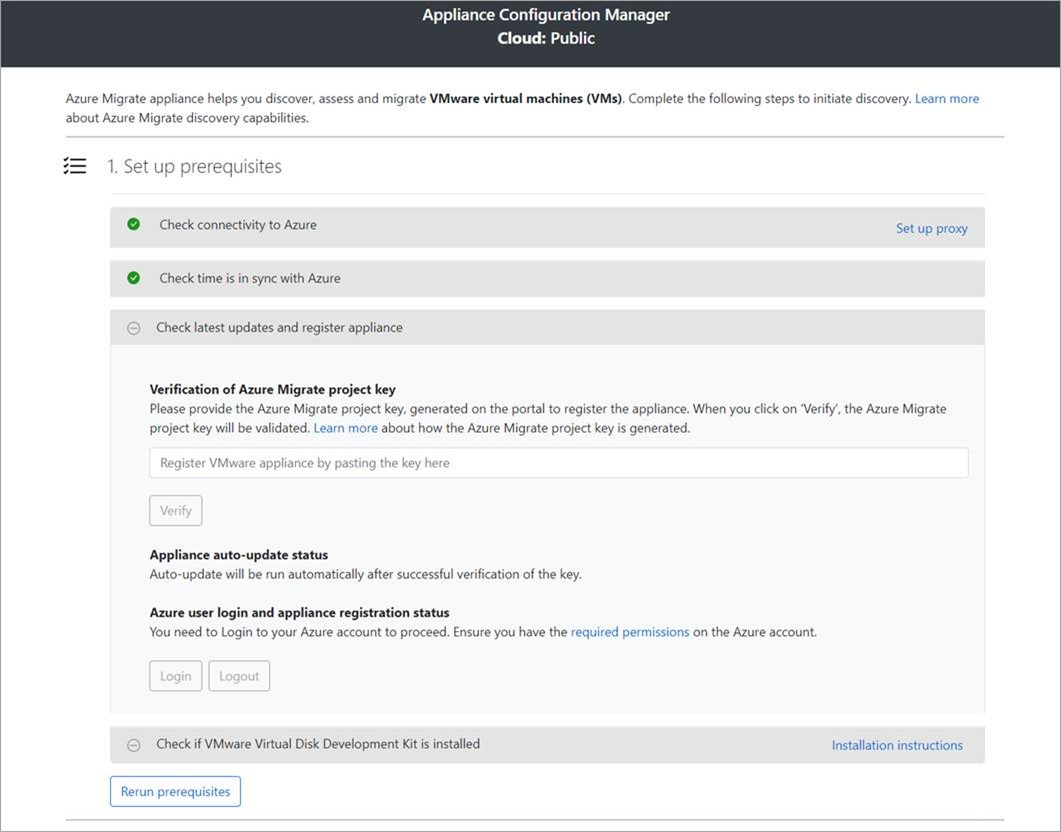
Set up prerequisites and register the appliance
In the configuration manager, select Set up prerequisites, and then complete these steps:
Connectivity: The appliance checks that the server has internet access. If the server uses a proxy:
Select Setup proxy to specify the proxy address (in the form
http://ProxyIPAddressorhttp://ProxyFQDN, where FQDN refers to a fully qualified domain name) and listening port.Enter credentials if the proxy needs authentication.
If you have added proxy details or disabled the proxy or authentication, select Save to trigger connectivity and check connectivity again.
Only HTTP proxy is supported.
Time sync: Check that the time on the appliance is in sync with internet time for discovery to work properly.
Install updates and register appliance: To run auto-update and register the appliance, follow these steps:
Note
This is a new user experience in Azure Migrate appliance which is available only if you have set up an appliance using the latest OVA/Installer script downloaded from the portal. The appliances which have already been registered will continue seeing the older version of the user experience and will continue to work without any issues.
For the appliance to run auto-update, paste the project key that you copied from the portal. If you don't have the key, go to Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment > Overview > Manage existing appliances. Select the appliance name you provided when you generated the project key, and then copy the key that's shown.
The appliance will verify the key and start the auto-update service, which updates all the services on the appliance to their latest versions. When the auto-update has run, you can select View appliance services to see the status and versions of the services running on the appliance server.
To register the appliance, you need to select Login. In Continue with Azure Login, select Copy code & Login to copy the device code (you must have a device code to authenticate with Azure) and open an Azure Login prompt in a new browser tab. Make sure you've disabled the pop-up blocker in the browser to see the prompt.
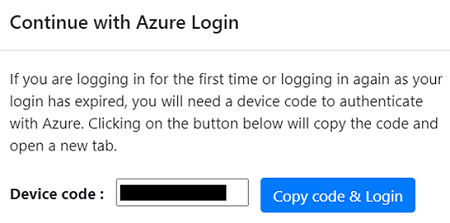
In a new tab in your browser, paste the device code and sign in by using your Azure username and password. Signing in with a PIN isn't supported.
Note
If you close the login tab accidentally without logging in, refresh the browser tab of the appliance configuration manager to display the device code and Copy code & Login button.
After you successfully log in, return to the browser tab that displays the appliance configuration manager. If the Azure user account that you used to log in has the required permissions for the Azure resources that were created during key generation, appliance registration starts.
After the appliance is successfully registered, to see the registration details, select View details.
You can rerun prerequisites at any time during appliance configuration to check whether the appliance meets all the prerequisites.
Delegate credentials for SMB VHDs
If you're running VHDs on SMBs, you must enable delegation of credentials from the appliance to the Hyper-V hosts. To do this from the appliance:
On the appliance, run this command. HyperVHost1/HyperVHost2 are example host names.
Enable-WSManCredSSP -Role Client -DelegateComputer HyperVHost1.contoso.com, HyperVHost2.contoso.com, HyperVHost1, HyperVHost2 -ForceAlternatively, do this in the Local Group Policy Editor on the appliance:
- In Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration, select Administrative Templates > System > Credentials Delegation.
- Double-click Allow delegating fresh credentials, and select Enabled.
- In Options, select Show, and add each Hyper-V host you want to discover to the list, with wsman/ as a prefix.
- In Credentials Delegation, double-click Allow delegating fresh credentials with NTLM-only server authentication. Again, add each Hyper-V host you want to discover to the list, with wsman/ as a prefix.
Start continuous discovery
Connect from the appliance to Hyper-V hosts or clusters, and start discovery.
Provide Hyper-V host/cluster details
In Step 1: Provide Hyper-V host credentials, select Add credentials to specify a friendly name for credentials, add Username and Password for a Hyper-V host/cluster that the appliance will use to discover servers. Select Save.
If you want to add multiple credentials at once, select Add more to save and add more credentials. Multiple credentials are supported for the discovery of servers on Hyper-V.
In Step 2: Provide Hyper-V host/cluster details, select Add discovery source to specify the Hyper-V host/cluster IP address/FQDN and the friendly name for credentials to connect to the host/cluster.
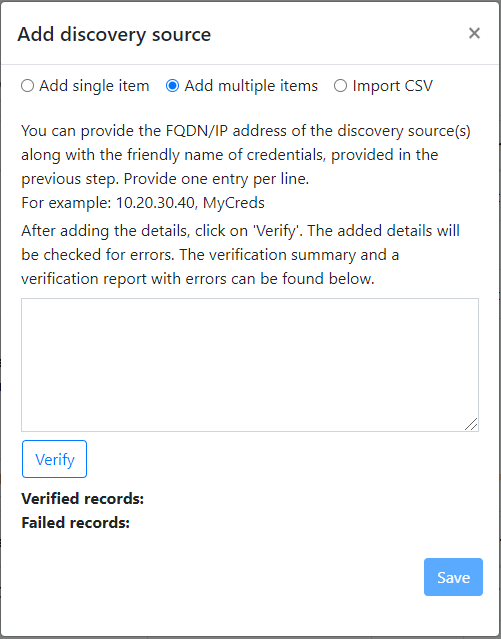
You can either Add single item at a time or Add multiple items in one go. There is also an option to provide Hyper-V host/cluster details through Import CSV.
- If you choose Add single item, you need to specify friendly name for credentials and Hyper-V host/cluster IP address/FQDN and select Save.
- If you choose Add multiple items (selected by default), you can add multiple records at once by specifying Hyper-V host/cluster IP address/FQDN with the friendly name for credentials in the text box. Verify** the added records and select Save.
- If you choose Import CSV, you can download a CSV template file, populate the file with the Hyper-V host/cluster IP address/FQDN and friendly name for credentials. You then import the file into the appliance, verify the records in the file and select Save.
On selecting Save, appliance will try validating the connection to the Hyper-V hosts/clusters added and show the Validation status in the table against each host/cluster.
- For successfully validated hosts/clusters, you can view more details by selecting their IP address/FQDN.
- If validation fails for a host, review the error by selecting Validation failed in the Status column of the table. Fix the issue, and validate again.
- To remove hosts or clusters, select Delete.
- You can't remove a specific host from a cluster. You can only remove the entire cluster.
- You can add a cluster, even if there are issues with specific hosts in the cluster.
You can revalidate the connectivity to hosts/clusters anytime before starting the discovery.
Provide server credentials
In Step 3: Provide server credentials to perform software inventory and agentless dependency analysis and to discover SQL Server instances and databases, you can provide multiple server credentials. If you don't want to use any of these appliance features, you can skip this step and proceed with discovery of servers running on Hyper-V hosts/clusters. You can change this option at any time.
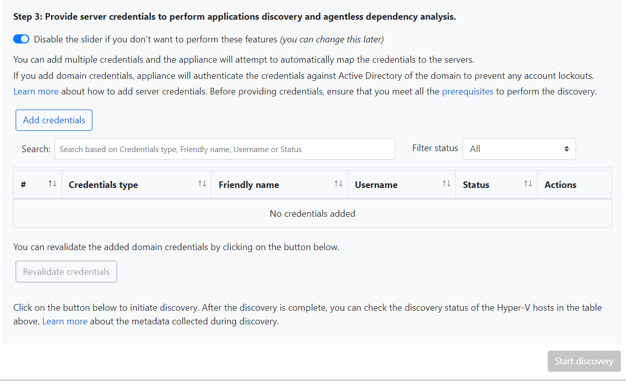
If you want to use these features, provide server credentials by completing the following steps. The appliance attempts to automatically map the credentials to the servers to perform the discovery features.
To add server credentials:
Select Add Credentials.
In the dropdown menu, select Credentials type.
You can provide domain/, Windows(non-domain)/, Linux(non-domain) credentials. Learn how to provide credentials and how we handle them.
For each type of credentials, enter:
- A friendly name.
- A username.
- A password. Select Save.
If you choose to use domain credentials, you also must enter the FQDN for the domain. The FQDN is required to validate the authenticity of the credentials with the Active Directory instance in that domain.
Review the required permissions on the account for discovery of installed applications and agentless dependency analysis.
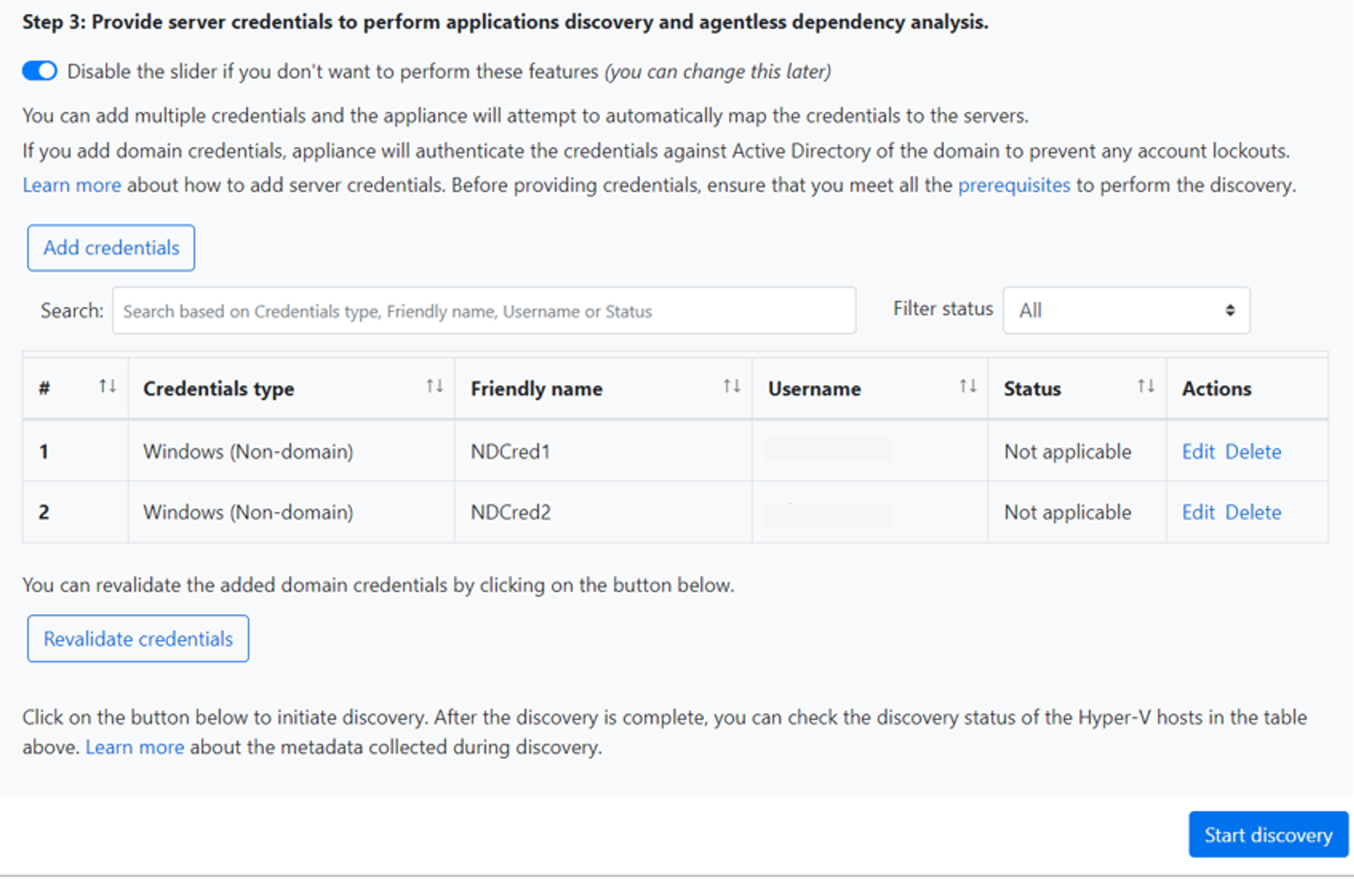
To add multiple credentials at once, select Add more to save credentials, and then add more credentials. When you select Save or Add more, the appliance validates the domain credentials with the domain's Active Directory instance for authentication. Validation is made after each addition to avoid account lockouts as during discovery, the appliance iterates to map credentials to respective servers.
To check validation of the domain credentials:
In the configuration manager, in the credentials table, see the Validation status for domain credentials. Only domain credentials are validated.
If validation fails, you can select the Failed status to see the validation error. Fix the issue, and then select Revalidate credentials to reattempt validation of the credentials.
Start discovery
Select Start discovery, to kick off server discovery from the successfully validated host(s)/cluster(s). After the discovery has been successfully initiated, you can check the discovery status against each host/cluster in the table.
How discovery works
- It takes approximately 2 minutes per host for metadata of discovered servers to appear in the Azure portal.
- If you have provided server credentials, software inventory (discovery of installed applications) is automatically initiated when the discovery of servers running on Hyper-V host(s)/cluster(s) is finished. Software inventory occurs once every 12 hours.
- During software inventory, the added server credentials are iterated against servers and validated for agentless dependency analysis. When the discovery of servers is finished, in the portal, you can enable agentless dependency analysis on the servers. Only the servers on which validation succeeds can be selected to enable agentless dependency analysis.
Verify servers in the portal
After discovery finishes, you can verify that the servers appear in the portal.
- Open the Azure Migrate dashboard.
- In Servers, databases and web apps > Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment page, select the icon that displays the count for Discovered servers.
Next steps
Try out Hyper-V assessment with Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment.