Authentication with Azure Repos
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
Selecting the right authentication method is crucial for secure access to your Azure Repos and Azure DevOps Server Git repositories. Whether you're working from a command prompt or using a Git client that supports HTTPS or SSH, it's important to choose credentials that not only provide the necessary access but also limit the scope to what's needed for your tasks.
Always revoke credentials when they're no longer required to maintain the security of your repositories. This approach ensures that you have the flexibility to work with your code securely and efficiently, while also safeguarding it against unauthorized access.
Authentication mechanisms
Microsoft Entra OAuth tokens
Use Microsoft Entra to generate tokens for accessing REST APIs. Microsoft Entra tokens can be used wherever personal access tokens are used. Here's a helpful tip on how to get a one-time access token from the Azure CLI to call git fetch:
$accessToken = az account get-access-token --resource 499b84ac-1321-427f-aa17-267ca6975798 --query "accessToken" --output tsv
git -c http.extraheader="AUTHORIZATION: bearer $accessToken" clone https://dev.azure.com/{yourOrgName}/{yourProjectName}/_git/{yourRepoName}
Tip
Look into the Git Credential Manager (GCM) instead to avoid entering your credentials everytime. Use GCM with default credential type as Oauth to generate Microsoft Entra tokens.
Personal access tokens
Personal access tokens (PATs) provide access to Azure DevOps without using your username and password directly. These tokens expire and allow you to restrict the scope of the data they can access.
Use PATs to authenticate if you don't have SSH keys set up on your system or need to limit the permissions granted by the credential.
Git interactions require a username, which can be anything except an empty string. To use a PAT with HTTP basic authentication, Base64-encode your $MyPat as shown in the following code block.
In PowerShell, enter the following code.
$MyPat = 'yourPat'
$headerValue = "Authorization: Basic " + [Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes(":" + $MyPat))
$env:GIT_AUTH_HEADER = $headerValue
git --config-env=http.extraheader=GIT_AUTH_HEADER clone https://dev.azure.com/yourOrgName/yourProjectName/_git/yourRepoName
Tip
If you are using PATs regularly, look into the Git Credential Manager (GCM) instead to avoid entering your credentials everytime. Even better, explore using GCM with default credential type as Oauth to generate Microsoft Entra tokens instead of PATs whenever possible.
SSH keys
Key authentication with SSH works through a public and private key pair that you create on your computer. You associate the public key with your username from the web. Azure DevOps will encrypt the data sent to you with that key when you work with Git. You decrypt the data on your computer with the private key, which is never shared or sent over the network.
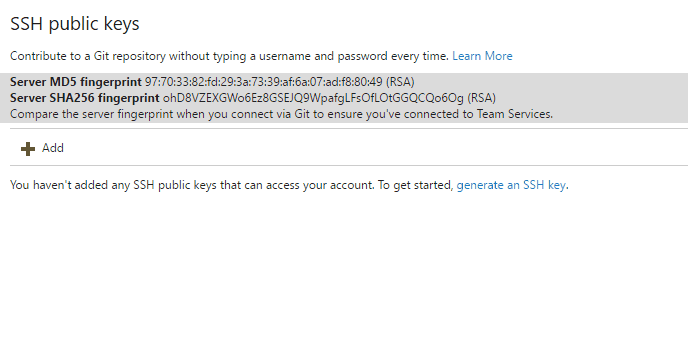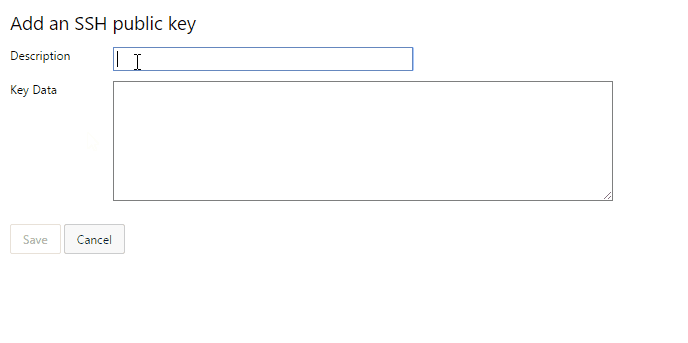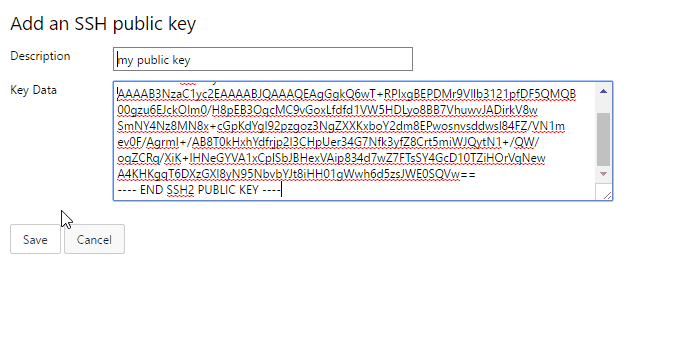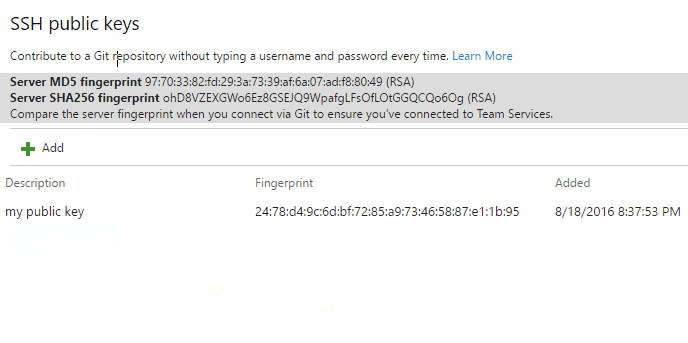
SSH is a great option if you've already got it set up on your system—just add a public key to Azure DevOps and clone your repos using SSH. SSH might be preferred for those on Linux, macOS, or Windows running Git for Windows who can't use Git credential managers or personal access tokens for HTTPS authentication.
For more information, see Set up SSH with Azure DevOps.
Use Git Credential Manager to generate tokens
Use the Git Credential Manager (GCM) to avoid entering your credentials every time and keep your token more secure when accessing Azure Repos. Sign in to the web portal, generate a token, and then use the token as your password when you're connecting to Azure Repos. Microsoft Entra tokens or PATs are generated on demand when you have the credential manager installed and saved locally for use with the Git command line or other client.
Existing repositories
Remove existing origin: If you previously added the origin using a username, remove it by running the following command:
git remote remove originAuthenticate with a PAT: If you encounter issues with standard authentication, run the following command to authenticate via the command line:
git remote add origin https://dev.azure.com/<PAT>@<company_machineName>:/<project-name>/_git/<repo_name>git push -u origin --allThe
path to git repo = /_git/dorefers to the URL path structure used in Azure DevOps for Git repositories. The/_git/segment indicates that you're accessing a Git repository, and you should replacedowith the actual name of your repository. For example, if your repository is namedmy-repo, the path would be '/_git/my-repo'.Clone repository: If you're using Git and need to authenticate, run the following command:
git clone https://{organization}@dev.azure.com/{organization}/_git/{repository}Replace
{organization}with your Azure DevOps organization name and{repository}with the name of your repository.