Track progress with status and trend query-based charts
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
You can quickly view the status of work in progress by charting the results of a flat-list query. Queries support different chart views, such as pie, column, pivot, or trend. Charts support viewing a count of work items or a sum of values for select numeric fields, such as Story Points, Effort, or Remaining Work. Group work by State, Assigned To, or other custom or system defined field.
In this article you learn how to perform the following tasks:
- Construct a flat-list query to support your chart
- Create and share your query-based chart
- Create a status pie, column, bar, or pivot chart
- Create a trend chart
- Add a chart to a dashboard
Note
This article describes how to configure work tracking query charts. To add existing query charts to dashboards, see Add charts to a dashboard. For information on configuring a Chart for Work Items widget, see Configure a chart for work items widget.
For an overview of all work tracking charts and in-context reports, see About dashboards, charts, reports, & widgets.
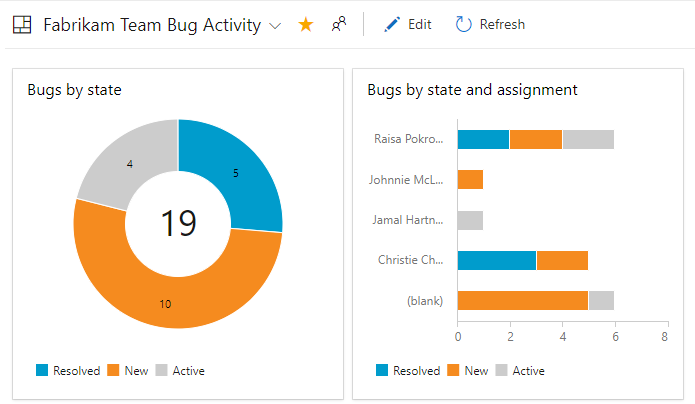
For example, the following image illustrates two different charts created from the same flat-list query. The pie chart groups the 19 bugs by state, and the bar chart groups the bugs by assignment and their current status.
Prerequisites
Have at least Basic access and a flat-list query. Only flat-list queries support charts.
If you want to add the chart to a dashboard, save the query under the Shared Queries folder and create the dashboard where you want to add the chart.
- To create a query chart, have at least Basic access. Users with Stakeholder access can't view or create charts from the Queries page. They can view charts added to a team dashboard. For more information, see Stakeholder access quick reference.
- To add a chart to a dashboard, you must save the query to a Shared Queries folder. To do that, have permissions to save queries under a folder. To get permissions, see Set permissions on queries and query folders.
- To add a query chart to a team dashboard, be a member of the team or be a member of the Project Administrators security group.
- To add a query chart to a project dashboard, you must create the dashboard or have permissions to edit the dashboard, or be a member of the Project Administrators security group.
- To view a query chart added to a dashboard, have Read permissions to the underlying query. If that permission is denied, the widget displays a Widget failed to load message.
Note
Users with Stakeholder access for a public project have full access to query chart features just like users with Basic access. For more information, see Stakeholder access quick reference.
- To create a query chart, have at least Basic access. Users with Stakeholder access can't view or create charts from the Queries page. They can view charts added to a team dashboard. For details, see Stakeholder access quick reference.
- To add a chart to a dashboard, you must save the query to a Shared Queries folder. To do that, have permissions to save queries under a folder. To get permissions, see Set permissions on queries and query folders.
- To add a query chart to a team dashboard, be a member of the team or be a member of the Project Administrators security group.
- To view a query chart added to a dashboard, have Read permissions to the underlying query. If that permission is denied, the widget displays a Widget failed to load message.
For more information about dashboard permissions, see Set dashboard permissions.
Create a flat-list query
When creating a query to support your chart, follow these guidelines.
Always select the Flat list of work items query type. Other query types aren't supported for charting. For more information, see Define a flat-list query.
Add those fields to either a query clause or the column options that you want to use within your chart. You can group charts by any field except date-time, free-form text, and tag fields. For example:
- To group by status, include the State field.
- To group by work assignments, include the Assigned To field.
- To group by sprints or iterations, include the Iteration Path.
- To group by team, include the Node Name field that displays the leaf node of the Area Path.
- To group by a custom field, include it.
To sum a numeric column, include the corresponding field in your query clause or column options. For more examples of charts created from numeric fields, see Query by numeric fields.
If you plan to add your query to a dashboard, save your query as a Shared query.
You can't group charts by the following field data types:
- ID
- Date-time, such as Created Date, Changed Date
- Plain text, such as Title
- Rich-text, such as Description, Repro Steps
- Tags
Note
You can't group a query-based chart by tags, however, you can group a Chart for Work Items widget by tags that you add to a dashboard as described in Configure a chart for work items widget.
You can't group charts by the following field data types:
- ID
- Date-time, such as Created Date, Changed Date
- Plain text, such as Title
- Rich-text, such as Description, Repro Steps
- Tags (You can filter a query using tags, but you can't use tags to configure your chart)
Display of areas and iterations
When you select Area Path or Iteration Path, only the leaf node appears in the chart. The leaf node is the last node of the full path. For example, Phone is the leaf node of FabrikamFiber/Fabrikam Website/Phone. If your query contains a mixed level of leaf nodes, your chart might not reflect expected results.
Select the Node Name field, the area path leaf node, to see if that improves your results.
Charts display in browsers that support Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG). Supported browsers include Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer 9 and later versions, Chrome, Firefox and Safari on Mac. Charts aren't optimized for mobile or touch displays.
Note
Internet Explorer is no longer supported for Azure DevOps Services or for Azure DevOps Server 2020.1.
Sort by Value or Label
Most charts allow you to choose how you want to sort the data. You can sort by Value or Label and select Ascending or Descending.
- Value: Sorts data by the numeric value
- Label: Sorts by the label selected for grouping the data
Limited display of series
When a chart contains more than 8 or 12 items within the data series, values in the 9 or 13-plus items are consolidated into a set labeled (other). However, if you increase the chart size through the configurable widget on a dashboard you can increase the series limit.
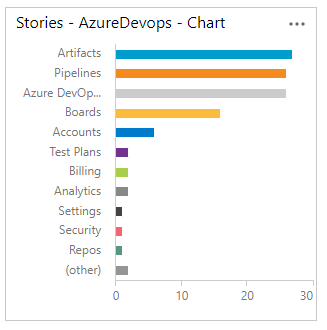
Chart availability
- All team members can view charts saved under Shared Queries, except members with Stakeholder access. You can add those charts to dashboards.
- Only you can view queries under your My Queries folder.
- You can copy and email the URL of any chart page to share it with a project member.
- To create similar charts for tests, see Track test status.
Create a query-based chart
From Queries, open the chart editor for a flat-list query. To create charts, belong to the Contributors group.
If you have Stakeholder access, the Charts and New Chart links don't appear.
Select the chart type and field for grouping values. When you use pie, bar, and column charts, select a single field to view a count of work items.
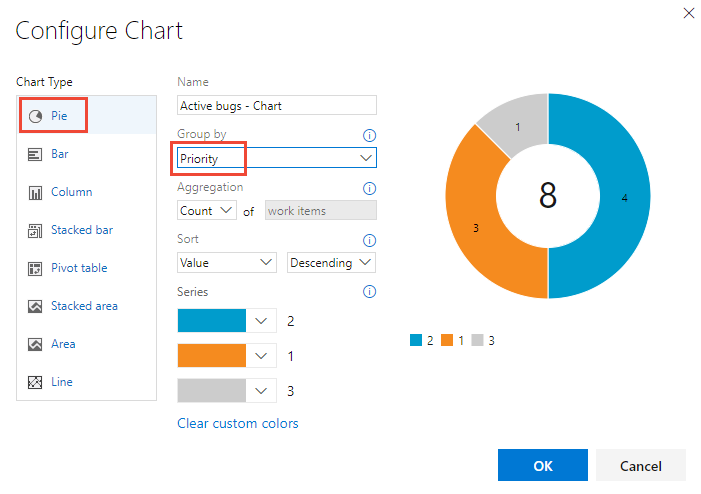
If you don't see the field you want in the Group by dropdown list, add the field as a column to the query and save the query. Also, the Aggregation options depend on the fields used in the query or the fields selected from the Column Options.
If you receive an error message when you close the chart editor, you need to request Basic access. For more information, see Change access levels.
To sort the results, select Value or Label as the sort option and then Ascending or Descending.
To change a color, select a color from the Series set of color pickers.

Charts automatically update when you edit the query or refresh the query results.
Add a Pie chart
Use a pie chart to show group percentages with six or fewer categories. Good examples of pie charts are:
- Active Bugs Status, group by State
- User Story Status, group by State
- User Story Progress, group by Completed, In Progress, or Cut
For example, the following query filters User Stories based on the State for Cut, In Progress, and Completed since the start of the year.
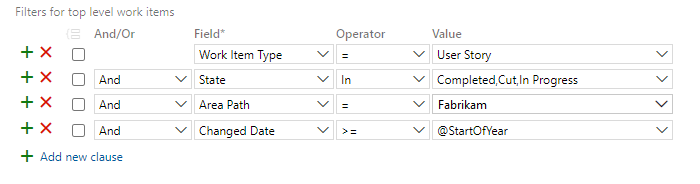
The pie chart configuration is as shown in the following image.
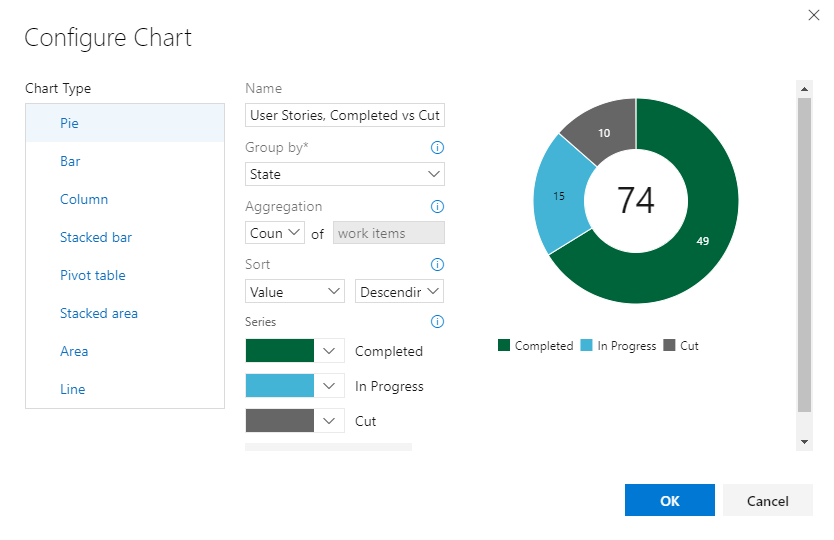
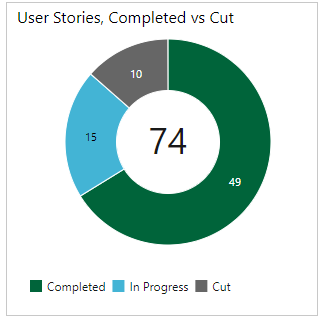
The combined query and chart configuration yield the following pie chart.
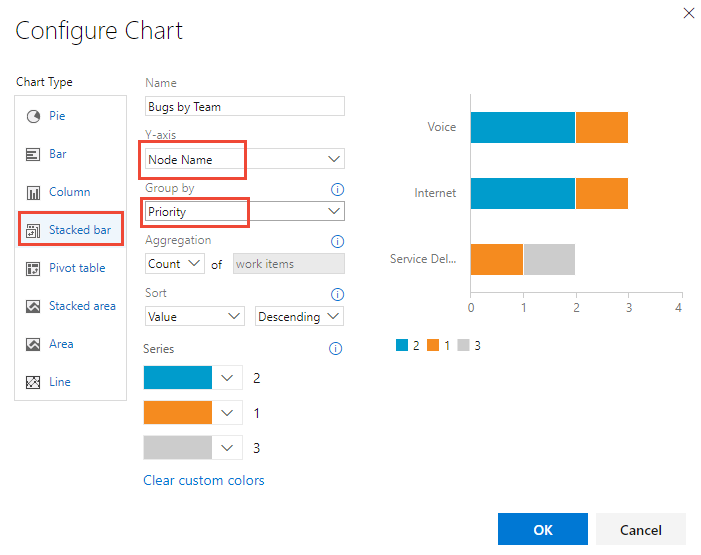
Add a Stacked bar chart
A stacked bar chart lets you track progress against two field values. Node Name displays the last leaf within an area path. Use this approach when you want to show data across teams and each node corresponds to a team.
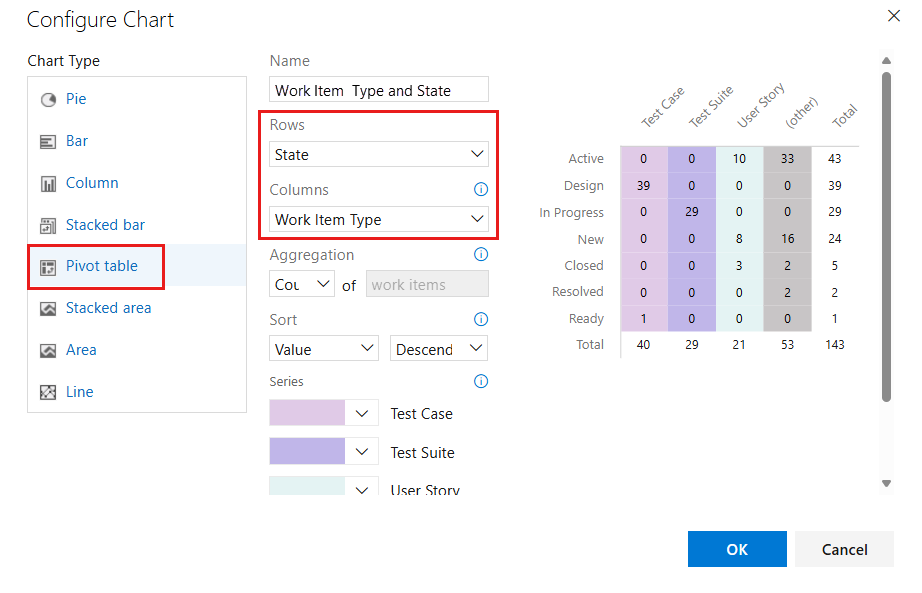
Add a Pivot table
The Pivot table displays a table of configurable rows and columns, with columns showing a count of work items or sum of a numeric field. Choose a Pivot table when you want to compare across areas the work being performed.
The following image shows an example of work item types and their current state.
Add a Trend chart
Trend charts let you view progress over time. You can select a rolling period ranging from the last week to the last year.
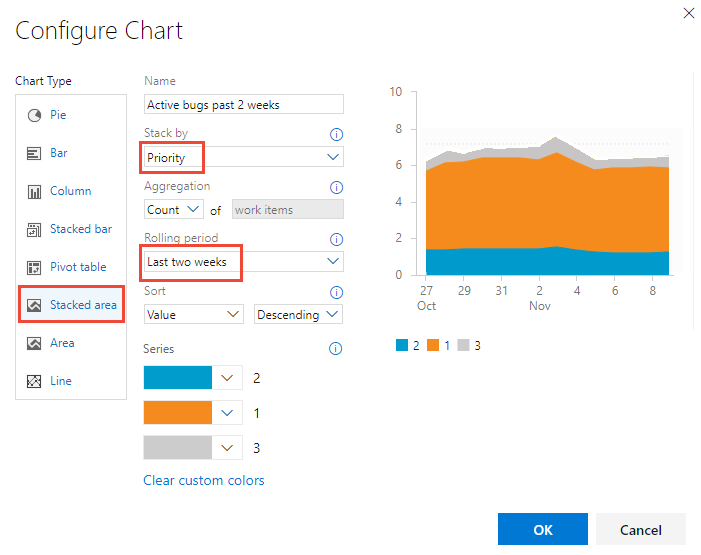
Trend data is extracted from the work tracking data store. Like most data stores, the schema of the relational database is designed and optimized for the online transactional processing of data. As the tool or plug-in performs an activity, it writes the latest information to the operational store. Data in the operational store is constantly changing and being updated. All data is current.
Add a Burndown chart
Burndown charts are useful for determining how quickly work is progressing based on a numeric field value, such as Story Points, Effort, or Remaining Work, or on a count of work items.
To create a burndown chart, add the numeric field you want to your query. To view a burndown chart of tasks, select the Sum operator for Remaining Work.
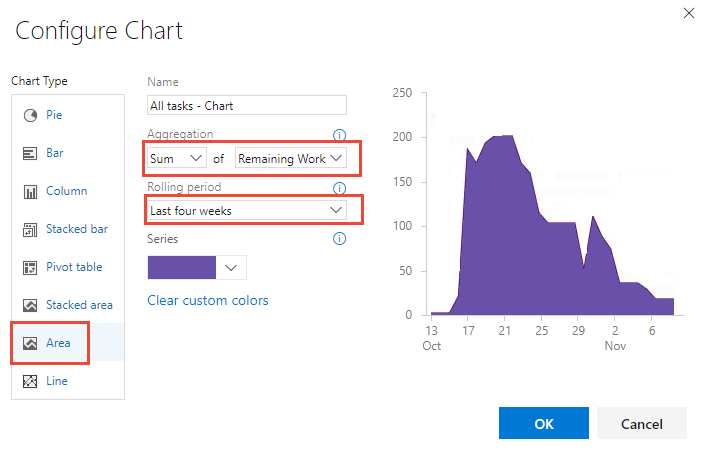
In addition to query-based burndown charts, you can Configure a burndown or burnup widget.
Add chart to a dashboard
Add a chart to a dashboard is through the addition of a Chart for Work Items widget. You can add the chart to a dashboard as shown in the following procedure, or by adding the Chart for Work Items widget directly. For more information, see Configure a chart for work items widget.
Tip
All query charts are limited in size. You can resize and configure charts that you add to a dashboard by opening the Chart for Work Items widget used to display them.
- Select the
 actions icon for the chart you want to add, and select Add to dashboard.
actions icon for the chart you want to add, and select Add to dashboard.
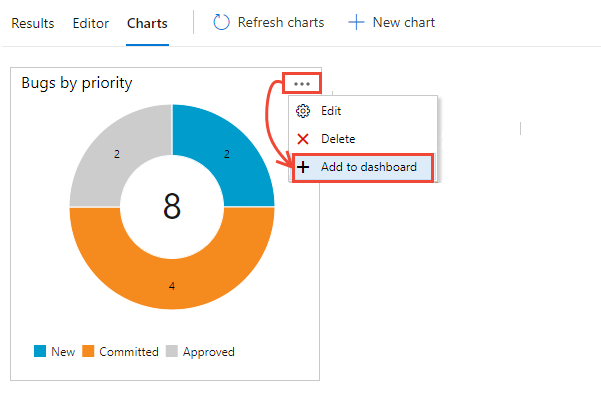
Only queries that are saved to a Shared Queries folder have the Add to dashboard menu option.
In the dialog that opens, select the dashboard to add the chart to.
To add other types of charts, such as test results and build summary charts, see Add widgets and chart to a dashboard.
Query-based charts versus Excel-generated PivotCharts
Query-based charts generate data from the work item tracking data store. The charts display the most recent data. Excel PivotCharts access data published to the Analysis Services cube, which is refreshed every two hours by default. Excel charts require that your project's project collection is configured with SQL Server Reporting Services and Analysis Services.
Related articles
- Review example query charts
- Configure a chart for work items widget
- Read FAQs on Azure DevOps dashboards, charts, and reports
- View and configure a Cumulative Flow Diagram
- View and configure team velocity
- Configure and monitor sprint burndown
- Track test status
- Add widgets to a dashboard
- View the Widget catalog