Create a query based on build and test integration fields
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
Work item fields that support build and test integration offer powerful functionalities to enhance your development workflow. These integrations enable the following key actions:
- Associate bugs with builds: Link bugs directly to the specific builds where they were discovered or resolved, ensuring precise tracking and accountability.
- Query bugs by build: Retrieve and analyze bugs associated with particular builds to identify trends and areas needing improvement.
- Mark test cases as Manual or Automated: Categorize test cases accordingly and store relevant information to support automated testing processes.
- Define action and validation steps for test cases and shared steps: Specify the actions to perform, validation criteria, and the data required to execute tests effectively.
This article provides guidance on how to use build and test integrations to improve your project's quality and efficiency.
Prerequisites
- Project-level permissions:
- Contributors: Can create and edit queries.
- Readers: Can view queries but can't create or edit them.
- Project Administrators: Have full control over all project settings, including queries.
- Specific permissions for Test Artifacts:
- Manage Test Plans: Allows creating, editing, and deleting test plans.
- Manage Test Suites: Allows creating, editing, and deleting test suites.
- Edit Work Items in this Node: Required to add or edit test-specific work items like test cases and test suites.
Supported operators and macros
Most build and test integration fields have a data type of String, PlainText, or HTML. Query clauses that specify a text or rich-text field can use the operators and macros listed in the following table.
Data type
Supported operators and macros
Rich-text (HTML) and
Multi-line text strings (PlainText)
Contains Words, Does Not Contain Words, Is Empty, Is Not Empty.
Single text (String)
= , <> , > , < , >= , <= , =[Field], <>[Field], >[Field], <[Field], >=[Field], <=[Field], Contains, Does Not Contain, In, Not In, In Group, Not In Group, Was Ever
Macros: [Any], valid with the Work Item Type field; and @Project, valid with the Team Project field. The system automatically defaults to filtering based on the current project. For more information, see Query across projects.
Useful filters
Filter for
Include these query clauses
Automated test cases
Work Item Type = Test Case And Automation Status = Automated
Query-based test suites
Work Item Type = Test Suite And Test Suite Type = Query Based
Requirement-based test suites
Work Item Type = Test Suite And Test Suite Type = Requirement Based
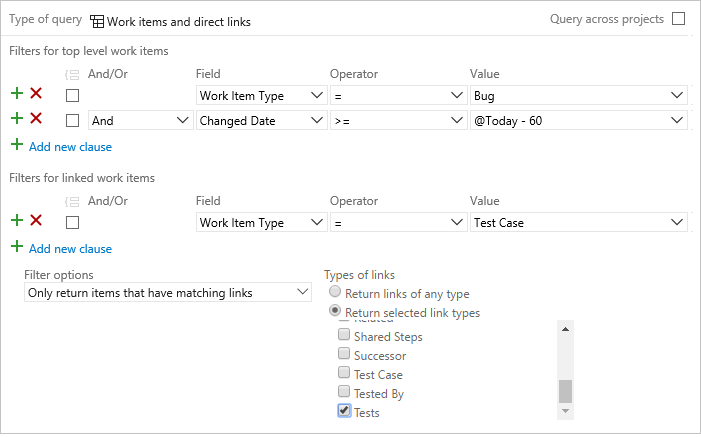
List bugs and the test cases that test them
Open a new query, set the query type to Work items and direct links. Filter for bugs in the top level and add the filter for Test Cases in the linked work items filter.
Note
You can't construct a query that shows a hierarchical view of Test Plans, Test Suites, and Test Cases. These items aren't linked together using parent-child link types. You can view the hierarchy through the Test>Test Plans page.
Build and test data fields
The following table describes the fields that are defined in one or more of the test work item types. For information about data types and field attributes, see Work item fields and attributes.
To customize a field or picklist, see Add or modify a field to support queries, reports, and workflow.
Field name
Description
Work item type
Automation Status 1
The status of a test case. You can specify the following values:
- Automated
- Not Automated
- Planned
To run automated tests, see Run automated tests from test plans.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.AutomationStatus, Data type=String
Test Case
Found In 2
Product build number, also known as a revision, in which a bug was found.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.Build.FoundIn, Data type=String
Note
You can also use the Found in build link type to link a work item to a build. This link type is available from Azure DevOps and only works with the current build processes (not XAML builds).
Bug
Integration Build 2
Product build number that incorporates the code or fixes a bug.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.Build.IntegrationBuild, Data type=String
Note
You can also use the Integrated in build link type to link a work item to a build. This link type is available from Azure DevOps and only works with the current build processes (not XAML builds).
All
Issue
Indicates that the Shared Steps are associated with an expected result. Allowed values are Yes and No. Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.Common.Issue, Data type=String
Shared Steps
Parameters
Contains the parameters to use when running a manual test.
Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.Parameters, Data type=HTML
Shared Parameters, Shared Steps, Test Case
Steps
The action and validation steps that are required to run the test. Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.Steps, Data type=HTML
Shared Steps, Test Case
System Info
Information about the software and system configuration that is relevant to the test.
Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.SystemInfo, Data type=HTML
Bug, Feedback Response
Repro Steps (or Steps to reproduce)
The steps that are required to reproduce unexpected behavior. Capture enough information so that other team members can understand the full impact of the problem and whether they've fixed the bug. This includes actions taken to find or reproduce the bug and expected behavior. Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.ReproSteps, Data type=HTML
Bug
Test Suite Type 1
The test suite category. Allowed values are:
- Query Based: Use to group together test cases that have a particular characteristic - for example, all the tests that have Priority=1. The suite automatically includes every test case that gets returned by the query that you define.
- Requirement Based: Use to group together test cases designed to track the test status of backlog items. Each test case that you add to a requirement-based test suite is automatically linked to the backlog item.
- Static: Use to group together test cases with any characteristics or test suites.
For more information, see Create a test plan.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.TestSuiteType, Data type=String
Test Suite
Note
- Do not customize the pick list for these fields. The system accepts only those values listed.
- By adding a
GLOBALLISTelement to theFIELDdefinition, you can provide a drop-down menu of builds that users can choose from. To learn how, see Builds and global list auto-population later in this article.
Other fields
The following fields don't appear on work item forms, but these fields are tracked for test cases or test suites. You can use some of these fields to filter queries and create reports. (None of these fields are added to the data warehouse nor indexed.)
Field name
Description
Work item type
Automated Test Storage
The assembly that contains the test that automates the test case.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.AutomatedTestStorage, Data type=String
Test Case
Automated Test Type
The type of test that automates the test case.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.AutomatedTestType, Data type=String
Test Case
AutomatedTestId
The ID of the test that automates the test case.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.AutomatedTestId, Data type=String
Test Case
AutomatedTestName
The name of the test that is used to automate the test case.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.AutomatedTestName, Data type=String
Test Case
LocalDataSource
The local data source that supports the test.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.LocalDataSource, Data type=HTML
Test Case
Query Text
Field used to capture the query defined for a Query-based suite type.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.QueryText, Data type=PlainText
Test Suite
Test Suite Audit
Tracks other operations run when modifying a test suite, for example: adding tests to a test suite or changing configurations. This field can be viewed through the History tab or through a separate query. There's a combined history view, including changes done to work items field and changes resulting from related artifacts such as test points and configurations.
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.TestSuiteAudit, Data type=PlainText
Test Suite
Test Suite Type ID 1
A system assigned value that corresponds to the test suite category and only applicable to test suites. Assigned values are:
1 (Static)
2 (Query-based)
3 (Requirement- based)
Reference name=Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.TestSuiteTypeId, Data type=Integer
Test Suite
Note
- Do not customize the pick list for these fields. The system accepts only those values listed.
Fields that integrate with Team Foundation Build
Team Foundation Build is the on-premises build system you can use with Azure DevOps Server. You can configure your build process by using Team Foundation Build, and Team Foundation Build can generate work items when a build fails. It can also add build information to work items that were resolved in a particular build. Team Foundation Build requires that the following two fields get added to the work item type definition: Found In and Integration Build.
Found In and Integrated in Build fields are defined for Bugs in the default processes. These fields associate bugs with the builds where they were found or fixed.
You can use the following code snippet to add these fields to a WIT definition.
<FIELD name="Found In" refname="Microsoft.VSTS.Build.FoundIn" type="String" reportable="dimension">
<HELPTEXT>Product build number (revision) in which this item was found</HELPTEXT>
<SUGGESTEDVALUES>
<LISTITEM value="<None>" />
</SUGGESTEDVALUES>
</FIELD>
<FIELD name="Integration Build" refname="Microsoft.VSTS.Build.IntegrationBuild" type="String" reportable="dimension">
<HELPTEXT>Product build number this bug was fixed in</HELPTEXT>
<SUGGESTEDVALUES>
<LISTITEM value="<None>" />
</SUGGESTEDVALUES>
</FIELD>
When the Found In field is present in a WIT definition, Team Foundation Build creates a work item when a build fails, and sets the Found In field to the build number of the build that failed. If the Found In field is missing, Team Foundation Build doesn't create a work item for the failed build, and everything else works as expected.
When the Integration Build field is present in the WIT definition, Team Foundation Build identifies work items that were resolved with each build and then updates those work items to set the build number in which they were resolved in the Integration Build field. If the Integration Build field is missing, Team Foundation Build doesn't store the build number in the work items, and everything else works as expected.
Builds and global list autopopulation
The first time you queue a build for a project using Team Foundation Build, it automatically adds a global list labeled Build - ProjectName. Each time a build is run, a LISTITEM is added to this global list with the name of the build.
By adding a GLOBALLIST element to the FIELD definition, you can provide a drop-down menu of builds that users can choose from. For example:
<FIELD name="Found In" refname="Microsoft.VSTS.Build.FoundIn" type="String" reportable="dimension">
<HELPTEXT>Product build number (revision) in which this item was found</HELPTEXT>
<SUGGESTEDVALUES>
<LISTITEM value="<None>" />
</SUGGESTEDVALUES>
<SUGGESTEDVALUES expanditems="true" filteritems="excludegroups">
<GLOBALLIST name="Builds - TeamProjectName" />
</SUGGESTEDVALUES>
</FIELD>
Fields that Integrate with Test Plans
With Test Plans, you can automate the creation of a bug or other type of work item when a test fails. For more information, see Add findings to existing bugs with exploratory testing.
When you create a work item in this manner, information about the system and the steps to reproduce the bug gets captured in the System Info and Repro Steps fields.
You can add these fields to work item types that you create for tracking defects using the following code snippet.
<FIELD name="System Info" refname="Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.SystemInfo" type="HTML" />
<FIELD name="Repro Steps" refname="Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.ReproSteps" type="HTML" />
Fields that integrate with Team Foundation Version Control
Associating and resolving work items with TFVC
Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) offers a feature that allows you to associate or resolve work items directly during the code check-in process. When you work on a specific work item and make corresponding code changes, you can link that work item from within the source-control check-in window upon completing your changes.
How TFVC resolves work items
The ability of TFVC to resolve a work item depends on the presence of a specific action within the work item. Here's how the process works:
- Action verification: The source control system queries the work item tracking system to determine if the work item supports the required action.
- State transition: If the action is supported, TFVC retrieves the source and destination states associated with the transition.
- Work item update: Upon checking in the code, TFVC transitions the work item's state according to the predefined transition.
This integration ensures that work items accurately reflect the status of associated code changes, enhancing traceability and accountability within your development workflow.
Note
When you use the Checkin action, you must set appropriate from and to states to reflect the state transition that you want.
For more information, see Automate field assignments based on State, Transition, or Reason.
Limitations
There are the following limitations when querying by test case:
- Hierarchical views: You can’t construct a query that shows a hierarchical view of Test Plans, Test Suites, and Test Cases. These items aren’t linked together using parent-child link types.
- Query-based test suites: While you can create query-based test suites, the suite automatically includes every test case that gets returned by the query you define, which can sometimes lead to unintended test cases being included if the query isn’t precise.
- Field limitations: Some fields related to test cases, such as detailed execution results, might require creative usage of existing fields or customization of payload data to be fully utilized.
- Performance and rate limits: Azure DevOps imposes limits on the resources individuals can consume and the number of requests they can make. Nonoptimized queries or excessive API calls can lead to delays or blocked requests.
- Test case linking: Test cases aren’t automatically linked to other work items in a way that supports complex queries. For example, you can’t easily query for a hierarchical view of test cases linked to specific requirements or user stories.