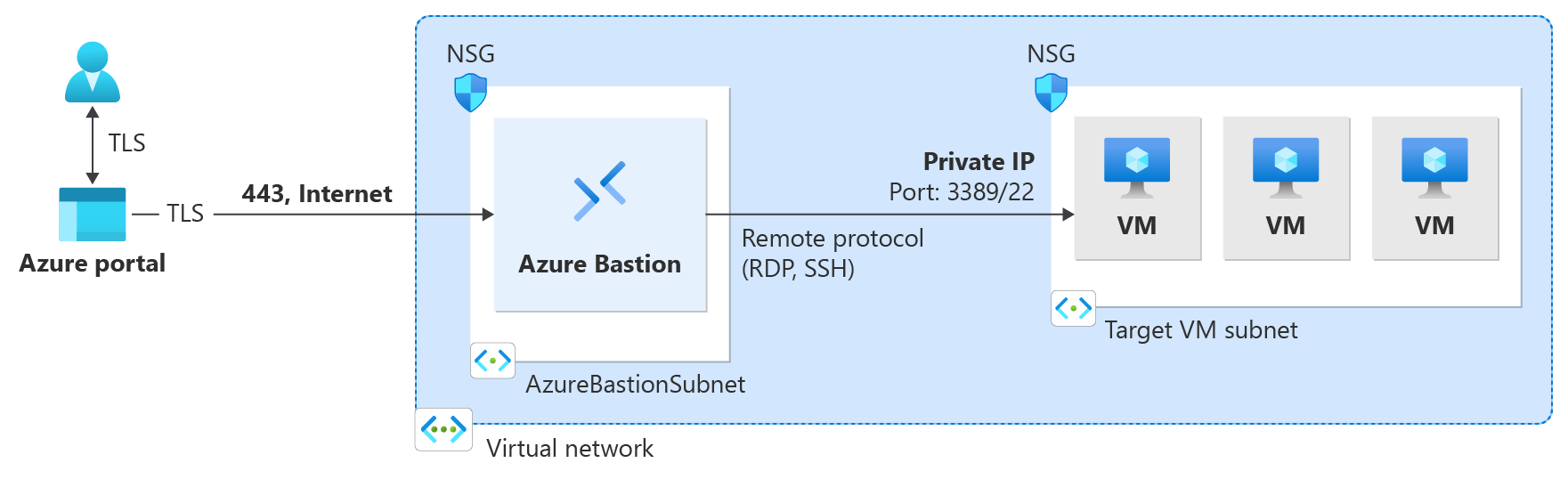
Quickstart: Deploy Azure Bastion automatically
In this quickstart, you learn how to deploy Azure Bastion automatically in the Azure portal by using default settings and the Basic SKU. After you deploy Bastion, you can use SSH or RDP to connect to virtual machines (VMs) in the virtual network via Bastion by using the private IP addresses of the VMs. The VMs that you connect to don't need a public IP address, client software, an agent, or a special configuration. For more information about Bastion, see What is Azure Bastion?
At this time, when you deploy Bastion automatically, Bastion is deployed with Basic SKU.
- If you want to deploy with the Developer SKU instead, see Quickstart: Deploy Azure Bastion - Developer SKU.
- If you want to specify features, configuration settings, or use a different SKU when you deploy Bastion, see Tutorial: Deploy Azure Bastion by using specified settings.
The steps in this article help you:
- Deploy Bastion with default settings (Basic SKU) from your VM resource by using the Azure portal. When you deploy by using default settings, the settings are based on the virtual network in which the VM resides.
- Connect to your VM via the portal by using SSH or RDP connectivity and the VM's private IP address.
- Remove your VM's public IP address if you don't need it for anything else.
Important
Hourly pricing starts from the moment that Bastion is deployed, regardless of outbound data usage. For more information, see Pricing and SKUs. If you're deploying Bastion as part of a tutorial or test, we recommend that you delete this resource after you finish using it.
Prerequisites
To complete this quickstart, you need these resources:
An Azure subscription. If you don't already have one, you can activate your MSDN subscriber benefits or sign up for a free account.
A VM in a virtual network. When you deploy Bastion by using default values, the values are pulled from the virtual network in which your VM resides. This VM doesn't become a part of the Bastion deployment itself, but you connect to it later in the exercise.
- If you don't already have a VM in a virtual network, create a VM by using Quickstart: Create a Windows VM or Quickstart: Create a Linux VM.
- If you don't have a virtual network, you can create one at the same time that you create your VM. If you already have a virtual network, make sure that it's selected on the Networking tab when you create your VM.
Required VM roles:
- Reader role on the virtual machine
- Reader role on the network adapter (NIC) with the private IP of the virtual machine
Required VM inbound ports:
- 3389 for Windows VMs
- 22 for Linux VMs
Note
The use of Azure Bastion with Azure Private DNS zones is supported. However, there are restrictions. For more information, see the Azure Bastion FAQ.
Example values
You can use the following example values when you're creating this configuration, or you can substitute your own.
Virtual network and VM example values
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Virtual machine | TestVM |
| Resource group | TestRG1 |
| Region | East US |
| Virtual network | VNet1 |
| Address space | 10.1.0.0/16 |
| Subnets | FrontEnd: 10.1.0.0/24 |
Bastion values
When you deploy from VM settings, Bastion is automatically configured with the following default values from the virtual network.
| Name | Default value |
|---|---|
| AzureBastionSubnet | Created within the virtual network as a /26 |
| SKU | Basic |
| Name | Based on the virtual network name |
| Public IP address name | Based on the virtual network name |
Deploy Bastion
When you create an Azure Bastion instance in the portal by using Deploy Bastion, you deploy Bastion automatically by using default settings and the Basic SKU. You can't modify, or specify additional values when you select Deploy Bastion. After deployment completes, you can later go to the Configuration page for the bastion host to configure additional settings or upgrade the SKU. For more information, see About Azure Bastion configuration settings.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- In the portal, go to the VM that you want to connect to. The values from the virtual network where this VM resides will be used to create the Bastion deployment.
- On the page for your VM, in the left menu, select Bastion to open the Bastion page. The Bastion page has different interfaces, depending on the region to which your VM is deployed. Certain features aren't available in all regions. You might need to expand Dedicated Deployment Options to access Deploy Bastion.
- Select Deploy Bastion. Bastion begins deploying. This process can take around 10 minutes to complete.
Connect to a VM
When the Bastion deployment is complete, the screen changes to the Connect pane.
- Enter your authentication credentials. Then, select Connect.
- The connection to this virtual machine via Bastion opens directly in the Azure portal (over HTML5) by using port 443 and the Bastion service. When the portal asks you for permissions to the clipboard, select Allow. This step lets you use the remote clipboard arrows on the left of the window.
Using keyboard shortcut keys while you're connected to a VM might not result in the same behavior as shortcut keys on a local computer. For example, when you're connected to a Windows VM from a Windows client, Ctrl+Alt+End is the keyboard shortcut for Ctrl+Alt+Delete on a local computer. To do this from a Mac while you're connected to a Windows VM, the keyboard shortcut is Fn+Ctrl+Alt+Backspace.
Enable audio output
You can enable remote audio output for your VM. Some VMs automatically enable this setting, whereas others require you to enable audio settings manually. The settings are changed on the VM itself. Your Bastion deployment doesn't need any special configuration settings to enable remote audio output.
Note
Audio output uses bandwidth on your internet connection.
To enable remote audio output on a Windows VM:
- After you're connected to the VM, an audio button appears on the lower-right corner of the toolbar. Right-click the audio button, and then select Sounds.
- A pop-up message asks if you want to enable the Windows Audio Service. Select Yes. You can configure more audio options in Sound preferences.
- To verify sound output, hover over the audio button on the toolbar.
Remove VM public IP address
When you connect to a VM by using Azure Bastion, you don't need a public IP address for your VM. If you aren't using the public IP address for anything else, you can dissociate it from your VM:
Go to your virtual machine. On the Overview page, click the Public IP address to open the Public IP address page.
On the Public IP address page, go to Overview. You can view the resource that this IP address is Associated to. Select Dissociate at the top of the pane.
Select Yes to dissociate the IP address from the VM network interface. After you dissociate the public IP address from the network interface, verify that it's no longer listed under Associated to.
After you dissociate the IP address, you can delete the public IP address resource. On the Public IP address pane for the VM, at the top of the Overview page, select Delete.
Select Yes to delete the public IP address.
Clean up resources
When you finish using the virtual network and the virtual machines, delete the resource group and all of the resources that it contains:
Enter the name of your resource group in the Search box at the top of the portal, and then select it from the search results.
Select Delete resource group.
Enter your resource group for TYPE THE RESOURCE GROUP NAME, and then select Delete.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you deployed Bastion to your virtual network. You then connected to a virtual machine securely via Bastion. Next, you can configure more features and work with VM connections.